Legacy impacts of all‐time anthropogenic emissions on the global mercury cycle
Reads0
Chats0
TLDR
In this article, a global biogeochemical model with fully coupled atmospheric, terrestrial, and oceanic Hg reservoirs is presented to better understand human influence on Hg cycling and timescales for responses.Abstract:
[1] Elevated mercury (Hg) in marine and terrestrial ecosystems is a global health concern because of the formation of toxic methylmercury. Humans have emitted Hg to the atmosphere for millennia, and this Hg has deposited and accumulated into ecosystems globally. Here we present a global biogeochemical model with fully coupled atmospheric, terrestrial, and oceanic Hg reservoirs to better understand human influence on Hg cycling and timescales for responses. We drive the model with a historical inventory of anthropogenic emissions from 2000 BC to present. Results show that anthropogenic perturbations introduced to surface reservoirs (atmosphere, ocean, or terrestrial) accumulate and persist in the subsurface ocean for decades to centuries. The simulated present-day atmosphere is enriched by a factor of 2.6 relative to 1840 levels, consistent with sediment archives, and by a factor of 7.5 relative to natural levels (2000 BC). Legacy anthropogenic Hg re-emitted from surface reservoirs accounts for 60% of present-day atmospheric deposition, compared to 27% from primary anthropogenic emissions, and 13% from natural sources. We find that only 17% of the present-day Hg in the surface ocean is natural and that half of its anthropogenic enrichment originates from pre-1950 emissions. Although Asia is presently the dominant contributor to primary anthropogenic emissions, only 17% of the surface ocean reservoir is of Asian anthropogenic origin, as compared to 30% of North American and European origin. The accumulated burden of legacy anthropogenic Hg means that future deposition will increase even if primary anthropogenic emissions are held constant. Aggressive global Hg emission reductions will be necessary just to maintain oceanic Hg concentrations at present levels.read more
Figures
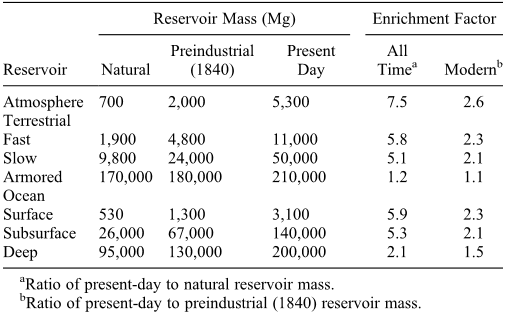
Table 2. Hg Reservoir Masses and Historical Anthropogenic Enrichments 
Figure 3. Simulated present-day global Hg budget and all-time anthropogenic enrichments factors. Terrestrial-atmosphere exchange is given in the top panel for the sum of terrestrial reservoirs. The bottom panel shows the breakdown and cycling between the different terrestrial reservoirs. All terrestrial reservoirs receive inputs from Hg(II) deposition (fast = 800, slow= 510, and armored = 280Mg a 1). The fast reservoir also receives inputs from Hg(0) deposition (1600Mg a 1). All terrestrial reservoirs lose Hg through respiration (fast = 520, slow= 360, and armored =30Mg a 1) and biomass burning (fast = 320, slow = 9, and armored = 5Mg a 1). Photoreduction from the fast terrestrial reservoir is 950Mg a 1. 
Table 1. Present-Day Hg Reservoirs and Flowsa 
Figure 8. Change in reservoir masses relative to 2015 under a scenario of zero primary anthropogenic emissions after 2015. 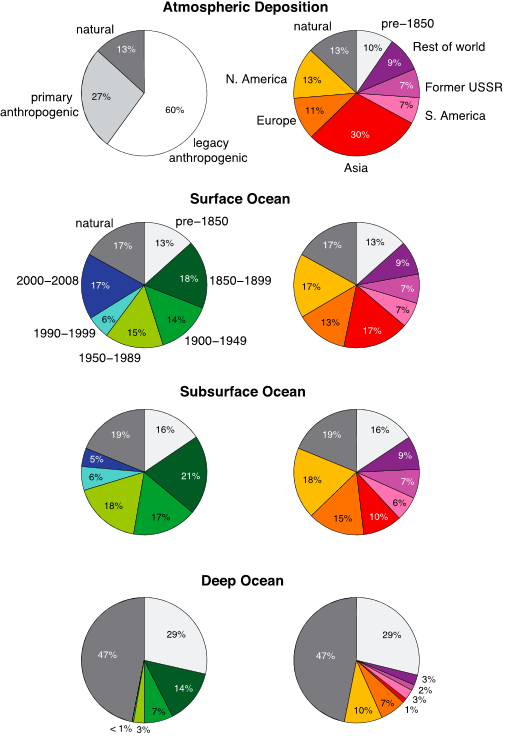
Figure 7. Natural and anthropogenic contributions to present-day atmospheric deposition and ocean reservoirs. The contribution from natural Hg is defined by steady state in our biogeochemical model without anthropogenic emissions. The primary anthropogenic contribution to deposition is from direct emissions (Figure 2a), while the legacy contribution is from anthropogenic Hg previously deposited and then re-emitted by surface reservoirs. The contribution from legacy Hg is calculated as total deposition minus primary anthropogenic emissions and natural emissions. For the ocean reservoirs, we partition the anthropogenic contribution by time period (left column) and region (right column). “Rest of world” includes Africa, the Middle East, and Oceania. 
