Acceptability of oral solid medicines in older adults with and without dysphagia: A nested pilot validation questionnaire based observational study
TLDR
Assessment of acceptability of oral solid medicines in older ambulatory patients with and without dysphagia found that higher acceptability scores were seen in the dysphagic population than in the non-dysphagic population for all of the dosage forms that were easier to swallow than tablets and capsules.About:
This article is published in International Journal of Pharmaceutics.The article was published on 2016-10-30 and is currently open access. It has received 71 citations till now. The article focuses on the topics: Dysphagia & Population.read more
Figures
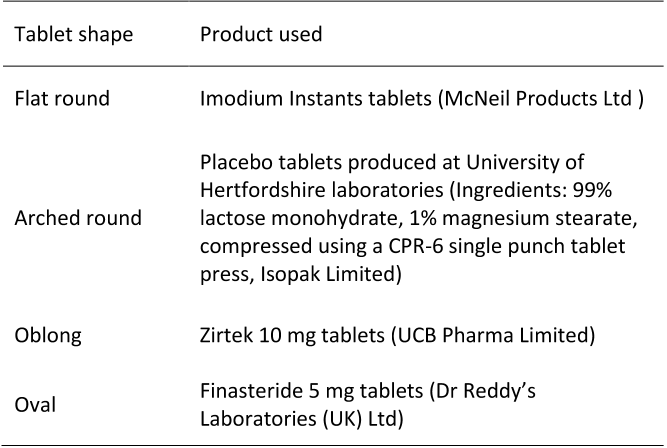
Table 1. Products used to represent 9 mm tablets in different shapes 
Table 2. Products used to represent various oral formulations 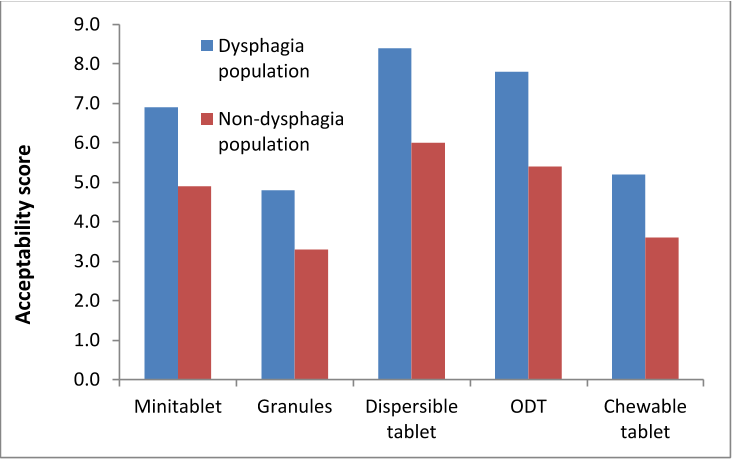
Fig 3. Acceptability scores of different oral solid dosage forms (ODT: orally disintegrating tablet). 
Table 4. Participants’ impression on the flexible solid oral dosage forms. 2 
Figure 1. Percentage of participants selecting the tablet size and shape that started to cause difficulty in swallowing. 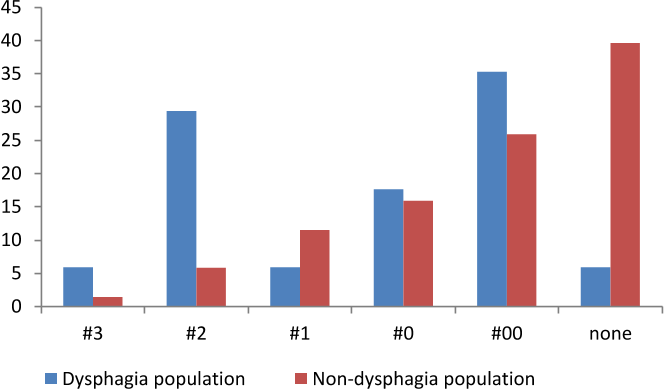
Fig 2. Percentage of participants selecting the capsule size that might start to cause difficulty in swallowing
Citations
More filters
Journal ArticleDOI
The development of a test battery to assess the hand-eye functions relevant in predicting easy and accurate tablet subdivision in older people: A pilot study.
