A Sentiment Information Collector-Extractor Architecture Based Neural Network for Sentiment Analysis
TLDR
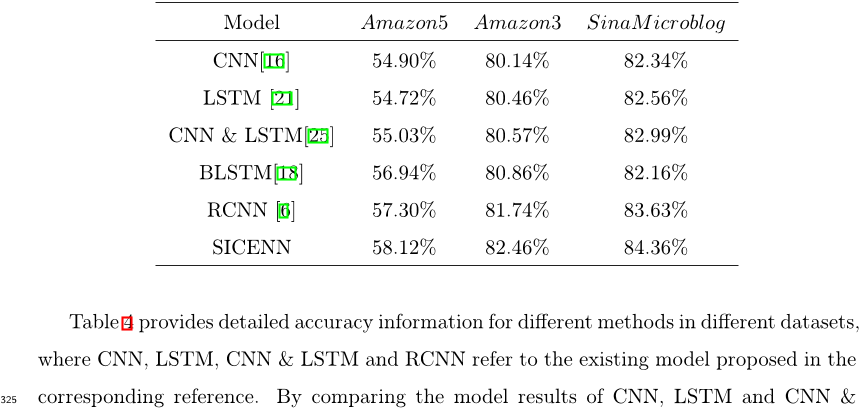
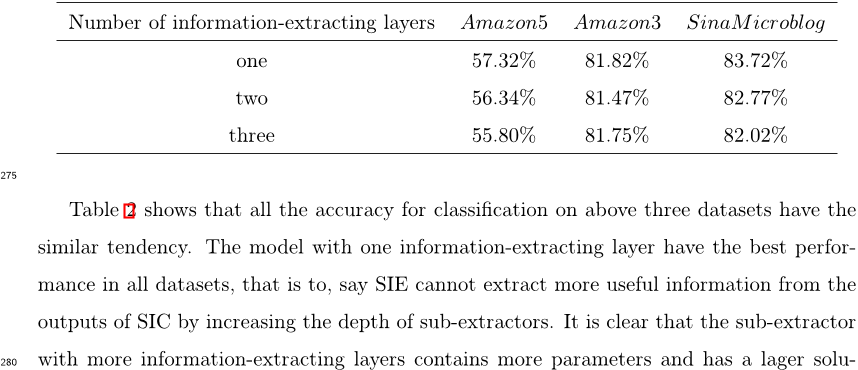
A new ensemble strategy is applied to combine the results of different sub-extractors, making the SIE more universal and outperform any single sub- Extractor and outperforms the state-of-the-art methods on three datasets of different language.About:
This article is published in Information Sciences.The article was published on 2018-10-01 and is currently open access. It has received 21 citations till now. The article focuses on the topics: Sentiment analysis & Deep learning.read more
Figures
Citations
More filters
Journal ArticleDOI
Carrying out consensual Group Decision Making processes under social networks using sentiment analysis over comparative expressions
Juan Antonio Morente-Molinera,Gang Kou,K. Samuylov,Raquel Ureña,Enrique Herrera-Viedma,Enrique Herrera-Viedma +5 more
TL;DR: This paper presents a novel model for experts to carry out Group Decision Making processes using free text and alternatives pairwise comparisons and introduces two ways of applying consensus measures over the Group decision Making process.
Journal ArticleDOI
A comparative study of machine translation for multilingual sentence-level sentiment analysis
TL;DR: This work evaluates existing efforts proposed to do language specific sentiment analysis with a simple yet effective baseline approach and suggests that simply translating the input text in a specific language to English and then using one of the existing best methods developed for English can be better than the existing language-specific approach evaluated.
Journal ArticleDOI
Convolution-deconvolution word embedding: an end-to-end multi-prototype fusion embedding method for natural language processing
TL;DR: In this paper, an end-to-end multi-prototype fusion embedding that fuses context-specific and task-specific information was proposed to solve the problem of polysemous-unaware word embedding.
References
More filters
Proceedings ArticleDOI
Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition
TL;DR: In this article, the authors proposed a residual learning framework to ease the training of networks that are substantially deeper than those used previously, which won the 1st place on the ILSVRC 2015 classification task.
Journal ArticleDOI
Long short-term memory
TL;DR: A novel, efficient, gradient based method called long short-term memory (LSTM) is introduced, which can learn to bridge minimal time lags in excess of 1000 discrete-time steps by enforcing constant error flow through constant error carousels within special units.
Journal ArticleDOI
Gradient-based learning applied to document recognition
Yann LeCun,Léon Bottou,Léon Bottou,Yoshua Bengio,Yoshua Bengio,Yoshua Bengio,Patrick Haffner +6 more
TL;DR: In this article, a graph transformer network (GTN) is proposed for handwritten character recognition, which can be used to synthesize a complex decision surface that can classify high-dimensional patterns, such as handwritten characters.
Proceedings Article
Distributed Representations of Words and Phrases and their Compositionality
TL;DR: This paper presents a simple method for finding phrases in text, and shows that learning good vector representations for millions of phrases is possible and describes a simple alternative to the hierarchical softmax called negative sampling.