Q1. What contributions have the authors mentioned in the paper "Pii: s0025-3227(00)00083-9" ?
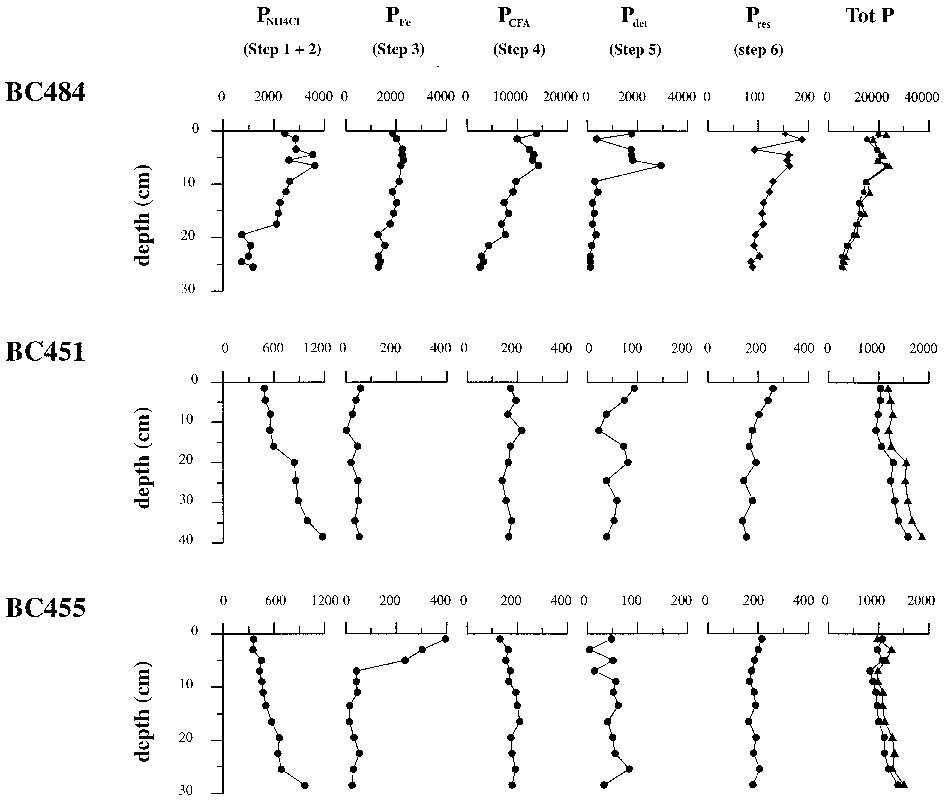
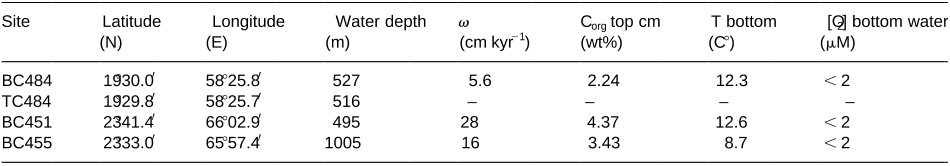
In this study, porewater chemistry, solid-phase analysis and microscopic observations were combined to evaluate phosphogenesis in three boxcores located within the intensive oxygen minimum zone of the Arabian Sea. Authigenic apatite precipitation rates vary between 0. 076 and 1. 04 mmolP cm yr, and are of the same order of magnitude as reported for other high productivity areas. This observation contrasts with previous reports of only old phosphorites in this area. Model results suggest that sediment mixing is essential in promoting early diagenetic phosphogenesis.