Diana van Riet–Nales,Linda Donkerbroek,Agnes E. Nicia,C. Oussoren,Anthonius de Boer,Bart J F van den Bemt +5 more
TL;DR: A test battery is developed to assess the hand–eye functions relevant in predicting easy and accurate tablet subdivision in older people.
Journal ArticleDOI
Validation of The Pill-5: A 5-Item Patient Reported Outcome Measure for Pill Dysphagia
Nogah Nativ-Zeltzer,Ahmed S. Bayoumi,Van Pierre Mandin,Matthew Kaufman,Indulaxmi Seeni,Maggie A. Kuhn,Peter C. Belafsky +6 more
TL;DR: The PILL-5 is the first validated patient reported outcome measure for pill dysphagia and demonstrated excellent criterion based validity and reliability, and healthy individuals report some degree of swallowing difficulty with pills.
Journal ArticleDOI
Heuristics for designing user-centric drug products: Lessons learned from Human Factors and Ergonomics
TL;DR: The presented heuristics can be applied prospectively to include existing knowledge about user‐centric design at every step during drug discovery, pharmaceutical drug development, and pre‐clinical and clinical trials.
Journal ArticleDOI
Identifying and addressing pill aversion in adults without physiological‐related dysphagia: A narrative review
TL;DR: Healthcare professionals must recognise that pill aversion is a problem requiring identification through effective screening and resolution by training interventions, appropriate formulation selection, or specialist referral.
Journal ArticleDOI
The Role of Pharmaceutical Compounding in Promoting Medication Adherence
Maria Carvalho,Isabel Almeida +1 more
TL;DR: The role of pharmaceutical compounding in promoting medication adherence is underexploited and the results of such studies could support health policies including proper regulatory framework, pharmacist training, and information to health care practitioners.
References
More filters
Journal ArticleDOI
Polypharmacy cutoff and outcomes: five or more medicines were used to identify community-dwelling older men at risk of different adverse outcomes.
Danijela Gnjidic,Sarah N. Hilmer,Sarah N. Hilmer,Fiona M. Blyth,Fiona M. Blyth,Vasi Naganathan,Vasi Naganathan,Louise M. Waite,Louise M. Waite,Markus J. Seibel,Markus J. Seibel,Andrew J. McLachlan,Andrew J. McLachlan,Robert G. Cumming,Robert G. Cumming,David J. Handelsman,David J. Handelsman,David G. Le Couteur,David G. Le Couteur +18 more
TL;DR: The study supports the use of five or more medications in the current definition of polypharmacy to estimate the medication-related adverse effects for frailty, disability, mortality, and falls.
Journal ArticleDOI
Prevalence of dysphagia among community-dwelling elderly individuals as estimated using a questionnaire for dysphagia screening
TL;DR: After matching for age and sex, there were significant differences in the competence scores, history of stroke, and perceived ill health status observed between the group with dysphagia and the group without dysphagIA.
Journal ArticleDOI
Mealtime Difficulties in a Home for the Aged: Not Just Dysphagia
TL;DR: The results clearly demonstrate that the prevalence of a wide range of eating-related problems far exceeds accepted estimates of dysphagia alone and support a multidisciplinary approach to mealtime interventions for the institutionalized elderly.
Journal ArticleDOI
Development and validation of a self-report symptom inventory to assess the severity of oral-pharyngeal dysphagia.
TL;DR: Applied to patients with neuromyogenic dysphagia, the 17-question inventory shows strong test-retest reliability over 2 weeks as well as face, content, and construct validity.
Journal ArticleDOI
Prevalence and predictors of polypharmacy among older primary care patients in Germany
TL;DR: This older general practice population in Germany is among the top pharmaceutical user group of European study samples and GPs should be aware that low subjective health and medication disagreement are independent predictors of polypharmacy.