Q2. What was the next Internet application that increased the risk of being addicted to the Internet?
The next Internet application that significantly increased the risks of being addicted to the Internet was online chat/forums (i.e., increased chance by 60%).
Q3. What is the main reason for the use of online forums?
As with online chat rooms, online forums may be a substitute for real life contacts, and engagement with them could lead to excess, as suggested by the results of this study.
Q4. What was the baseline model including no predictors?
The baseline model including no predictors was significant (b = -3.340, Wald Χ2 (1) = 761.17, p < .01), indicating that the chance for being addicted to the Internet by the overall study population was .03.
Q5. What is the effect of neuroticism on the odds of being addicted to the Internet?
the interaction between neuroticism and online shopping decreased the odds of being addicted to the Internet by 45% (b = -.60, Wald Χ2 (1) = 5.50, p < .05).
Q6. What is the reason for the increase in the risk of being addicted to the Internet?
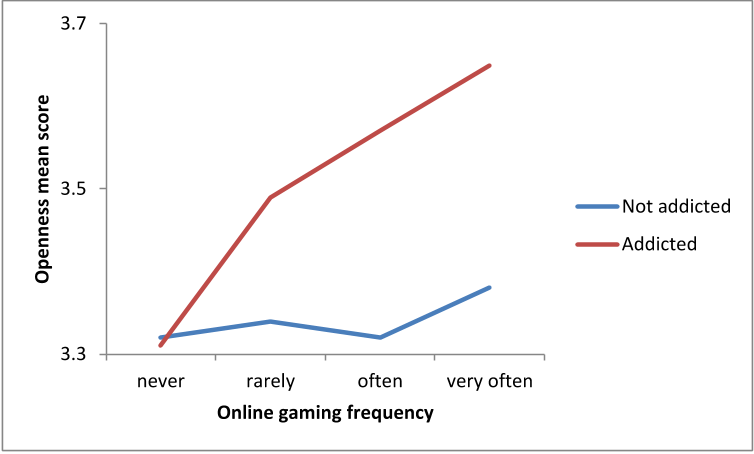
This study also demonstrated that engaging in online gaming increased the risks of being addicted to the Internet when paired with higher openness to experience.
Q7. What is the main reason why some individuals become addicted to the Internet?
it suggests that SNSs are mostly used for the maintenance of established offline networks that are important for academic and professional opportunities, and thus might explain why some individuals become addicted to using them (Kuss & Griffiths, 2011).
Q8. What are the reasons for the increased use of instant messengers in young populations?
Previous research has found that the reasons for increased use of instant messengers (e.g., ICQ, MSN) in young populations are media richness and presentational control (Sheer, 2010).