Acceptability of oral solid medicines in older adults with and without dysphagia: A nested pilot validation questionnaire based observational study
Reads0
Chats0
TLDR
Assessment of acceptability of oral solid medicines in older ambulatory patients with and without dysphagia found that higher acceptability scores were seen in the dysphagic population than in the non-dysphagic population for all of the dosage forms that were easier to swallow than tablets and capsules.About:
This article is published in International Journal of Pharmaceutics.The article was published on 2016-10-30 and is currently open access. It has received 71 citations till now. The article focuses on the topics: Dysphagia & Population.read more
Figures
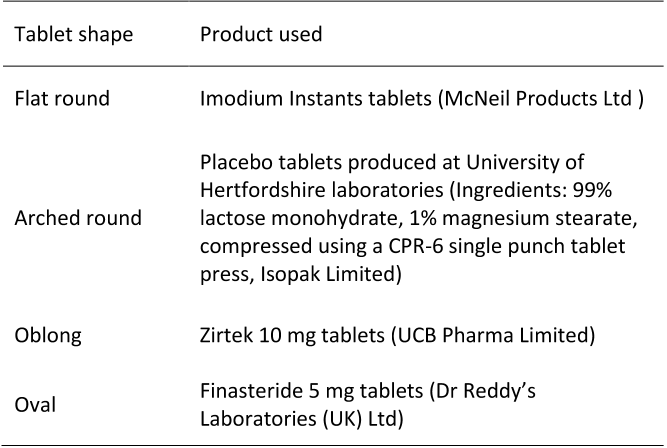
Table 1. Products used to represent 9 mm tablets in different shapes 
Table 2. Products used to represent various oral formulations 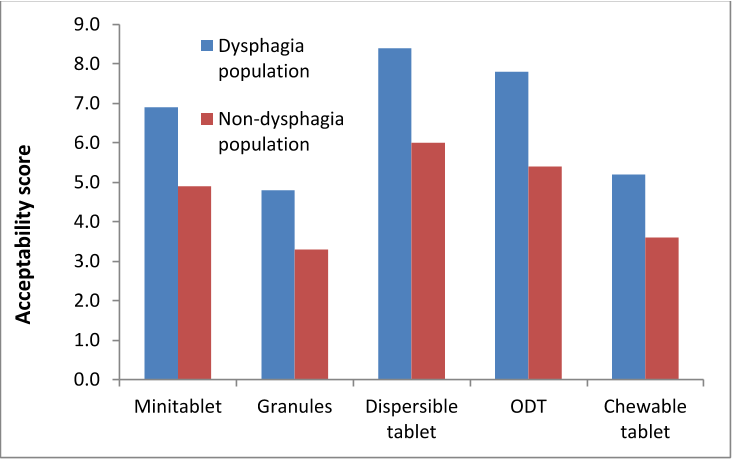
Fig 3. Acceptability scores of different oral solid dosage forms (ODT: orally disintegrating tablet). 
Table 4. Participants’ impression on the flexible solid oral dosage forms. 2 
Figure 1. Percentage of participants selecting the tablet size and shape that started to cause difficulty in swallowing. 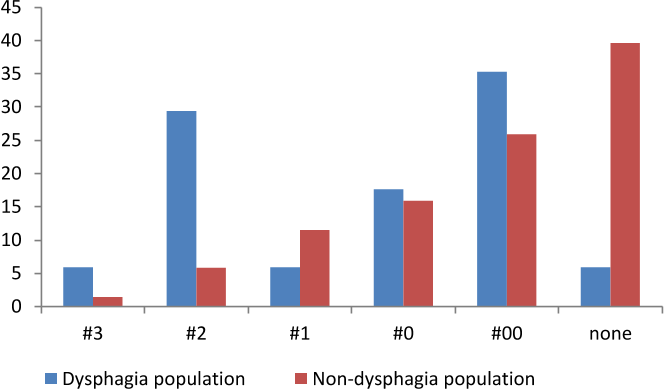
Fig 2. Percentage of participants selecting the capsule size that might start to cause difficulty in swallowing
Citations
More filters
Journal ArticleDOI
Learning from patients: Identifying design features of medicines that cause medication use problems.
