A novel strategy to enhance interfacial adhesion in fiber-reinforced calcium phosphate cement
TLDR
The aim of the present work was to improve the interfacial adhesion between fibers and matrix to obtain tougher biocompatible fiber-reinforced calcium phosphate cements (FRCPCs), which resulted in an increase of the work of fracture (several hundred-fold increase), while the elastic modulus and bending strength were maintained similar to the materials without additives.Abstract:
Calcium phosphate cements (CPCs) are extensively used as synthetic bone grafts, but their poor toughness limits their use to non-load-bearing applications. Reinforcement through introduction of fibers and yarns has been evaluated in various studies but always resulted in a decrease in elastic modulus or bending strength when compared to the CPC matrix. The aim of the present work was to improve the interfacial adhesion between fibers and matrix to obtain tougher biocompatible fiber-reinforced calcium phosphate cements (FRCPCs). This was done by adding a polymer solution to the matrix, with chemical affinity to the reinforcing chitosan fibers, namely trimethyl chitosan (TMC). The improved wettability and chemical affinity of the chitosan fibers with the TMC in the liquid phase led to an enhancement of the interfacial adhesion. This resulted in an increase of the work of fracture (several hundred-fold increase), while the elastic modulus and bending strength were maintained similar to the materials without additives. Additionally the TMC-modified CPCs showed suitable biocompatibility with an osteoblastic cell line.read more
