Q1. What have the authors contributed in "The influence of scope, depth, and orientation of external technology sources on the innovative performance of chinese firms" ?
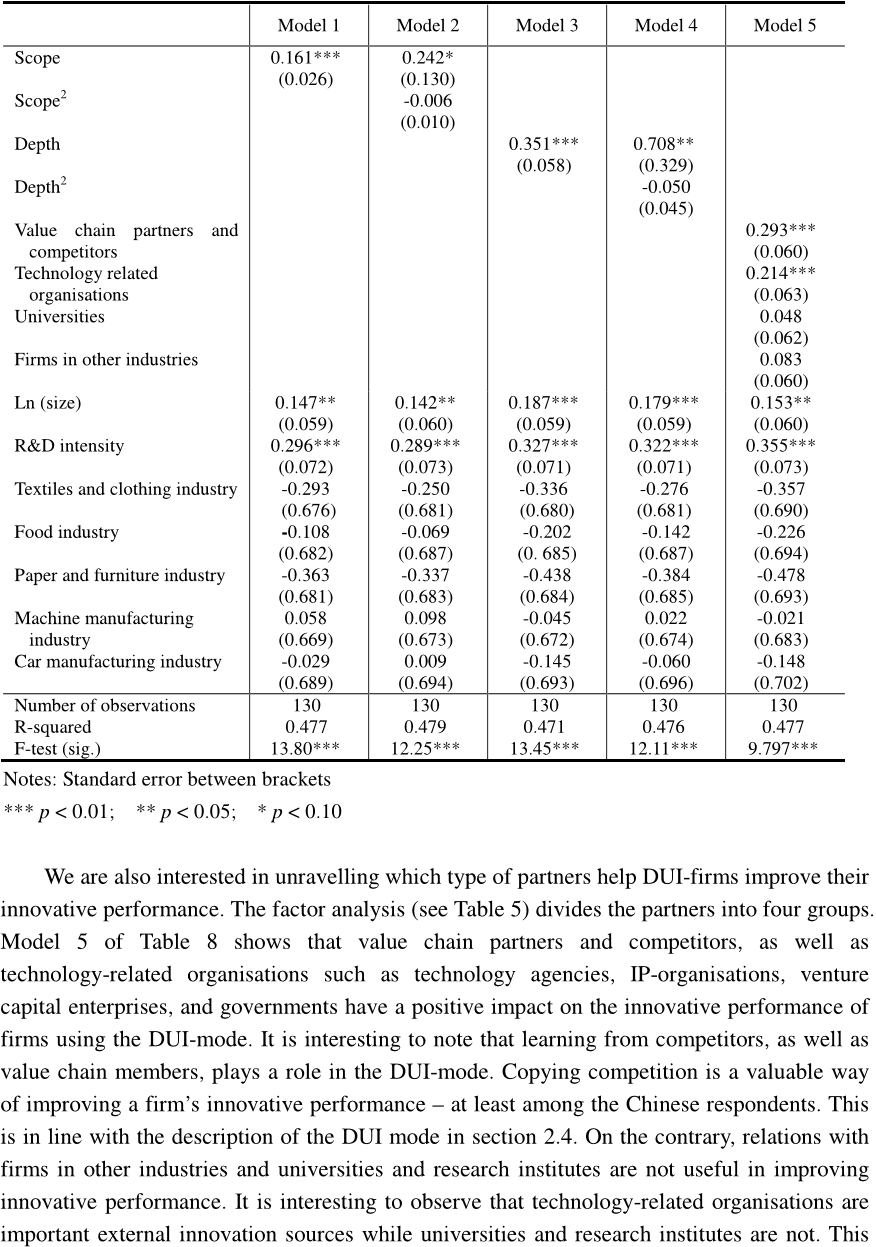
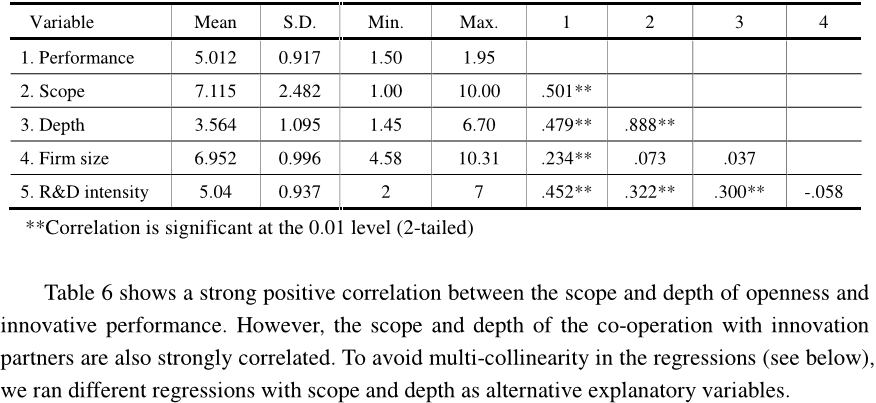
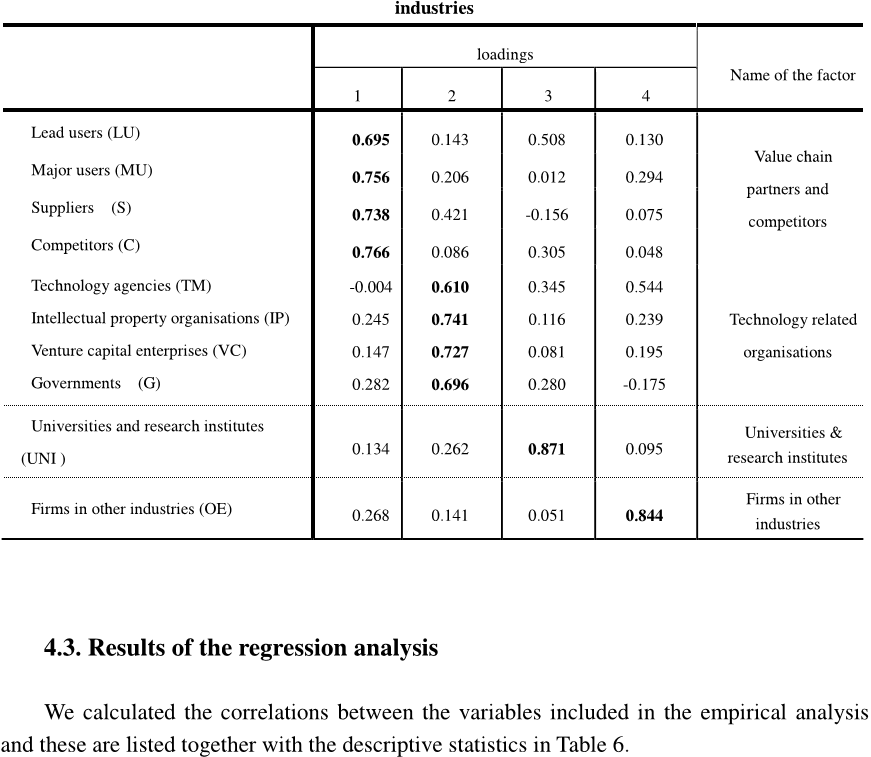
In this study, the authors analyze how the innovative performance is affected by the scope, depth, and orientation of firms ’ external search strategies. Based on a survey among firms in China, the authors find that greater scope and depth of openness for both innovation modes improves innovative performance indicating that open innovation is also relevant beyond science and technology based innovation. Furthermore, the authors find that decreasing returns in external search strategies, suggested by Laursen and Salter ( 2006 ), are not always present and are contingent on the innovation modes. Next, the authors find that the type of external partners ( they label it “ orientation of openness ” ) is crucial in explaining innovative performance and that firms using DUI or STI innovation modes have different sets of relevant innovation partners. As respondents are located in China, this study provides evidence that open innovation is also relevant in developing countries.