TL;DR: Design features of oral medicines that cause use problems among older patients in daily practice are identified to help developers of medicinal products to proactively address potential usability issues with their medicines.
Journal ArticleDOI
Buccal drug delivery technologies for patient-centred treatment of radiation-induced xerostomia (dry mouth).
TL;DR: This analysis makes a strong case for the development of ODTs for the buccal delivery of cholinergic agents: these must be patient-friendly delivery platforms with variable loading capacities that release the drug rapidly in fluid volumes typical of residual saliva in xerostomia (0.05-0.1 mL).
Journal ArticleDOI
Acceptability in the Older Population: The Importance of an Appropriate Tablet Size
Thibault Vallet,Hugues Michelon,Mine Orlu,Yogini Jani,Patrick Leglise,Sandra Laribe-Caget,Matthieu Piccoli,Aurélie Le Fur,Fang Liu,Fabrice Ruiz,Vincent Boudy +10 more
TL;DR: Reducing the tablet size had a significant impact on acceptability in this subpopulation: tablets <6.5 mm appeared to be accepted by patients with swallowing disorders, which underlines the need to develop and prescribe medicines with the best adapted characteristics to reach an optimalacceptability in targeted users.
Journal ArticleDOI
Developing methodology to evaluate the oral sensory features of pharmaceutical tablet coatings
Justyna Hofmanová,A. Rajabi-Siahboomi,Sayeed Haque,Julie Mason,J. Teckoe,D. To,Hannah Batchelor +6 more
TL;DR: The presence of a coating improved ease of swallowing, mouthfeel and overall palatability and the value of VAS was demonstrated to measure the sensory attributes of coated tablets.
Journal ArticleDOI
Appropriateness of oral dosage form modification for aged care residents: a video-recorded observational study
Aida Sefidani Forough,Esther Lau,Esther Lau,Kathryn J. Steadman,Kathryn J. Steadman,Greg Kyle,Julie A. Y. Cichero,Julie A. Y. Cichero,Jose Manuel Serrano Santos,Lisa Nissen,Lisa Nissen +10 more
TL;DR: Healthcare workers in aged care facilities need to be supported and upskilled with effective training to promote the best and safest practices of ODF modification.
References
More filters
Journal ArticleDOI
Polypharmacy cutoff and outcomes: five or more medicines were used to identify community-dwelling older men at risk of different adverse outcomes.
Danijela Gnjidic,Sarah N. Hilmer,Sarah N. Hilmer,Fiona M. Blyth,Fiona M. Blyth,Vasi Naganathan,Vasi Naganathan,Louise M. Waite,Louise M. Waite,Markus J. Seibel,Markus J. Seibel,Andrew J. McLachlan,Andrew J. McLachlan,Robert G. Cumming,Robert G. Cumming,David J. Handelsman,David J. Handelsman,David G. Le Couteur,David G. Le Couteur +18 more
TL;DR: The study supports the use of five or more medications in the current definition of polypharmacy to estimate the medication-related adverse effects for frailty, disability, mortality, and falls.
Journal ArticleDOI
Prevalence of dysphagia among community-dwelling elderly individuals as estimated using a questionnaire for dysphagia screening
TL;DR: After matching for age and sex, there were significant differences in the competence scores, history of stroke, and perceived ill health status observed between the group with dysphagia and the group without dysphagIA.
Journal ArticleDOI
Mealtime Difficulties in a Home for the Aged: Not Just Dysphagia
TL;DR: The results clearly demonstrate that the prevalence of a wide range of eating-related problems far exceeds accepted estimates of dysphagia alone and support a multidisciplinary approach to mealtime interventions for the institutionalized elderly.
Journal ArticleDOI
Development and validation of a self-report symptom inventory to assess the severity of oral-pharyngeal dysphagia.
TL;DR: Applied to patients with neuromyogenic dysphagia, the 17-question inventory shows strong test-retest reliability over 2 weeks as well as face, content, and construct validity.
Journal ArticleDOI
Prevalence and predictors of polypharmacy among older primary care patients in Germany
TL;DR: This older general practice population in Germany is among the top pharmaceutical user group of European study samples and GPs should be aware that low subjective health and medication disagreement are independent predictors of polypharmacy.