Kinetic-energy induced smoothening and delay of epitaxial breakdown in pulsed-laser deposition
Byungha Shin,Michael J. Aziz +1 more
TLDR
In this paper, the effect of kinetic energy of depositing species from flux pulsing during pulsed-laser deposition (PLD) on surface morphology evolution of Ge(001) homoepitaxy at low temperature was isolated.Abstract:
We have isolated the effect of kinetic energy of depositing species from the effect of flux pulsing during pulsed-laser deposition (PLD) on surface morphology evolution of Ge(001) homoepitaxy at low temperature $(100\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}\ifmmode^\circ\else\textdegree\fi{}\mathrm{C})$. Using a dual molecular beam epitaxy (MBE) PLD chamber, we compare morphology evolution from three different growth methods under identical experimental conditions except for the differing nature of the depositing flux: (a) PLD with average kinetic energy $300\phantom{\rule{0.3em}{0ex}}\mathrm{eV}$ (PLD-KE); (b) PLD with suppressed kinetic energy comparable to thermal evaporation energy (PLD-TH); and (c) MBE. The thicknesses at which epitaxial breakdown occurs are ranked in the order $\mathrm{PLD}\text{\ensuremath{-}}\mathrm{KE}g\mathrm{MBE}g\mathrm{PLD}\text{\ensuremath{-}}\mathrm{TH}$; additionally, the surface is smoother in PLD-KE than in MBE. The surface roughness of the films grown by PLD-TH cannot be compared due to the early epitaxial breakdown. These results demonstrate convincingly that kinetic energy is more important than flux pulsing in the enhancement of epitaxial growth, i.e., the reduction in roughness and the delay of epitaxial breakdown.read more
Figures
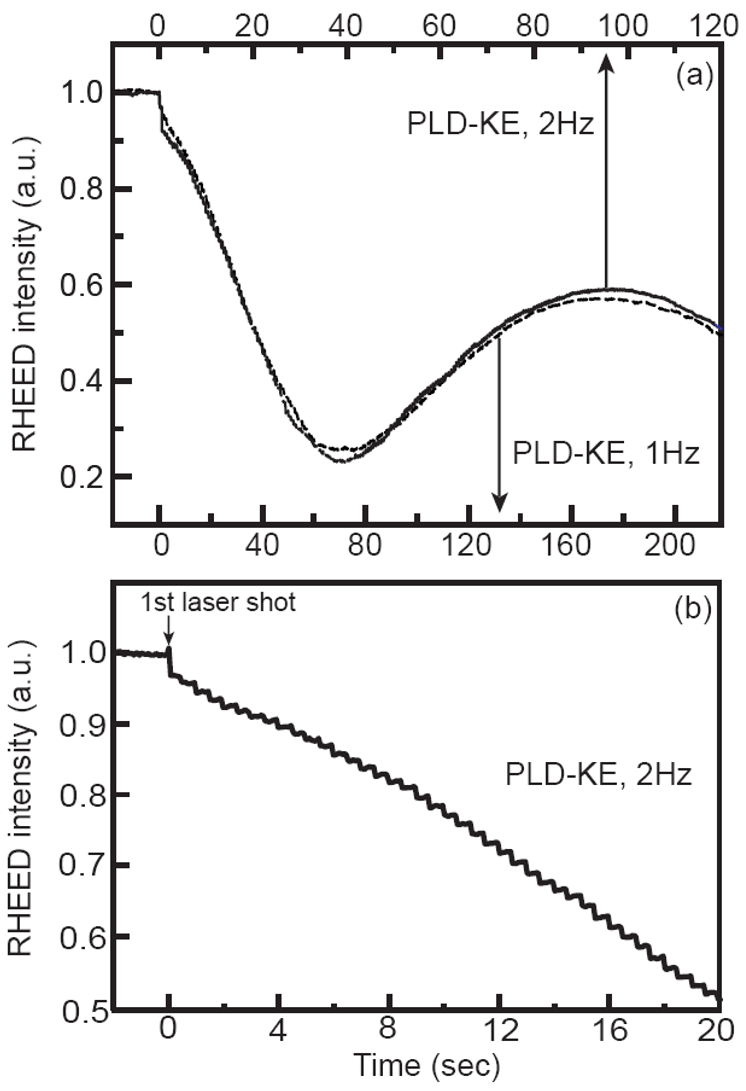
Fig. 4. (a) RHEED specular intensity variations during PLD-KE with 1 Hz (dashed line) and 2 Hz (solid line) of repetition rate while keeping instantaneous flux the same in both cases. Time axes are adjusted such that intensity minima and maxima for both cases are aligned at the same positions on abscissa. (b) First 20 seconds of RHEED intensity variation of PLD-KE with 1 Hz from (a). Modulations from individual laser pulses are visible. 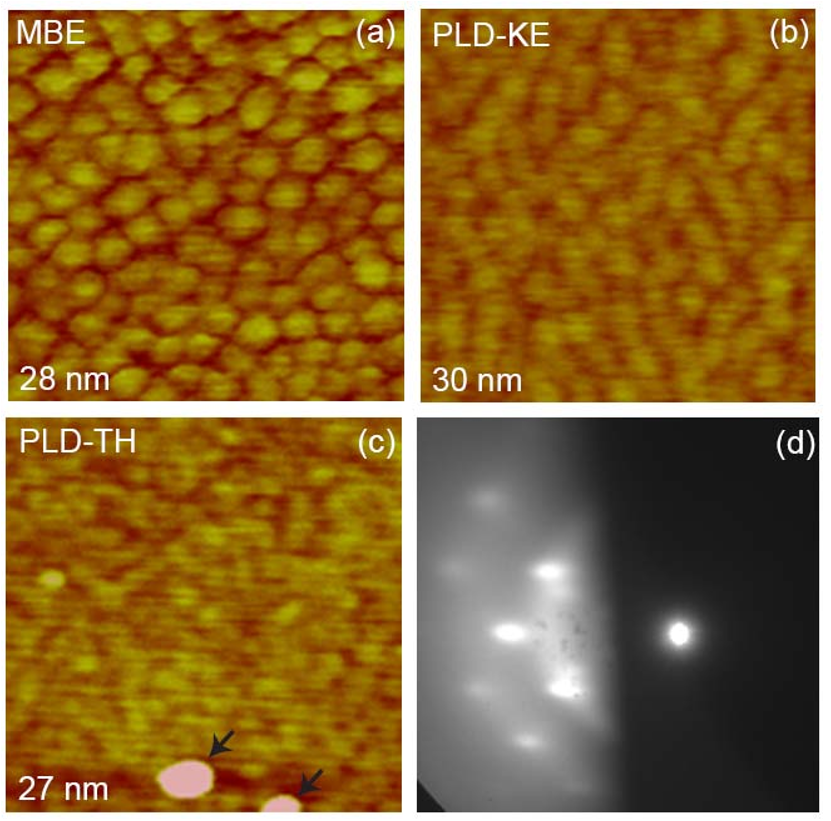
Fig. 2. (Color online) AFM images of films grown at 100 °C by (a) MBE, (b) PLD-KE, and (c) PLD-TH, and (d) RHEED pattern taken from surface shown in (c). Scan size and vertical scale of (a) – (c) are 0.25 x 0.25 μm2 and 5 nm, respectively. Thickness of films in (a) – (c) is shown in the left bottom corner of each image. 
