Memristor-based memory
Reads0
Chats0
TLDR
The read operation of memristor-based memories is investigated and a new technique for solving the sneak paths problem by gating the memory cell using a three-terminal memistor device is introduced.About:
This article is published in Microelectronics Journal.The article was published on 2013-02-01 and is currently open access. It has received 378 citations till now. The article focuses on the topics: Memristor & Memistor.read more
Figures

Figure 1: A simple memristor-based memory array showing how a memristor device is located at the intersection between two bars of the array. 
Figure 10: Simple memory array showing the added column capacitors for the AC sense. 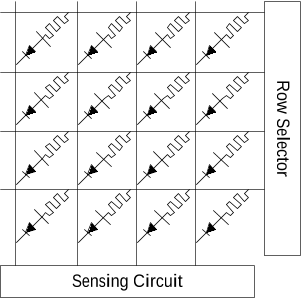
Figure 9: Simple memory array with 1D1M used for each memory cell. ![Table 1: Detailed comparison between memristor-based memory, traditional memories, and other emerging memories according to the 2011 ITRS report [1]. The abbreviations used are: T – transistor, C – capacitor, R – resistor, and D – diode. The bold font indicates the best value per row.](/figures/table-1-detailed-comparison-between-memristor-based-memory-1jvhbfr7.png)
Table 1: Detailed comparison between memristor-based memory, traditional memories, and other emerging memories according to the 2011 ITRS report [1]. The abbreviations used are: T – transistor, C – capacitor, R – resistor, and D – diode. The bold font indicates the best value per row. 
Figure 11: Examples of different organizations with different aspect ratios for a 16-cell memory array. 
Figure 12: Noise margin (∆′) versus aspect ratio for different array sizes.
Citations
More filters
Proceedings ArticleDOI
Sub-crosspoint RRAM decoding for improved area efficiency
Ravi Patel,Eby G. Friedman +1 more
TL;DR: Two sub-crosspoint physical topologies are proposed that places the decode circuitry beneath the metal-oxide RRAM crosspoint array, and one of these integrates both the row and column decoder.
Proceedings ArticleDOI
Adder implementation in reconfigurable resistive switching crossbar
TL;DR: An N-input stateful-NOR operation on Complementary Resistive Switch (CRS) based crossbar array is proposed and a comparison of 8-bit adder implementation with existing adder architectures on crossbar shows reduction in the number of execution steps required and number of CRS cells used for implementation.
Journal ArticleDOI
Multifunctional Double Active Layers Formed with Electrochemically Controlled Nanoparticle Dispersion for Resistive Switching Memory Arrays
Hee Won Suh,Dong Su Kim,Ji-Hoon Choi,Hak Hyeon Lee,Kun Woong Lee,Sung Hyeon Jung,Won-Seok Yang,Jeong-Jae Kim,Ji Sook Yang,Ho Seong Lee,Hyung-Koun Cho +10 more
TL;DR: In this article , a multi-functional active layer that enables a self-driving resistive random access memory is achieved by stacking two electrodeposited Cu 2 O layers having the unique structure of polycrystalline nanoparticles embedded in the amorphous matrix.
Proceedings ArticleDOI
A photo sensor with one-direction memristive behavior based on silicon-oxide
P Ghasemi,Mohammad Javad Sharifi +1 more
TL;DR: In this paper , a nonlinear, silicon-based, and photosensitive memristor structure with oxide as the active layer was constructed using a thin SiO2 grown layer on n-Si.
References
More filters
Journal ArticleDOI
The missing memristor found
TL;DR: It is shown, using a simple analytical example, that memristance arises naturally in nanoscale systems in which solid-state electronic and ionic transport are coupled under an external bias voltage.
Journal ArticleDOI
Memristor-The missing circuit element
TL;DR: In this article, the memristor is introduced as the fourth basic circuit element and an electromagnetic field interpretation of this relationship in terms of a quasi-static expansion of Maxwell's equations is presented.
Journal ArticleDOI
Nanoscale Memristor Device as Synapse in Neuromorphic Systems
TL;DR: A nanoscale silicon-based memristor device is experimentally demonstrated and it is shown that a hybrid system composed of complementary metal-oxide semiconductor neurons and Memristor synapses can support important synaptic functions such as spike timing dependent plasticity.
Journal ArticleDOI
Resistance Switching Memories Are Memristors
TL;DR: The memristor is a 2-terminal nonvolatile memory device that exhibits a pinched hysteresis loop confined to the first and third quadrants of the v-i plane whose contour shape in general changes with both the amplitude and frequency of any periodic sine-wave-like input voltage source, or current source as mentioned in this paper.
Resistance Switching Memories are Memristors.
TL;DR: The goal of this tutorial is to introduce some fundamental circuit-theoretic concepts and properties of the memristor that are relevant to the analysis and design of non-volatile nano memories where binary bits are stored as resistances manifested by the Memristor’s continuum of equilibrium states.