Figures
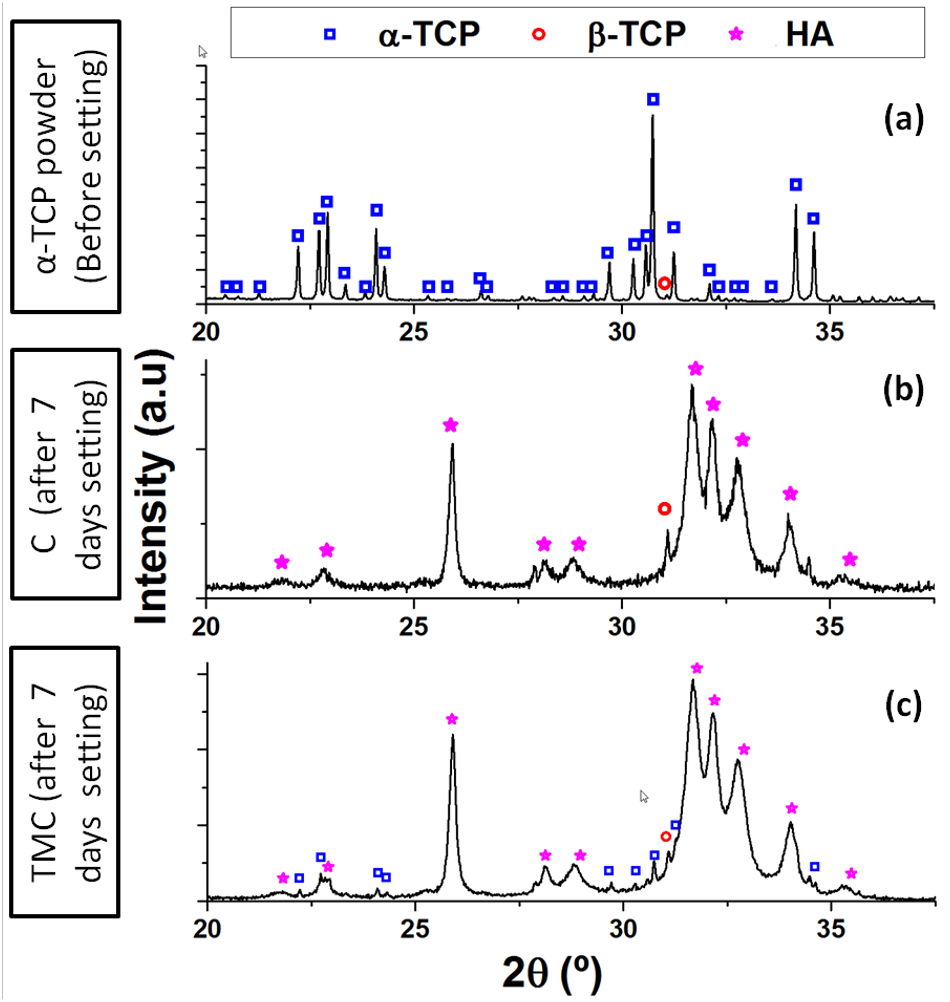
Figure 2. Crystalline phases determined by X-ray diffraction of a) initial powder α –TCP, b) sample C 7 days after setting, and c) sample TMC 7 days after setting. 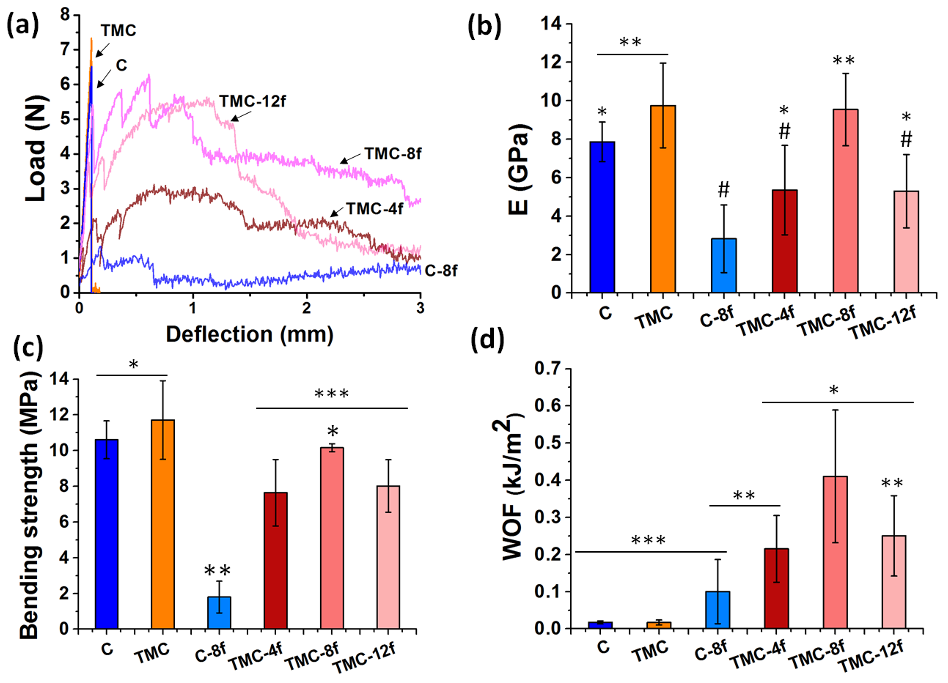
Figure 3. Mechanical properties under bending of unreinforced CPCs (C and TMC) and fiberreinforced CPCs (C-8f, TMC-4f, TMC-8f, TMC-12f): a) Typical load/deflection curves, b) Young’s modulus (E), c) bending strength, and d) work of fracture (WOF). Groups indicated with same symbol do not have statistically significant differences (p > 0.05). 
Figure 7. SEM images showing the morphology of cells cultured on C and TMC samples for 7 days. 
Figure 6. Live/dead images showing the alive cells (green) and the dead cells (red) on the C and TMC samples surface at different time points (bar = 100 μm) 
Figure 5. a) Number of cells adhered on the samples surface at different time points, and b) evolution with time of the pH of the cell culture medium (1 ml) in contact with a cement disc (15 mm diameter x 1.5 mm thickness). 
Table 3. Crystalline phases as determined by X-ray diffraction, and specific surface area measured by N2 adsorption of the initial powder and set cements.
