3D change detection – Approaches and applications
Reads0
Chats0
TLDR
This paper reviews the recent developments and applications of 3D CD using remote sensing and close-range data, in support of both academia and industry researchers who seek for solutions in detecting and analyzing 3D dynamics of various objects of interest.Abstract:
Due to the unprecedented technology development of sensors, platforms and algorithms for 3D data acquisition and generation, 3D spaceborne, airborne and close-range data, in the form of image based, Light Detection and Ranging (LiDAR) based point clouds, Digital Elevation Models (DEM) and 3D city models, become more accessible than ever before Change detection (CD) or time-series data analysis in 3D has gained great attention due to its capability of providing volumetric dynamics to facilitate more applications and provide more accurate results The state-of-the-art CD reviews aim to provide a comprehensive synthesis and to simplify the taxonomy of the traditional remote sensing CD techniques, which mainly sit within the boundary of 2D image/spectrum analysis, largely ignoring the particularities of 3D aspects of the data The inclusion of 3D data for change detection (termed 3D CD), not only provides a source with different modality for analysis, but also transcends the border of traditional top-view 2D pixel/object-based analysis to highly detailed, oblique view or voxel-based geometric analysis This paper reviews the recent developments and applications of 3D CD using remote sensing and close-range data, in support of both academia and industry researchers who seek for solutions in detecting and analyzing 3D dynamics of various objects of interest We first describe the general considerations of 3D CD problems in different processing stages and identify CD types based on the information used, being the geometric comparison and geometric-spectral analysis We then summarize relevant works and practices in urban, environment, ecology and civil applications, etc Given the broad spectrum of applications and different types of 3D data, we discuss important issues in 3D CD methods Finally, we present concluding remarks in algorithmic aspects of 3D CDread more
Figures

Table 4. Examples of 3D CD applications 
Figure 1. Different geometric comparison methods. (a) Height difference, distances are computed vertically. (b) Euclidean distances, distances are computed in the surface normal direction. (c) projection-based inter-correlation method, the geometric difference is computed by projecting image on to the object, and then back project to image as ; the differences are given by measuring the differences between and . 
Table 3. An overview of the current 3D change detection methods 
Table 5. Recommendations on data co-registration (ordered by priority) 
Table 1. Overview of the differences between 3D and 2D CD problems 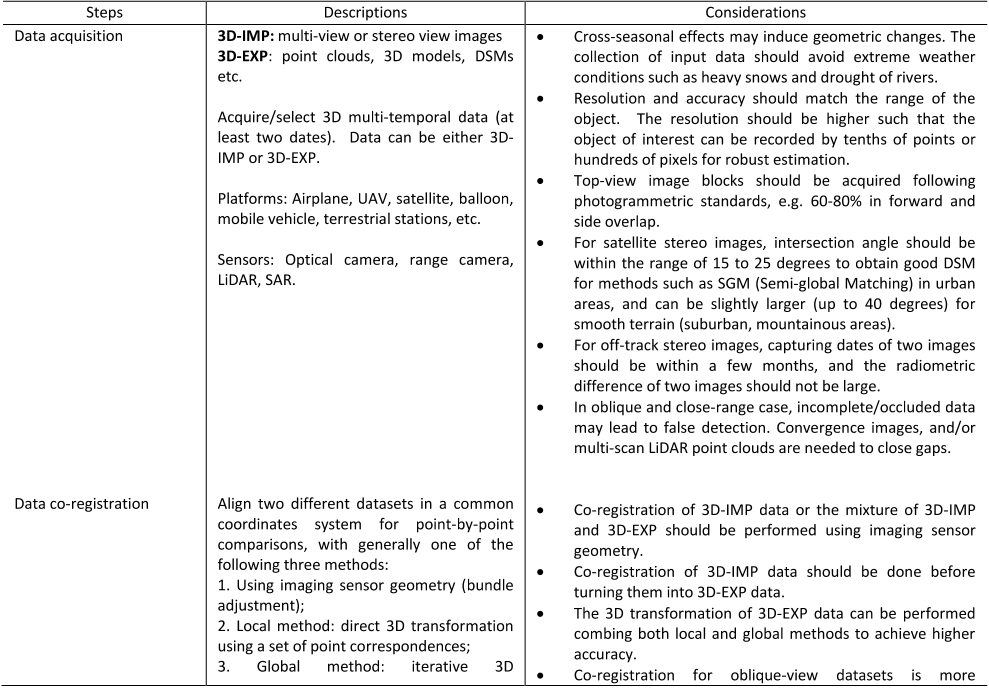
Table 2. Key considerations in a 3D CD task
Citations
More filters
Journal ArticleDOI
Airborne lidar change detection: An overview of Earth sciences applications
TL;DR: This review presents a comprehensive compilation of existing applications of ALS change detection to the Earth sciences, covering a wide scope of material pertinent to the broad field of Earth sciences to encourage the cross-pollination between sub-disciplines.
Journal ArticleDOI
Integrated Change Detection and Classification in Urban Areas Based on Airborne Laser Scanning Point Clouds.
TL;DR: A new approach for change detection in 3D point clouds that combines classification and CD in one step using machine learning is suggested.
Journal ArticleDOI
A Survey on Deep Learning-Based Change Detection from High-Resolution Remote Sensing Images
Huiwei Jiang,Min Peng,Yuanjun Zhong,Haofeng Xie,Zemin Hao,Jing-ming Lin,Xiaoli Ma,Xiangyun Hu +7 more
TL;DR: The main purpose of this paper is to provide a review of the available deep learning-based change detection algorithms using HR remote sensing images, and describes the change detection framework and classifies the methods from the perspective of the deep network architectures adopted.
Posted Content
A Review of Point Cloud Semantic Segmentation
TL;DR: In this article, the authors provide a needed up-to-date review of recent developments in 3D Point Cloud Semantic Segmentation (PCSS) and summarize existing studies on this topic.
Journal ArticleDOI
Building Change Detection Using Old Aerial Images and New LiDAR Data
TL;DR: This study proposes an automatic method to detect building changes in urban areas using aerial images and LiDAR data and demonstrates the promising performance of the proposed method.
References
More filters
Journal ArticleDOI
Random Forests
TL;DR: Internal estimates monitor error, strength, and correlation and these are used to show the response to increasing the number of features used in the forest, and are also applicable to regression.
Journal ArticleDOI
Random sample consensus: a paradigm for model fitting with applications to image analysis and automated cartography
TL;DR: New results are derived on the minimum number of landmarks needed to obtain a solution, and algorithms are presented for computing these minimum-landmark solutions in closed form that provide the basis for an automatic system that can solve the Location Determination Problem under difficult viewing.
Journal ArticleDOI
A method for registration of 3-D shapes
Paul J. Besl,H.D. McKay +1 more
TL;DR: In this paper, the authors describe a general-purpose representation-independent method for the accurate and computationally efficient registration of 3D shapes including free-form curves and surfaces, based on the iterative closest point (ICP) algorithm, which requires only a procedure to find the closest point on a geometric entity to a given point.
Journal ArticleDOI
Self-organized formation of topologically correct feature maps
TL;DR: In this paper, the authors describe a self-organizing system in which the signal representations are automatically mapped onto a set of output responses in such a way that the responses acquire the same topological order as that of the primary events.
Journal ArticleDOI
Comparing images using the Hausdorff distance
TL;DR: Efficient algorithms for computing the Hausdorff distance between all possible relative positions of a binary image and a model are presented and it is shown that the method extends naturally to the problem of comparing a portion of a model against an image.