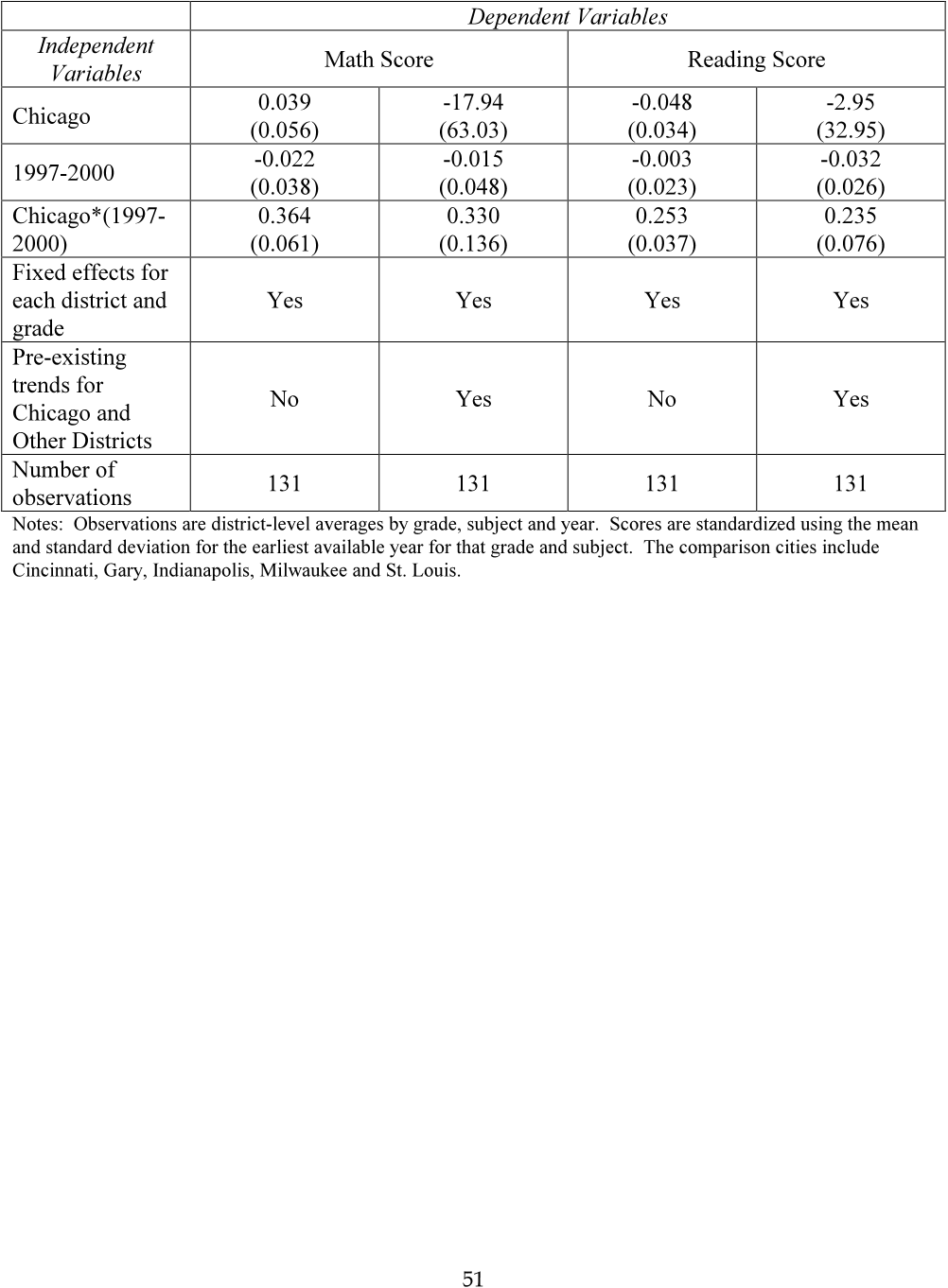
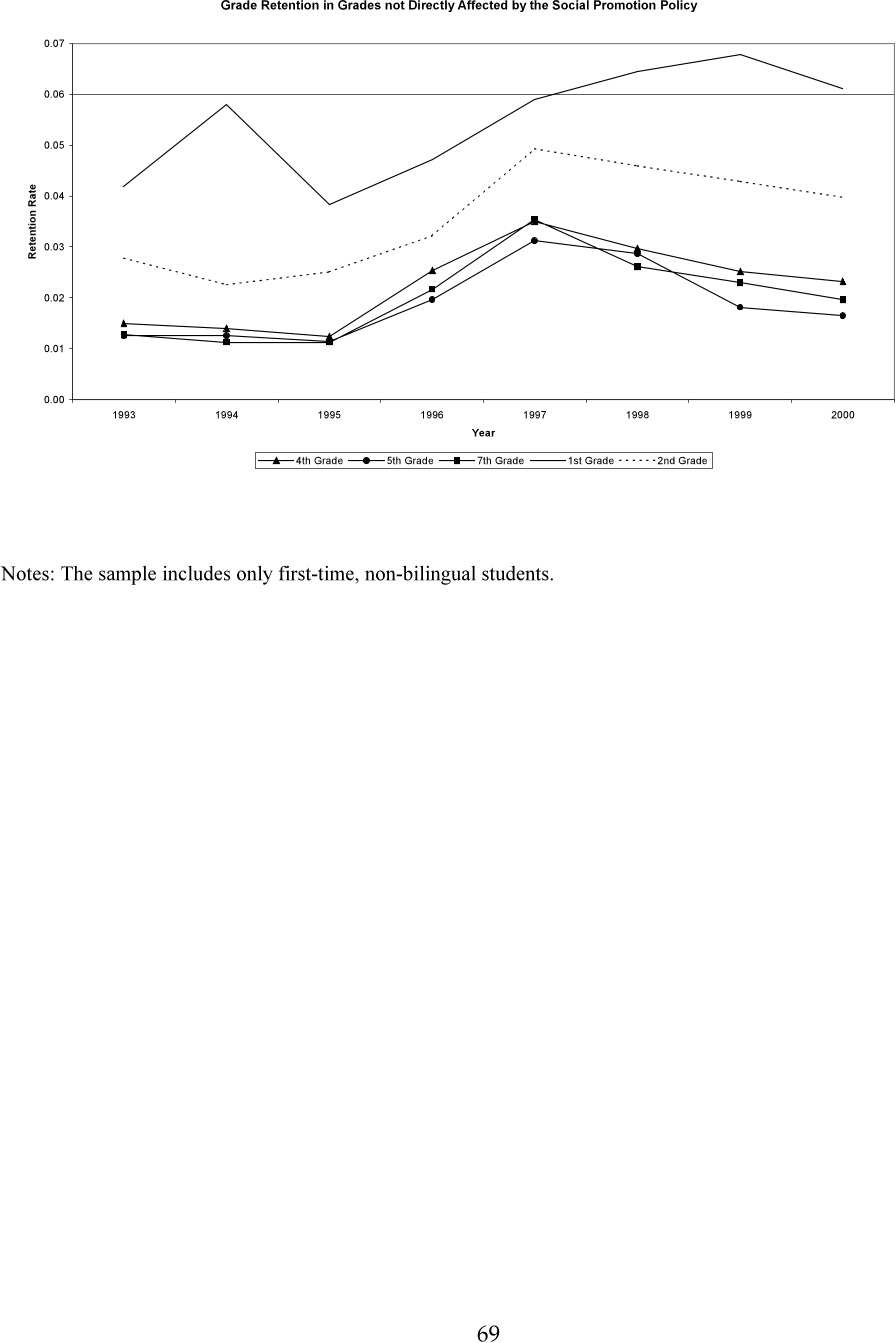
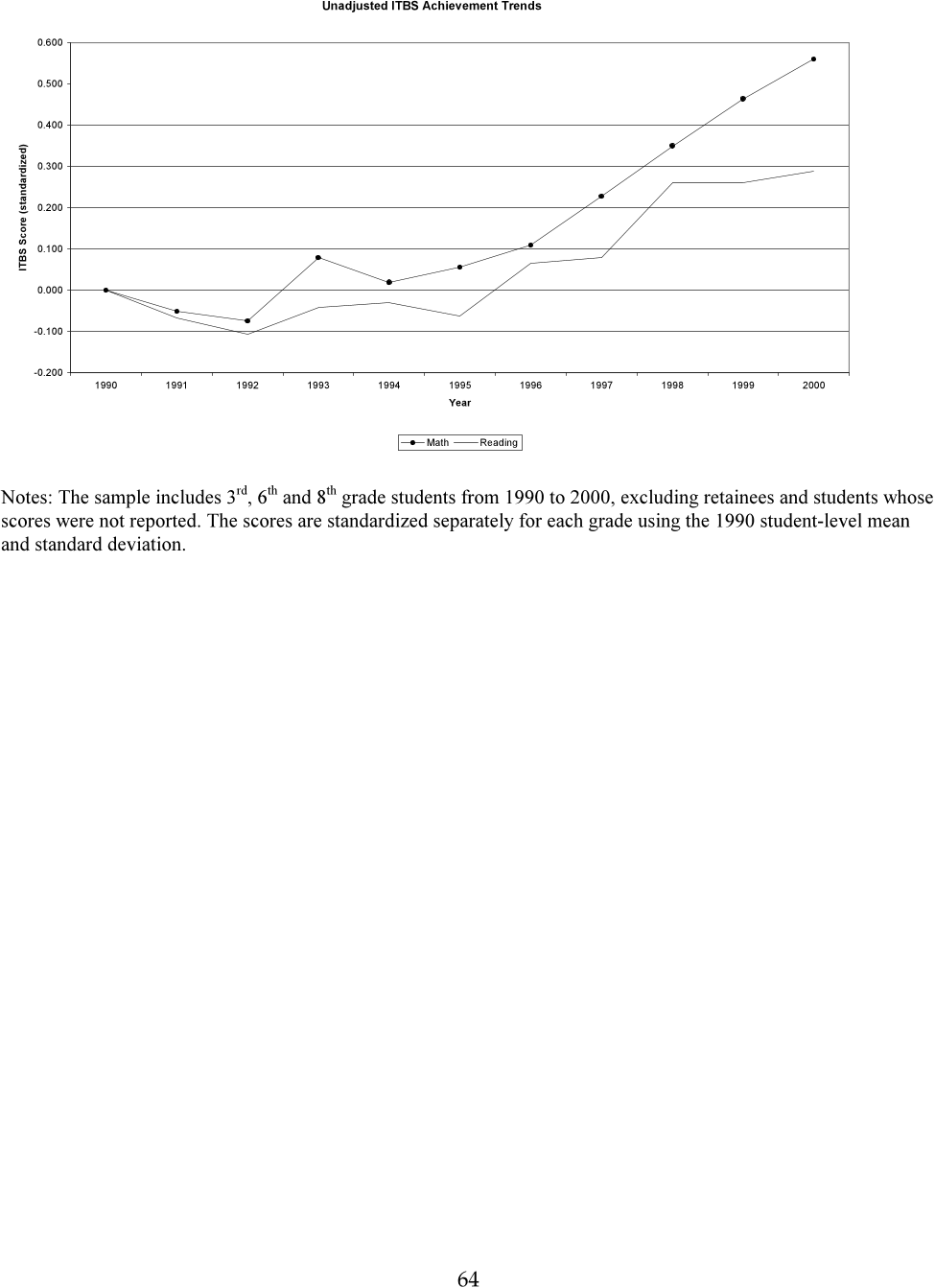
Abstract: Abstract: The school reforms put in place in New Orleans after Hurricane Katrina represent the most intensive test-based and market-based school accountability system ever created in the United States. Collective bargaining was ended, yielding flexible human capital management. Traditional attendance zones were eliminated, expanding choice for families. And almost all public schools were taken over by the state, which turned over management to outside non-profit charter management organizations working under performance contracts. Ten years later, this study provides the first examination of the effects of this package of reforms on student achievement. Identification is based on multiple difference-in-difference (DD) strategies, using outcomes before and after the hurricane and reforms in New Orleans and a matched comparison group that experienced hurricane damage but not the school reforms. The estimation procedures address potential threats to identification, including changes in the population, strategic behavior in test scores from high-stakes accountability, the influence of the interim schools attended by evacuated students, and the trauma and disruption from the hurricane itself. With the possible exception of test-based accountability strategic behavior, these factors seem to have a small influence and, collectively, they appear to cancel each other out. The results suggest that, over time, as the reforms yielded a new system of schools, they had large positive cumulative effects of 0.2-0.4 standard deviations.