Q2. What are the possible techniques for characterizing chemical compounds?
Other possible techniques for characterizing chemical compounds include gas chromatography (GC), Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR), and gas chromatography- mass spectrometry (GC/MS), which also has the ability to monitor the isotope ratios of individual compounds (Degano and Colombini 2009; Evershed 1993; Gilbert et al.
Q3. What is the commonly used chemical technique in coprolite studies?
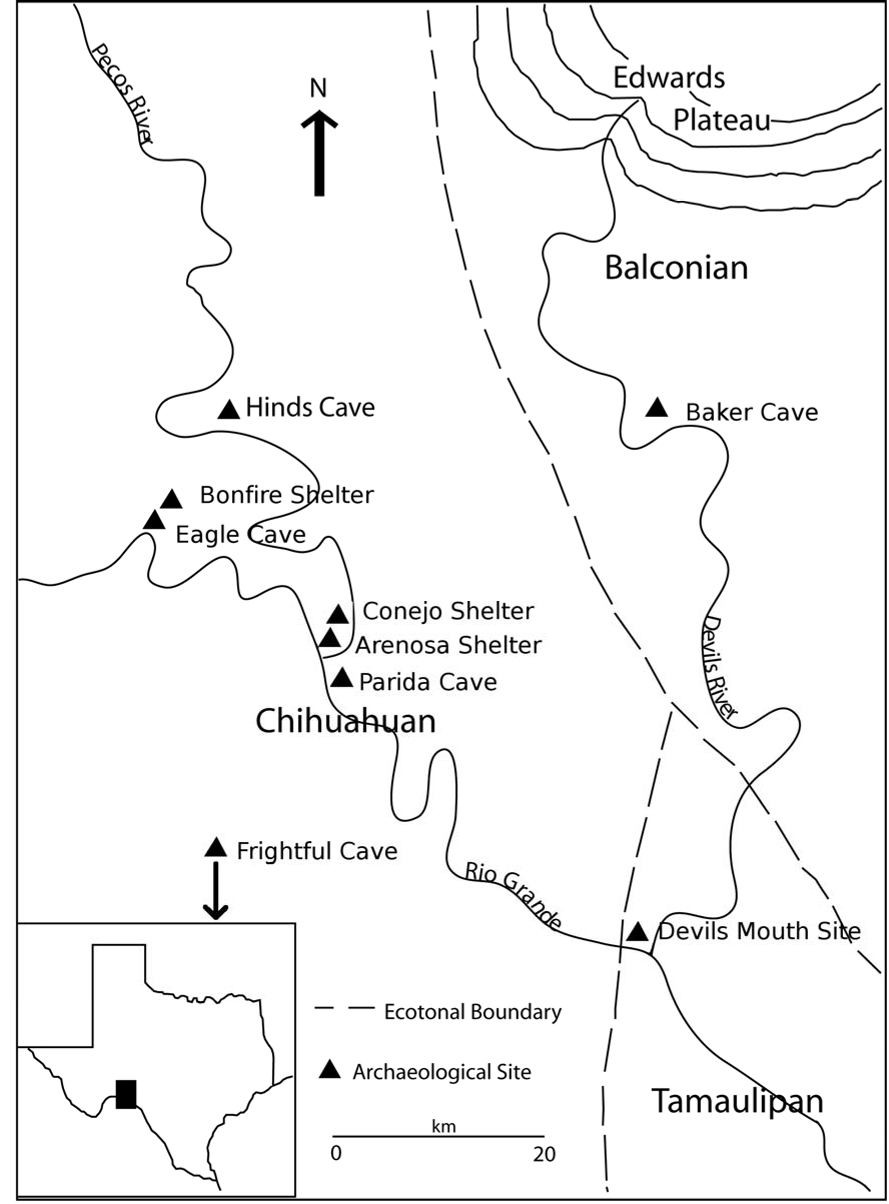
Prior to the advent of aDNA research, steroid analysis was themost commonly employed chemical technique in coprolite studies (Bull et al.
Q4. What is the potential of admixture of components within the specimen?
While coprolites do provide enough carbon to be dated directly using traditional radiocarbon methods (Williams-Dean 1978), there is the potential of external contamination and admixture of components within the specimen.
Q5. What is the main reason for the successful introduction of diet breadth models in anthropology?
These models deal with a biological necessity, food acquisition that humans share with all other animals, perhaps another reason for the successful introduction of these models in anthropology.
Q6. What is the caloric return rate of prickly pear tunas?
Despite having a relatively low caloric return by unit weight, prickly pear tunas have the highest caloric return rates of any resource considered in this model.
Q7. What are the common microfossils found in coprolite specimens?
Other microfossils have also been recovered from coprolite specimens, includingbacteria, fungal spores, diatoms, and phytoliths (Horrocks et al.
Q8. What are the main reasons for the difference in starch digestibility?
Storage techniques such as drying and freezing, which are both traditionally used among potato cultivators in the Andes (Johns 1988, 1996), can significantly decrease starch granule digestibility (Dreher et al. 1984; Szymonska 2000).