Q2. What is the way to increase starch content in a microalga?
Since accumulation of starch occurred at nitrogen depletion conditions under which the cell growth was much slower than that observed during nitrogen supplemented cultivations, compromising between increasing starch content and cell growth will be necessary in order to attain high values of both biomass concentration and starch productivity.
Q3. What is the common concern related to biofuels?
The increasing competition with agriculture for cultivable land used for food production has been considered one of the most common concerns related to current first generation biofuels [3,4].
Q4. What are the main reasons for the soaring petroleum prices?
The reliance of the global economy on fossil-derived fuels, coupled with the increasing energy demand in emerging countries (e.g. India and China) and the geo-political instability in some world’s oil-producing regions, have led to soaring petroleum prices in the last years.
Q5. What is the important factor in the growth of microalgae?
microalgae growth depends not only on an adequate supply of essential macronutrient elements (carbon, nitrogen, phosphorus, silicon) and major ions (Mg2+, Ca2+, Cl , and SO2 4 ) but also on a number of micronutrient metals such as iron, manganese, zinc, cobalt, copper, and molybdenum [12].
Q6. What is the effect of carbon on microalgae?
The carbon source and agitation during cultivation of microalgae were supplied by bubbling CO2-enriched air (2% v/v CO2) through a tube (inner diameter, 2 mm) that ended near the bottom of the column, at an aeration rate of 0.833 vvm (volume of gases per volume of culture suspension per minute).
Q7. How much starch was required for the growth of C. vulgaris strain P12?
The results described above hint that the optimum concentration of urea required for the growth of microalgae was 1.1 g L 1, while the lowest concentrations of nitrogen and iron sources led to the highest starch productivity (0.199 g L 1 day 1).
Q8. What was the effect of the initial nitrogen and iron source on starch content?
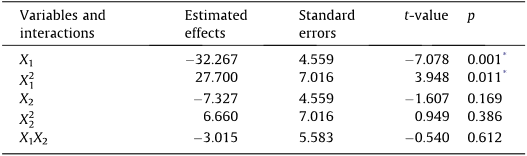
Due to the large differences observed in the amount of starch produced by C. vulgaris strain P12, a statistical analysis was carried out aiming at identifying which independent variable had significant influence on starch accumulation.
Q9. What is the property of rotatability developed for CCD?
The property of rotatability developed for CCD requires the variance of estimated values to be constant at points equally distant from the center of design [18].
Q10. What was the method for predicting the optimal starch content?
The highest starch contents (41.0%, 40.5% and 39.8%) were obtained under nitrogen-deprived conditions (initial urea concentration = 0 g L 1) and initial FeNa-EDTA concentrations of 0.04, 0 and 0.08 g L 1, respectively (Runs 5, 1 and 2).
Q11. How much starch did the microalga grow?
In this work, starch content of freshwater microalga C. vulgaris strain P12 reached up to 41.0% of dry cell weight, which was 8-fold higher than the control (central points of the experimental design).
Q12. What did Friedman et al. find to be the significant effect on starch?
The initial iron source concentration did not present a statistically significant effect on starch content, implying that chelatedFe(III) did not affect the starch accumulation in C. vulgaris.
Q13. What software was used for the analysis of the experimental results?
The statistical analysis of the results was carried out with the Experimental Design Module of the software Statistica 8.0 (Statsoft, USA).
Q14. What is the relationship between independent variables and starch content in C. vulgaris?
The relation between independent variables and starch content in C. vulgaris can be best visualized by examining the surface plot presented in Fig. 1.Fig. 1 clearly shows that decreasing initial urea concentration resulted in higher starch accumulation, with maxima values (P40%) being achieved under the minimum urea concentration (0 mg L 1).
Q15. What is the significance of the regression analysis?
regression analysis were effective in identifying the optimal conditions for maximum accumulation of microalgal starch for the different nutritional conditions.