Q1. What are the contributions mentioned in the paper "A behaviour-based control architecture for heterogeneous modular, multi-configurable, chained micro-robots" ?
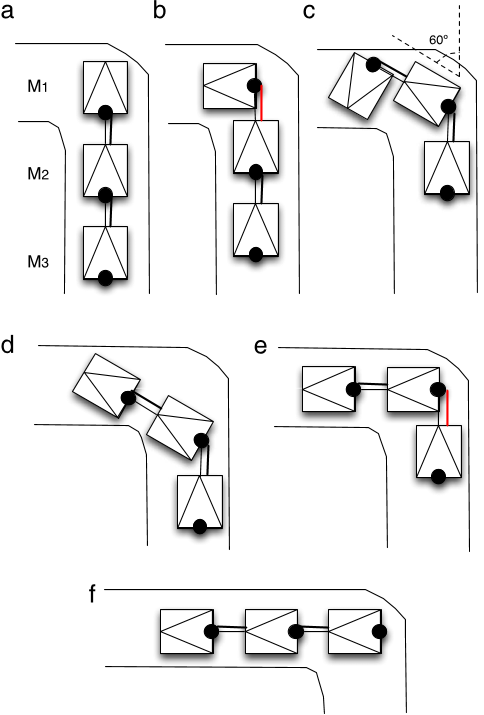
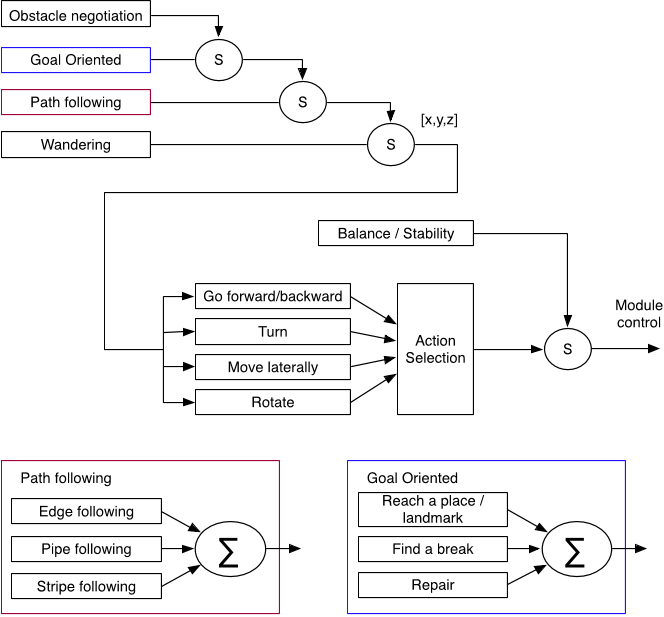
In this paper, the authors present a control solution for chained, modular robots composed of different types of module ( heterogeneous modules ) that can be arranged in different configurations, a feature called multi-configurability.