Q2. What is the immune system of crustaceans?
The immune system of crustaceans ismainly non-specific and relies on phagocytosis, encapsulation and agglutination alongside the phenoloxidase-mediated production ofmelanin through thepro-phenoloxidase cascade (Smith andSoderhall, 1983).
Q3. What is the way to test the immune system?
An exogenous source of nucleotides may optimize the functions of rapidly dividing cells, such as those of the immune system, that lack the capacity to synthesize nucleotides and therefore must depend on a pre-formed source (Carver andWalker, 1995).
Q4. How many days did the animals receive the white spot virus?
After 28 days of feeding the animals were challenged with white spot syndrome virus by feeding white spot virus infected frozen tissue at the rate of 1 g/animal.
Q5. What is the reason for the elevation of NBT?
A very prominent elevation in NBT level on day 3 after challenge could beattributed to an increase in phagocytosis and the resulting production of more superoxide anions.
Q6. What is the reason for the increase in adipose activity in the ly?
Signal transduction in the prophenoloxidase-activating system of Macrobarchium rosenbergii and intracellular phenoloxidase activity in haemocyte lysate supernatant (HLS) were found to be increased after treating with CpG oligonucleotides (Chuo et al., 2005).
Q7. How long did the shrimps stay in the aquarium?
The shrimps (60 Nos), after seven days quarantine, were transferred to four aquarium tanks of 500 L capacity and acclimatized for a week.
Q8. what is the halotolerent property of the yeast C. sake?
The halotolerent property of the yeast C. sake would be an advantage in this context and it can be used in brackish water and seawater aquaculture where it would not result in cell lysis and associated water quality deterioration.
Q9. Who is the author of this article?
The authors are grateful to the Department of Ocean Development, Govt. of India for a research grant with which the work was carried out.
Q10. What is the diet for shrimp?
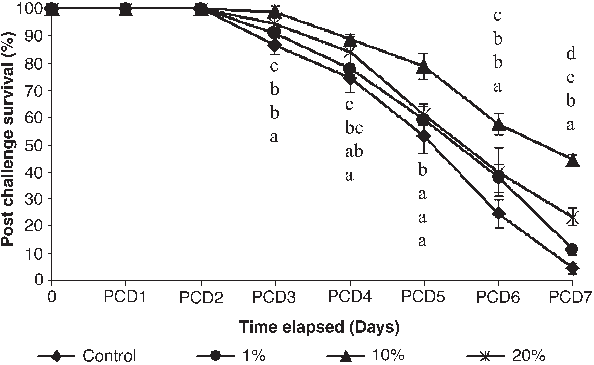
Shrimpsfed thediet containing10%yeast showed 44±2% survival while groups fed on diets containing 1% and 20% yeast showed only 11±2% and 23±3% survival respectively (Fig. 4).
Q11. What was the diet of C. sake?
Control diet: fish meal, 28 g; prawn shell powder, 20 g; rice bran, 10 g; soyabean meal, 10g;groundnutoil cake,8g;vitaminmix,2g; refinedwheat flour, 20 g.
Q12. How was the yeast biomass added to the test feeds?
Into the test feeds yeast biomass was added at a graded levels 1, 10 and 20 g and pelletised using a laboratory model pelletiser having 1 mm die.
Q13. Which diet was used for the treatment of white spot syndrome?
Group 1 received the control diet, Group 2, the feed containing 1% yeast, Groups 3 and 4 the diets containing 10% and 20% yeast, respectively.