Memristor-based memory
Reads0
Chats0
TLDR
The read operation of memristor-based memories is investigated and a new technique for solving the sneak paths problem by gating the memory cell using a three-terminal memistor device is introduced.About:
This article is published in Microelectronics Journal.The article was published on 2013-02-01 and is currently open access. It has received 378 citations till now. The article focuses on the topics: Memristor & Memistor.read more
Figures

Figure 1: A simple memristor-based memory array showing how a memristor device is located at the intersection between two bars of the array. 
Figure 10: Simple memory array showing the added column capacitors for the AC sense. 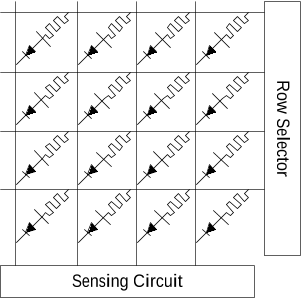
Figure 9: Simple memory array with 1D1M used for each memory cell. ![Table 1: Detailed comparison between memristor-based memory, traditional memories, and other emerging memories according to the 2011 ITRS report [1]. The abbreviations used are: T – transistor, C – capacitor, R – resistor, and D – diode. The bold font indicates the best value per row.](/figures/table-1-detailed-comparison-between-memristor-based-memory-1jvhbfr7.png)
Table 1: Detailed comparison between memristor-based memory, traditional memories, and other emerging memories according to the 2011 ITRS report [1]. The abbreviations used are: T – transistor, C – capacitor, R – resistor, and D – diode. The bold font indicates the best value per row. 
Figure 11: Examples of different organizations with different aspect ratios for a 16-cell memory array. 
Figure 12: Noise margin (∆′) versus aspect ratio for different array sizes.
Citations
More filters
Book ChapterDOI
Experimental Demonstration of Firing Rate Neural Networks Based on Metal-Oxide Memristive Crossbars
TL;DR: This chapter presents the basic principles of resistive Random Access Memories, alongside their performance as single devices and also when integrated in crossbars, and presents the results of the first experimental realizations of single- and multi-layer neural networks with synapses implemented through crossbar arrays.
Posted Content
Near-Optimal Detection for Both Data and Sneak-Path Interference in Resistive Memories with Random Cell Selector Failures.
TL;DR: In this article, the authors propose a near-optimal data detection scheme that can approach the performance bound of the optimal detection scheme, which leverages a joint data and sneak-path interference recovery and can use all intercell correlations.
Proceedings ArticleDOI
Designing a differential 3R-2bit RRAM cell for enhancing read margin in cross-point RRAM arrays
TL;DR: A 3R-2bit cross-point architecture has been proposed that stores two-bit data in three resistive RRAM elements and a sense-before-write technique has been applied to maintain endurance and power consumption by preventing excessive write operation.
Proceedings ArticleDOI
Minimal Disturbed Bits in Writing Resistive Crossbar Memories
TL;DR: In this paper, the write disturb problem is mathematically formulated in terms of the bias parameters and optimized analytically and a closed form solution for the optimal bias parameters is calculated.
Journal ArticleDOI
Research progress and applications of memristor emulator circuits
TL;DR: In this paper , the authors present the current research status of memristor emulator circuits, and analyses the design ideas, circuit composition, advantages and disadvantages of emulator circuits implemented by different schemes, then introduces the application of some emulators in real circuits.
References
More filters
Journal ArticleDOI
The missing memristor found
TL;DR: It is shown, using a simple analytical example, that memristance arises naturally in nanoscale systems in which solid-state electronic and ionic transport are coupled under an external bias voltage.
Journal ArticleDOI
Memristor-The missing circuit element
TL;DR: In this article, the memristor is introduced as the fourth basic circuit element and an electromagnetic field interpretation of this relationship in terms of a quasi-static expansion of Maxwell's equations is presented.
Journal ArticleDOI
Nanoscale Memristor Device as Synapse in Neuromorphic Systems
TL;DR: A nanoscale silicon-based memristor device is experimentally demonstrated and it is shown that a hybrid system composed of complementary metal-oxide semiconductor neurons and Memristor synapses can support important synaptic functions such as spike timing dependent plasticity.
Journal ArticleDOI
Resistance Switching Memories Are Memristors
TL;DR: The memristor is a 2-terminal nonvolatile memory device that exhibits a pinched hysteresis loop confined to the first and third quadrants of the v-i plane whose contour shape in general changes with both the amplitude and frequency of any periodic sine-wave-like input voltage source, or current source as mentioned in this paper.
Resistance Switching Memories are Memristors.
TL;DR: The goal of this tutorial is to introduce some fundamental circuit-theoretic concepts and properties of the memristor that are relevant to the analysis and design of non-volatile nano memories where binary bits are stored as resistances manifested by the Memristor’s continuum of equilibrium states.