"2-:)67-8=3*)227=0:%2-%"2-:)67-8=3*)227=0:%2-%
',30%60=311327 ',30%60=311327
-2%2')%4)67 #,%6832%'908=)7)%6',
3279148-32%7)(3()03*8,)!)61 869'896)3*28)6)783279148-32%7)(3()03*8,)!)61 869'896)3*28)6)78
%8)7%8)7
)77-'%#%',8)6
"2-:)67-8=3*)227=0:%2-%
3003;8,-7%2(%((-8-32%0;36/7%8,88476)437-836=94)22)(9*2')$4%4)67
%683*8,)-2%2')311327%2(8,)-2%2')%2(-2%2'-%0%2%+)1)28311327
)'311)2()(-8%8-32)'311)2()(-8%8-32
#%',8)63279148-32%7)(3()03*8,)!)61 869'896)3*28)6)78%8)7
3962%03*
-2%2'-%0'3231-'7
,884(<(3-36+..@2)'3
!,-74%4)6-74378)(%8 ',30%60=311327,88476)437-836=94)22)(9*2')$4%4)67
36136)-2*361%8-3240)%7)'328%'86)437-836=43&3<94)22)(9

3279148-32%7)(3()03*8,)!)61 869'896)3*28)6)78%8)73279148-32%7)(3()03*8,)!)61 869'896)3*28)6)78%8)7
&786%'8&786%'8
!,-74%4)6463437)7%'3279148-32&%7)(13()08,%8%''39287*361%2=*)%896)73*8,)231-2%08)61
7869'896)3*-28)6)786%8)7!,)(6-:-2+*36')&),-2(8,)13()0-7%8-1):%6=-2+46-')3*6-7/+)2)6%8)(&=
)<8)62%0,%&-831-2%0&32(7()4)2(324%78'3279148-32+63;8,8,639+,,%&-8%2(32)<4)'8)(
-2A%8-32#,)2'%0-&6%8)(83(%8%32'3279148-32-2A%8-32%2(8,)%++6)+%8)1%6/)88,)13()0
463(9')76)%0-78-'1)%27%2(:30%8-0-8-)73*&32(=-)0(7%2(%''39287*368,))<4)'8%8-32749>>0)!,)
13()0%073'%4896)78,),-+,)59-8=46)1-91%2()<')77783'/1%6/)8:30%8-0-8=
-7'-40-2)7-7'-40-2)7
-2%2')?-2%2')%2(-2%2'-%0%2%+)1)28
!,-7.3962%0%68-'0)-7%:%-0%&0)%8 ',30%60=311327,88476)437-836=94)22)(9*2')$4%4)67

The Rodney L. White Center for Financial Research
A Consumption-Based Model of the
Term Structure of Interest Rates
Jessica A. Wachter
27-04

A Consumption-Based Model of the Term Structure
of Interest Rates
∗
Jessica A. Wachter
†
University of Pennsylvania and NBER
July 9, 2004
∗
I thank Andrew Ang, Ravi Bansal, Michael Brandt, Geert Bekaert, John Campbell, John Cochrane,
Francisco Gomes, Vassil Konstantinov, Martin Lettau, Anthony Lynch, David Marshall, Lasse Pederson,
Andre Perold, Ken Singleton, Christopher Telmer, Jeremy Stein, Matt Richardson, Stephen Ross, Robert
Whitelaw, Yihong Xia, seminar participants at the 2004 Western Finance Association meeting in Vancouver,
the 2003 Society of Economic Dynamics meeting in Paris, and the 2001 NBER Asset Pricing meeting in
Los Angeles, the the NYU Macro lunch, the New York Federal Reserve, Washington University, and the
Wharton School. I thank Lehman Brothers for financial support.
†
Address: The Wharton School, University of Pennsylvania, 3620 Locust Walk, Philadelphia, PA 19104;
Tel: (215) 898-7634; Email: jwachter@wharton.upenn.edu; http://finance.wharton.upenn.edu/˜ jwachter/

A Consumption-Based Model of the Term Structure
of Interest Rates
Abstract
This paper proposes a consumption-based model that can account for many features of the
nominal term structure of interest rates. The driving force behind the model is a time-varying
price of risk generated by external habit. Nominal bonds depend on past consumption growth
through habit and on expected inflation. When calibrated to data on consumption, inflation, and
the average level of bond yields, the model produces realistic volatility of bond yields and can
explain key aspects of the expectations puzzle documented by Campbell and Shiller (1991) and
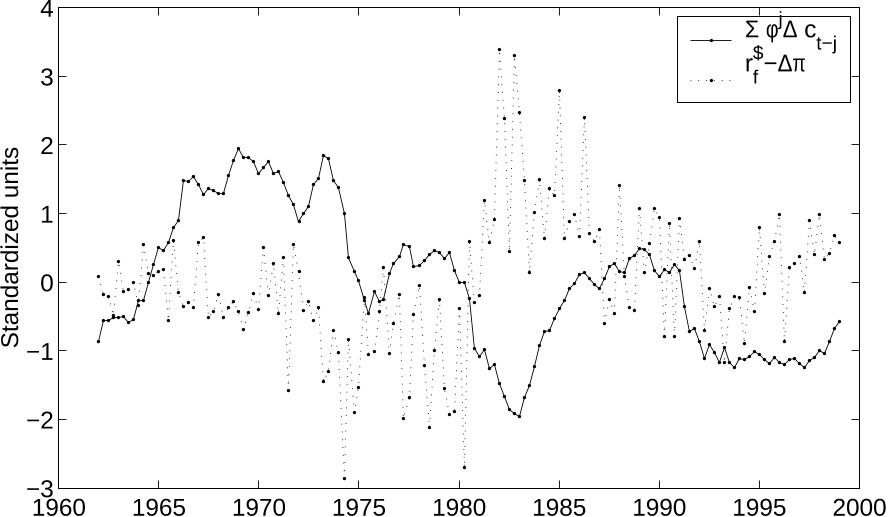
Fama and Bliss (1987). When actual consumption and inflation data are fed into the model, the
model is shown to account for many of the short and long-run fluctuations in the short-term interest
rate and the yield spread. At the same time, the model captures the high equity premium and
excess stock market volatility.