A brain-actuated wheelchair: asynchronous and non-invasive Brain-computer interfaces for continuous control of robots.
Ferran Galán,Ferran Galán,Marnix Nuttin,Eileen Lew,Pierre W. Ferrez,G. Vanacker,Johan Philips,J. del R. Millan,J. del R. Millan +8 more
Reads0
Chats0
TLDR
The results show that subjects can rapidly master the authors' asynchronous EEG-based BCI to control a wheelchair and can autonomously operate the BCI over long periods of time without the need for adaptive algorithms externally tuned by a human operator to minimize the impact of EEG non-stationarities.About:
This article is published in Clinical Neurophysiology.The article was published on 2008-09-01 and is currently open access. It has received 644 citations till now. The article focuses on the topics: Wheelchair.read more
Figures

Fig. 6. Top view of the random paths in Task 2. Trial 1 placed in upper row, first column. Trial 10 placed in second row, last column. 
Fig. 7. Top view of the world and the path stretches. Stretches F1 and F2 were labelled as Forward, R1 and R2 labelled as Right, L labelled as Left, and SD1 and SD2 labelled as strategy dependent. The subjects can go through SD1 by means of two strategies, either executing Forward or executing Right followed by Left. Through SD2, subjects can execute either Forward or Left followed by Right. 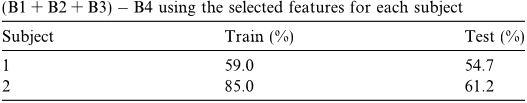
Table 1 LDA train-test classification accuracies on the configuration 
Fig. 1. (Left) Monitor display in a first person view from the Start. The white cursor at the center is the fixation point. The rectangle at the bottom is the simulated wheelchair. (Right) Top view of the simulated world and the pre-specified path. 
Fig. 8. Percentage of reached final goals over sessions. The time elapsed between sessions was: 1 day between sessions 1 and 2, 2 months between sessions 2 and 3, 1 h between sessions 3 and 4, and 1 day between sessions 4 and 5. 
Fig. 2. Electrode discrimination index values De (see Section 2.3.2) for the selected frequencies for each subject, and the associated scalp distribution of the averaged logarithmic transform of the power spectral density, Log(PSDe), for each class. For subject 1, De is higher at left temporal, central and right occipital areas. For subject 2, at 10 Hz it is higher at right centro-parietal areas, and at 12 and 14 Hz it is higher at bilateral parietal areas. These areas correspond with those where the differences between the averaged Log(PSDe) patterns associated to each mental task is the biggest.
Citations
More filters
Proceedings ArticleDOI
Modular Robot Arm Design for Physical Human-Robot Interaction
Ty Tremblay,Taskin Padir +1 more
TL;DR: The aim of this research is to develop a system to control a modular cable-driven arm which will allow locked-in individuals, who are unable to interact with the physical world through movement and speech, to perform activities of daily living (ADL).
Towards Hierarchical BCls for Robotic Control
TL;DR: These problems are addressed using a new adaptive and hierarchical approach to brain-computer interfacing that allows a user to teach the BCI system new skills on-the-f1y; these learned skills are later invoked directly as high-level commands, relieving the user of tedious lower-level control.
Asynchronous detection of error-related potentials using a generic classifier
TL;DR: The results hint at the feasibility of transferring ErrPs between participants as a reliable strategy to reduce or even remove the calibration period when training ErrP classifiers to be used in an asynchronous manner.
Book ChapterDOI
Chapter 15 Matching Brain–Machine Interface Performance to Space Applications
TL;DR: A method is presented for pointing out effective combinations of HMIs and applications of robotics and automation to space, and the performance of classes of interfaces with the requirements of Classes of applications is compared, both in terms of latency and throughput.
Journal ArticleDOI
An Ssvep-Based Bci System and its Applications
Jzau-Sheng Lin,Cheng-Hung Shieh +1 more
TL;DR: A Brain-Computer-Interface (BCI) based system with a System on a Programmable Chip (SOPC) platform by using of the Steady-State Visually Evoked Potentials (SSVEP) through a Bluetooth interface was proposed in this paper and experimental results had shown that the proposed system can easily control electric wheelchairs.
References
More filters
Journal ArticleDOI
Learning to Control a Brain–Machine Interface for Reaching and Grasping by Primates
Jose M. Carmena,Mikhail A. Lebedev,Roy E. Crist,Joseph E. O'Doherty,David M. Santucci,Dragan F. Dimitrov,Parag G. Patil,Craig S. Henriquez,Miguel A. L. Nicolelis +8 more
TL;DR: It is demonstrated that primates can learn to reach and grasp virtual objects by controlling a robot arm through a closed-loop brain–machine interface (BMIc) that uses multiple mathematical models to extract several motor parameters from the electrical activity of frontoparietal neuronal ensembles.
Journal ArticleDOI
Control of a two-dimensional movement signal by a noninvasive brain-computer interface in humans
TL;DR: It is shown that a noninvasive BCI that uses scalp-recorded electroencephalographic activity and an adaptive algorithm can provide humans, including people with spinal cord injuries, with multidimensional point-to-point movement control that falls within the range of that reported with invasive methods in monkeys.
Journal ArticleDOI
A spelling device for the paralysed
Niels Birbaumer,N. Ghanayim,Thilo Hinterberger,Iver H. Iversen,Boris Kotchoubey,Andrea Kübler,J. Perelmouter,Edward Taub,Herta Flor +8 more
TL;DR: A new means of communication for the completely paralysed that uses slow cortical potentials of the electro-encephalogram to drive an electronic spelling device is developed.