Memristor-based memory
Reads0
Chats0
TLDR
The read operation of memristor-based memories is investigated and a new technique for solving the sneak paths problem by gating the memory cell using a three-terminal memistor device is introduced.About:
This article is published in Microelectronics Journal.The article was published on 2013-02-01 and is currently open access. It has received 378 citations till now. The article focuses on the topics: Memristor & Memistor.read more
Figures

Figure 1: A simple memristor-based memory array showing how a memristor device is located at the intersection between two bars of the array. 
Figure 10: Simple memory array showing the added column capacitors for the AC sense. 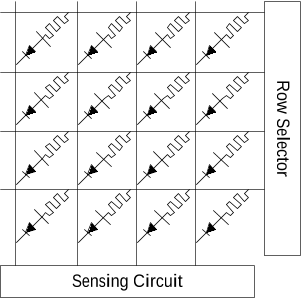
Figure 9: Simple memory array with 1D1M used for each memory cell. ![Table 1: Detailed comparison between memristor-based memory, traditional memories, and other emerging memories according to the 2011 ITRS report [1]. The abbreviations used are: T – transistor, C – capacitor, R – resistor, and D – diode. The bold font indicates the best value per row.](/figures/table-1-detailed-comparison-between-memristor-based-memory-1jvhbfr7.png)
Table 1: Detailed comparison between memristor-based memory, traditional memories, and other emerging memories according to the 2011 ITRS report [1]. The abbreviations used are: T – transistor, C – capacitor, R – resistor, and D – diode. The bold font indicates the best value per row. 
Figure 11: Examples of different organizations with different aspect ratios for a 16-cell memory array. 
Figure 12: Noise margin (∆′) versus aspect ratio for different array sizes.
Citations
More filters
Journal ArticleDOI
An All-Inorganic, Transparent, Flexible, and Nonvolatile Resistive Memory
TL;DR: In this article, a transparent and flexible nonvolatile perovskite oxide resistive memory (ReRAM) was presented, which has a high/low resistance ratio of over 106 and can be maintained over 104 s without notable substantial fluctuation under bending and stretching cycling.
Journal ArticleDOI
Fully Printed Memristors from Cu–SiO2 Core–Shell Nanowire Composites
Matthew J. Catenacci,Patrick F. Flowers,Changyong Cao,Joseph B. Andrews,Aaron D. Franklin,Benjamin J. Wiley +5 more
TL;DR: In this article, a composite of Cu-SiO2 nanowires dispersed in ethylcellulose acts as a resistive switch between printed Cu and Au electrodes, and a 16-cell crossbar array of these memristors was printed with an aerosol jet.
Journal ArticleDOI
Modeling Physarum space exploration using memristors
TL;DR: A two-dimensional mesh grid memristor based model is presented as an approach to emulate Physarum's foraging strategy, which includes space exploration and reinforcement of the optimally formed interconnection network in the presence of multiple aliment sources.
Book ChapterDOI
mMPU—A Real Processing-in-Memory Architecture to Combat the von Neumann Bottleneck
TL;DR: This chapter presents mMPU memristive memory processing unit, which relies on a Memristor-Aided loGIC (MAGIC), a technique to compute logical functions using memristors within the memory array, and therefore directly tackles the von Neumann bottleneck.
Journal ArticleDOI
Design and analysis of 2T2M hybrid CMOS-Memristor based RRAM
Noha Shaarawy,Ahmed Emara,A.M. El-Naggar,Mohammed E. Elbtity,Maged Ghoneima,Ahmed G. Radwan,Ahmed G. Radwan +6 more
TL;DR: The proposed analysis is applied to diverse types of RRAM cells, and a comparison between the performance of such cells is discussed, and the effect of the exponential memristor model on thememristor behaviour in terms of switching speed and the range of the Memristor resistance is discussed.
References
More filters
Journal ArticleDOI
The missing memristor found
TL;DR: It is shown, using a simple analytical example, that memristance arises naturally in nanoscale systems in which solid-state electronic and ionic transport are coupled under an external bias voltage.
Journal ArticleDOI
Memristor-The missing circuit element
TL;DR: In this article, the memristor is introduced as the fourth basic circuit element and an electromagnetic field interpretation of this relationship in terms of a quasi-static expansion of Maxwell's equations is presented.
Journal ArticleDOI
Nanoscale Memristor Device as Synapse in Neuromorphic Systems
TL;DR: A nanoscale silicon-based memristor device is experimentally demonstrated and it is shown that a hybrid system composed of complementary metal-oxide semiconductor neurons and Memristor synapses can support important synaptic functions such as spike timing dependent plasticity.
Journal ArticleDOI
Resistance Switching Memories Are Memristors
TL;DR: The memristor is a 2-terminal nonvolatile memory device that exhibits a pinched hysteresis loop confined to the first and third quadrants of the v-i plane whose contour shape in general changes with both the amplitude and frequency of any periodic sine-wave-like input voltage source, or current source as mentioned in this paper.
Resistance Switching Memories are Memristors.
TL;DR: The goal of this tutorial is to introduce some fundamental circuit-theoretic concepts and properties of the memristor that are relevant to the analysis and design of non-volatile nano memories where binary bits are stored as resistances manifested by the Memristor’s continuum of equilibrium states.