
Mobile Edge Computing: A
Survey
architecture, applications, approaches and challenges
Nasir Abbas
Master’s Thesis Autumn 2016


Mobile Edge Computing: A Survey
Nasir Abbas
December 12, 2016

ii

Abstract
Mobile edge computing (MEC) is an emergent architecture where cloud
computing services are extended to the edge of networks into the mobile
base stations. As a promising edge technology, it can be applied to mobile,
wireless and wireline scenarios, using software and hardware platforms,
located at the network edge in the vicinity of end users. MEC provides
seamless integration of multiple application service providers and vendors
towards mobile subscribers, enterprises and other vertical segments. It is
an important component in the proposed 5G architecture that supports
variety of innovative applications and services where ultra low latency
is required. However, there are some challenges exists in the MEC eco
system. To address these challenges, first off need to understand the
network infrastructure of MEC, cloud and cellular network.
Some questions and problems are addressed in this thesis that outlines
the importance and challenges of MEC deployment. Impact of MEC
integration with the traditional mobile and cloud network appears in
this paper. A survey has been presented that contributes in general
understanding of mobile edge computing (MEC). Readers will have
an overview of MEC, such as definition, advantages, architectures and
applications. Moreover, related research and future directions are pointed
out in this thesis. Finally, security and privacy issues and their possible
solutions are also discussed.
iii
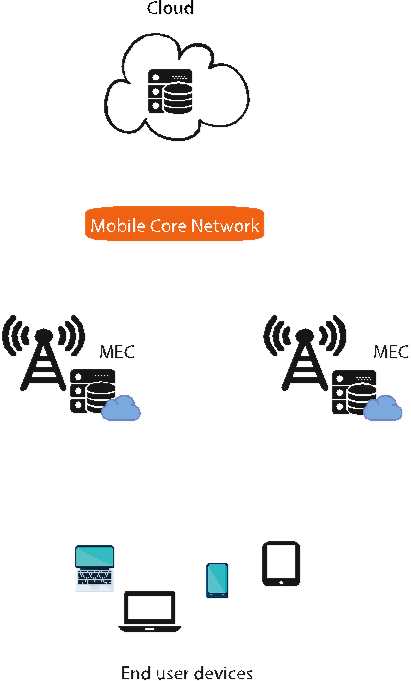
![Figure 2.3: Three-layer architecture [90]](/figures/figure-2-3-three-layer-architecture-90-3v6zel4r.png)
![Figure 4.1: MEC Server Platform [26]](/figures/figure-4-1-mec-server-platform-26-26vpbbwc.png)
![Figure 3.5: Femto Architecture [31]](/figures/figure-3-5-femto-architecture-31-s0py2j7g.png)

