Q2. What was the significance of TAVR in patients with CKD?
Ourfindings demonstrated that patients who underwent TAVR had a significantly lower incidence of AKIin comparison to those who underwent SAVR, and TAVR was associated with decreasing incidence ofAKI during study periods.
Q3. What was the significance of the TAVR and SAVR?
AKI significantly increased the risk of 5-year mortality aftereither TAVR or SAVR and increasing severity of AKI was incrementally associated with 5-yearmortality.
Q4. What was the significance of the TAVR in patients without CKD?
Patients withAKI had significantly increased 5-year mortality compared to those without AKI (unmatched 36.0%vs 19.1%, log-rank P<0.001; matched 36.3% vs 24.0%, log-rank P<0.001).
Q5. What is the name of the registry?
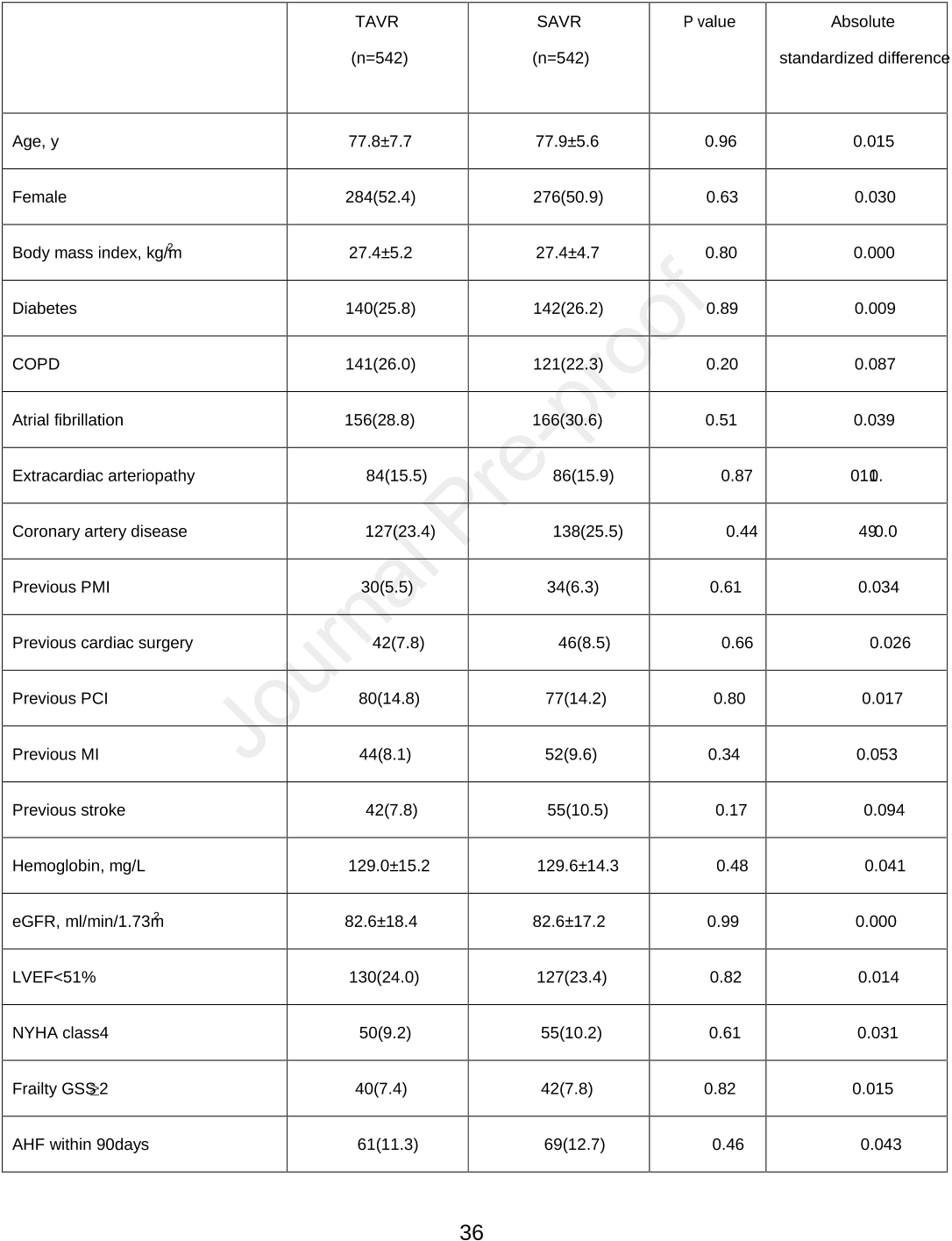
Clinical Trial Registration: ClinicalTrials.gov, Identifier: NCT03385915.(URL https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03385915)4From the nationwide registry, 4555 consecutive patients with pre-procedural normal kidneyfunction who underwent TAVR and SAVR (TAVR, n=1215 and SAVR, n=3340) were evaluated.
Q6. What was the hazard ratio for TAVR in patients without CKD?
The adjusted hazard ratiosfor 5-year mortality were 1.58 (95%CI 1.20-2.08) for AKI grade 1, 3.27 (95%CI 2.09-5.06) for grade 2and 4.82 (95%CI 2.93-8.04) for grade 3.3Conclusions: TAVR in patients without CKD was associated with significantly less frequentincidence of AKI compared with SAVR.