Figure 1. Rate coefficients kij (a 1) driving our sevenreservoir global biogeochemical box model for Hg. kij defines the first-order transfer from reservoir i to reservoir j as Fij = kijmi, where Fij (Mg a 1) is the Hg flow from reservoir i to reservoir j and mi (Mg) is the mass of Hg in reservoir i. Values of kij are derived from best estimates of present-day flows andmasses from the literature (Table 1) and are assumed to be constant in time. The red arrow represents the external forcing by primary emissions (geogenic or anthropogenic) from the deep mineral reservoir. Geogenic emissions are constant (90Mg a 1), and anthropogenic emissions are time dependent (Figure 2).
Citations
More filters
Journal ArticleDOI
Mercury as a Global Pollutant: Sources, Pathways, and Effects
TL;DR: Understanding of sources, atmosphere-land-ocean Hg dynamics and health effects are synthesized, and integration of Hg science with national and international policy efforts is needed to target efforts and evaluate efficacy.
Journal ArticleDOI
Biomagnification of Mercury in Aquatic Food Webs: A Worldwide Meta-Analysis
Raphael A. Lavoie,Timothy D. Jardine,Matthew M. Chumchal,Karen A. Kidd,Linda M. Campbell,Linda M. Campbell +5 more
TL;DR: In this article, a simple linear regression between log10 transformed mercury (Hg) concentration and stable nitrogen isotope values (δ15N), hereafter called trophic magnification slope (TMS), was used to represent the overall degree of Hg biomagnification.
Journal ArticleDOI
A review of global environmental mercury processes in response to human and natural perturbations: Changes of emissions, climate, and land use
TL;DR: Estimates of gaseous Hg0 emissions to the atmosphere over land, long considered a critical Hg source, have been revised downward, and most terrestrial environments now are considered net sinks of atmospheric Hg due to substantial Hg uptake by plants.
Journal ArticleDOI
A global ocean inventory of anthropogenic mercury based on water column measurements
Carl H. Lamborg,Chad R. Hammerschmidt,Katlin L. Bowman,Gretchen J. Swarr,Kathleen M. Munson,Daniel C. Ohnemus,Phoebe J. Lam,Lars-Eric Heimbürger,Micha J. A. Rijkenberg,Mak A. Saito +9 more
TL;DR: In this paper, the authors present an estimate of the total amount and spatial distribution of anthropogenic mercury in the global ocean based on oceanographic measurements of mercury and related parameters from several expeditions including data from recent GEOTRACES cruises.
Journal ArticleDOI
Mercury physicochemical and biogeochemical transformation in the atmosphere and at atmospheric interfaces: a review and future directions.
Parisa A. Ariya,Marc Amyot,Ashu Dastoor,Daniel A. Deeds,Aryeh Feinberg,Gregor Kos,Alexandre J. Poulain,Andrei Ryjkov,Kirill Semeniuk,Mahamud Subir,K. Toyota +10 more
TL;DR: Atmosphere and at Atmospheric Interfaces: A Review and Future Directions Parisa A. Ariya, Marc Amyot, Ashu Dastoor, Daniel Deeds, Aryeh Feinberg, Gregor Kos, Andrei Ryjkov, Kirill Semeniuk, M. Subir, and Kenjiro Toyota are authors.
References
More filters
Journal ArticleDOI
Greenhouse Gas Emissions Scenarios
TL;DR: In this paper, the authors present a set of 40 emissions scenarios developed by five different modeling teams over the last three years, based on an extensive assessment of the literature and shared assumptions about the main driving forces of future emissions.
Journal ArticleDOI
Vertical mercury distributions in the oceans
TL;DR: The vertical distribution of mercury (Hg) was determined at coastal and open ocean sites in the northwest Atlantic and Pacific Oceans as mentioned in this paper, and diagnostic Hg distributions were obtained, permitting major processes governing the marine biogeochemistry of Hg to be identified.
Journal ArticleDOI
Spatial and temporal patterns of mercury accumulation in lacustrine sediments across the Laurentian Great Lakes region
Paul E. Drevnick,Daniel R. Engstrom,Charles T. Driscoll,Edward B. Swain,Steven J. Balogh,Neil C. Kamman,David T. Long,Derek G.C. Muir,Matthew J. Parsons,Kristofer R. Rolfhus,Ronald Rossmann +10 more
TL;DR: A consistent region-wide decrease of sediment-Hg flux suggests that controls on local and regional atmospheric Hg emissions have been effective in decreasing the supply of Hg to Lake Superior and inland lakes.
Journal ArticleDOI
(Pre-) historic changes in natural and anthropogenic heavy metals deposition inferred from two contrasting Swiss Alpine lakes
TL;DR: In this article, a high-resolution sedimentary record of heavy metals (chromium (Cr), copper (Cu), lead (Pb), zinc (Zn), manganese (Mn), and mercury (Hg), from lakes Lucerne and Meidsee (Switzerland), provides pollutant deposition history from two contrasting Alpine environments over the last millennia.