Q2. What is the effect of system irreversibilities on the efficiency of a gas turbine?
System irreversibilities tend to reduce expansion work outputs and increase compressor work inputs during both charge and discharge.
Q3. What is the effect of a sloping front?
The sloping front constitutes a loss of stored available energy and also prevents the reservoir from being fully charged without hot (or cold) gas first issuing from the exit, thereby incurring an exit loss.
Q4. What is the effect of a compression heat loss during the charging phase?
A compression heat loss during the charging phase, for example, will reduce the storage temperature (and hence reduce the stored energy), but it will also reduce the work input for the compression process.
Q5. How can one estimate the thermal losses of a reservoir?
Since reservoir thermal losses clearly depend on the charge-discharge history, accurate modelling can only really be undertaken by developing an overall system model that couples unsteady heat transfer calculations with thermodynamic cycle calculations, and includes the time-varying characteristics of the electrical network to which the storage system is connected.
Q6. What is the impact of the reciprocating device on the round trip efficiency?
In terms of impact on the round-trip efficiency, it is the fractional pressure loss, f = Δp/p, in each device that is most relevant since this is proportional to the entropy increase and hence to the lost work.
Q7. What is the advantage of reducing the ratio between hot and cold store discharged temperatures?
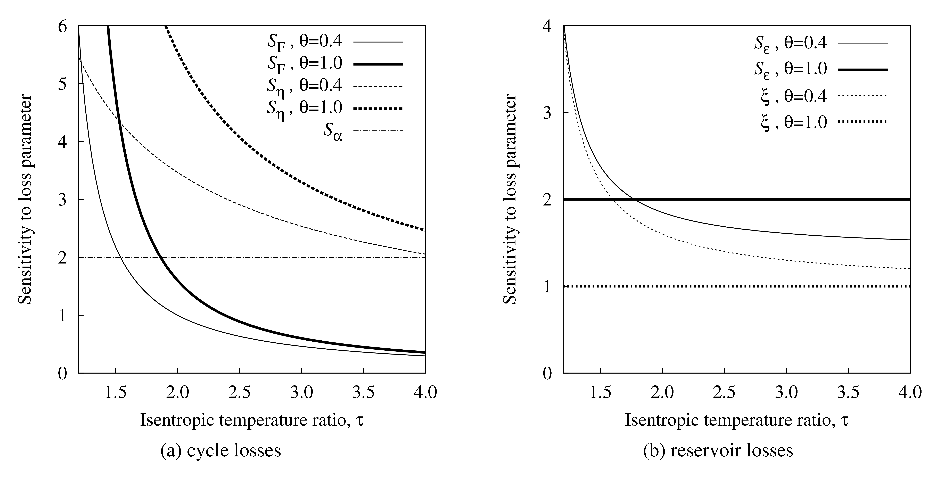
For a turbomachinery-based PTES system, the effects of compression and expansion irreversibility can be mitigated by reducing the ratio between hot and cold store discharged temperatures, which also has the advantage of increasing the energy and power densities.
Q8. What is the effect of a in the periodic cyclic mode?
It is most likely that PTES will be used in the periodic cyclic mode and, in any case, the effect of a is relatively small so it is set to zero in what follows.
Q9. What is the way to reduce the discharge pressure ratio between successive cycles?
Note also that using a lower discharge pressure ratio and then bypassing HX1 enables θ = T3/T1 to be reduced between successive cycles in order to obtain the benefits described in sections 2.1 and 2.2.
Q10. What is the entropy generation rate for the gas-solid interfacial area?
The net entropy generation rate due to heat transfer between gas and solid is given by:g sg s( )T T S h dA T T − = ∫ [12]where h is a surface heat transfer coefficient, Tg and Ts are the local gas and solid temperatures, and the integration is carried out over the entire solid-gas interfacial area, A.
Q11. Why is Argon proposed as the working fluid?
It is for this reason that Argon is proposed as the working fluid, rather than air, since the same value of τ can be achieved at a lower pressure ratio due to Argon’s higher isentropic index.
Q12. What is the effect of the different temperature ratios on the compressor?
The various temperature ratios, τ, are related to the corresponding pressure ratios, β, by expressions of the form τ = βn, where n = (γ–1)(1–αe)ηe/γ for expanders and n = (γ–1)(1–αc)/ηcγ for compressors (see ref. [7] for derivation).
Q13. What is the round-trip efficiency for the reversible cycle?
The round-trip efficiency for the reversible cycle is unity by definition, irrespective of the cycle pressures and temperatures, but it is nonetheless useful to consider this case as it provides reasonable estimates for ρE and ρP.
Q14. How is the entropy generation rate calculated?
The loss in availability is given by integrating this entropy generation rate over the charge-discharge periods and multiplying by the environment temperature, T0.
Q15. What is the coefficient of a for high frequency cycles?
The coefficient a varies from 0 for high frequency cycles (analytical solution) to 1/12 for single charge operation (numerical approximation, but with very small error).
Q16. What is the way to restore HS to its initial discharged state?
If the discharge pressure ratio is the same as that for charging (Fig. 3a) then the compressor delivery temperature, T3′, lies above T3 and so heat rejected via HX2 (see Fig. 1) such that HS can be restored to its initial, discharged state.
Q17. What is the way to determine the efficiency of a PTES system?
Comparisons between technologies should be treated with caution, but it is nonetheless reasonable to conclude that PTES has very good energy density and a power density that is not too much below that of a low-spec gas turbine.


![Figure 4: Reservoir temperature profiles for different modes of operation (taken from [10])](/figures/figure-4-reservoir-temperature-profiles-for-different-modes-hfm1alcp.png)