Table I. Epitaxial thickness of PLD-KE, PLD-TH, and MBE at 100 °C and 150 °C. In the case of PLD-KE, the thickest samples – 270 nm at 100 °C and 410 nm at 150 °C – are still fully epitaxial.
Citations
More filters
Journal Article
Comparison of Morphology Evolution of Ge(001) Homoepitaxial Films Grown by Pulsed Laser Deposition and Molecular Beam Epitaxy
TL;DR: In this paper, a dual molecular-beam epitaxy (MBE)-pulsed laser deposition (PLD) ultrahigh vacuum chamber was used to compare Ge(001) homoepitaxial growth morphology in PLD and MBE.
Journal ArticleDOI
Microstructure-related piezoelectric properties of a ZnO film grown on a Si substrate
Qin Weiwei,Yu Tong Li,Li Tao,Jun Wen Qiu,Xian Jun Ma,Du Wei,Xiaoqiang Chen,Xuefeng Hu,Wei Zhang +8 more
TL;DR: In this paper, the effect of grain size on the piezoelectric properties of ZnO was investigated using films of different grain sizes and a fixed thickness of 800-nm.
Journal ArticleDOI
Structural and nanomechanical properties of InN films grown on Si(1 0 0) by femtosecond pulsed laser deposition
M A Hafez,M A Hafez,M. A. Mamun,M. A. Mamun,Abdelmageed Elmustafa,Abdelmageed Elmustafa,Hani E. Elsayed-Ali,Hani E. Elsayed-Ali +7 more
TL;DR: In this paper, the structural and nanomechanical properties of InN films grown on Si(1 0 0 0) using femtosecond pulsed laser deposition were studied for different growth conditions.
Journal ArticleDOI
Experimental and theoretical study on the energy-dependent surface evolution and microstructure changes in copper nanostructured composites
TL;DR: In this paper, the role of metal in addition to carbon ions as in diamond-like carbon (DLC) nanocomposites is investigated and the energy dependence of surface evolution and changes in microstructures due to the presence of metal were analyzed.
Journal ArticleDOI
Topography evolution of germanium thin films synthesized by pulsed laser deposition
TL;DR: Germanium thin films were deposited by Pulsed Laser Deposition (PLD) onto single crystal Ge and Si (100) substrates with a native oxide film on the surface as mentioned in this paper.
References
More filters
Book ChapterDOI
Pulsed laser deposition of thin films
TL;DR: Pulsed laser deposition of high-temperature superconducting thin films for active and passive device applications is discussed in this article, with a focus on the commercial scale-up of Pulsed Laser Deposition.
Journal ArticleDOI
Pulsed laser vaporization and deposition
P.R. Willmott,J. R. Huber +1 more
TL;DR: In this article, the authors outline the fundamental physics involved and go on to discuss recent experimental findings of pulsed laser deposition, as an alternative to chemical vapor deposition or molecular beam epitaxy.
Journal ArticleDOI
Pulsed laser deposition of thin films of (
TL;DR: In this paper, the magnetoresistance peak occurs around the Curie point, whereas for x = 0.5 the onset of magnetoreduction is somewhat below and increases monotonically as.
Journal ArticleDOI
Time-resolved imaging of gas phase nanoparticle synthesis by laser ablation
TL;DR: In this article, the dynamics of nanoparticle formation, transport, and deposition by pulsed laser ablation of c-Si into 1-10 Torr He and Ar gases are revealed by imaging laser-induced photoluminescence and Rayleigh-scattered light from gas-suspended 1−10 nm SiOx particles.
Journal ArticleDOI
Strategy of nanocluster and nanostructure synthesis by conventional pulsed laser ablation
TL;DR: In this article, the basic principles of nanoparticle synthesis by conventional pulsed laser ablation are described and the theoretical development and analysis of the experimental results are given for condensation, expansion and properties of silicon nanoclusters.
Related Papers (5)
Role of Cluster Transient Mobility in Pulsed Laser Deposition-Type Growth Kinetics
E. Vasco,J. L. Sacedón +1 more