Q1. What are the contributions mentioned in the paper "A cartesian grid embedded boundary method for the heat equation on irregular domains" ?
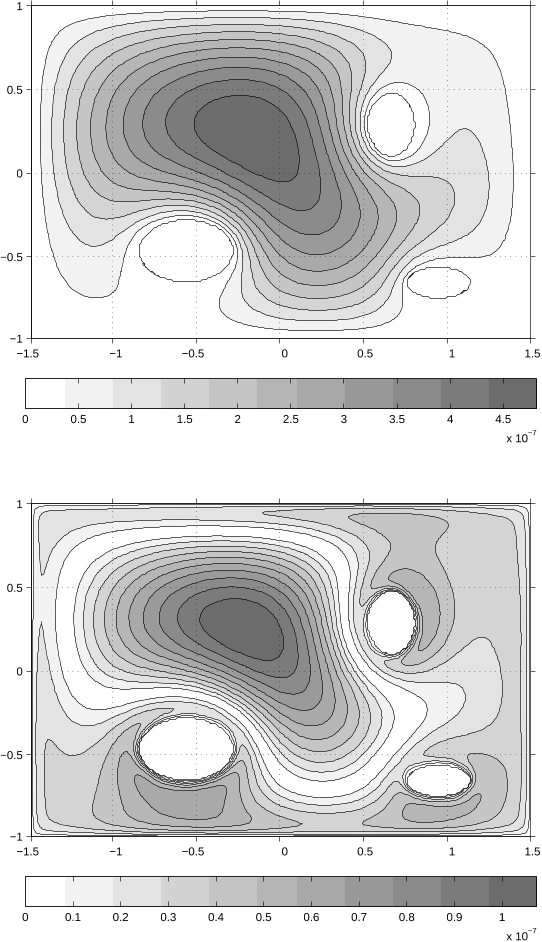
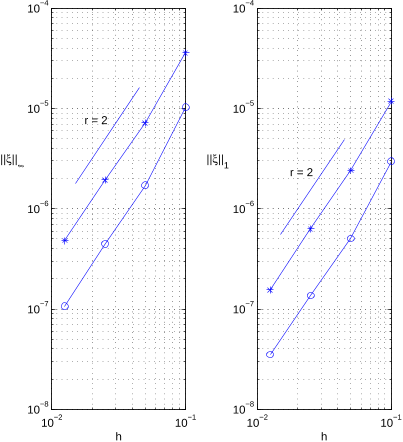
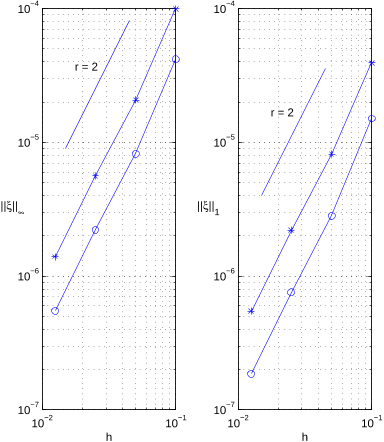
The authors present an algorithm for solving the heat equation on irregular time-dependent domains.
read more