Citations
More filters
Journal ArticleDOI
Self-assembling of fibers inside an injectable calcium phosphate bone cement: a feasibility study
Maria Di Filippo,Demetra Giuri,Gregorio Marchiori,Melania Maglio,Stefania Pagani,Massimiliano Fini,Claudia Tomasini,Silvia Panzavolta +7 more
TL;DR: In this article , the formation of fibers was achieved by introducing a low-molecular-weight gelator (MW < 1000 Da) derived from l-Dopa: Boc-l-dopa (Bn)2-OH, which can form supramolecular structures owing to weak interactions, and chelate Ca2+ ions to arrange into a fibrous network.
Journal ArticleDOI
Injectable macromolecules-based calcium phosphate bone substitutes
TL;DR: Injectable bone substitutes represent compelling options for bone regenerative medicine as they can be used to optimally fill a complex bone defect through minimally invasive intervention.
Journal ArticleDOI
State of the art of bone biomaterials and their interactions with stem cells: Current state and future directions
Ruyi Shao,Yongqiang Dong,Songou Zhang,Xudong Wu,Xiaogang Huang,Bin Sun,Bin Zeng,Fangming Xu,Wenqing Liang +8 more
TL;DR: A cell microenvironment with the desired pore magnitude is developed to stimulate stem cells to transform them from artificial to biological microenvironments in bone regeneration.
Journal ArticleDOI
Calcium phosphate cements improved by addition of carbonated Hydroxyapatite type B
TL;DR: In this paper , the use of a biodegradable nucleating agent, as it is Type B carbonated Hydroxyapatite (CHA-B), to improve the CPC performance was proposed.
Journal ArticleDOI
Optimization of the preparation process of α-tricalcium phosphate applied to bone cement
TL;DR: In this article, the optimal preparation of?-Ca3(PO4)2 was found to be to treat the mixture of wet synthetic Ca(HPO4) 2H2O and analytical pure CaCO3 with ball milling, subsequently the mixture was heated with the heating rate of 5?C/min, then helded at 1000?C for 3 h and calcined at 1350 C for 2 h finally.
References
More filters
Journal ArticleDOI
Quantitative interpretation of X-ray diffraction patterns of mixtures. II. Adiabatic principle of X-ray diffraction analysis of mixtures
TL;DR: In this article, the matrix-flushing theory and the adiabatic principle were applied in applied X-ray diffraction analysis to obtain the quantitative composition of a mixture.
Journal ArticleDOI
The mechanical properties of bone tissue in children.
John D. Currey,G Butler +1 more
TL;DR: Compared with the bone of adults, that of children had a lower modulus of elasticity, a lower bending strength, and a lower ash content, but the children's bone deflected more and absorbed more energy before breaking.
Journal ArticleDOI
A Biopolymer Chitosan and Its Derivatives as Promising Antimicrobial Agents against Plant Pathogens and Their Applications in Crop Protection
TL;DR: In this paper, the authors present an overview of the antimicrobial effects, mechanisms, and applications of a biopolymer chitosan and its derivatives in crop protection, and take a closer look at the physiochemical properties and chemical modifications of chitosa molecule.
Journal ArticleDOI
New method for the quaternization of chitosan
TL;DR: In this article, the role of sodium iodide as an electrostatic charges screening salt is discussed, and the reaction was performed in several steps to obtain derivatives of chitosan at various degrees of quaternization with a limit value near 64%.
Journal ArticleDOI
Injectable and macroporous calcium phosphate cement scaffold.
TL;DR: The injectability of a ceramic scaffold, a macroporous CPC, was studies for the first time and may be useful in surgical sites that are not freely accessible by open surgery or when using minimally invasive techniques.
Related Papers (5)
Reinforcement Strategies for Load-Bearing Calcium Phosphate Biocements
Fiber reinforced calcium phosphate cements -- on the way to degradable load bearing bone substitutes?
Reinhard Krüger,Jürgen Groll +1 more