
Downloaded 02 Apr 2006 to 131.215.240.9. Redistribution subject to AIP license or copyright, see http://jcp.aip.org/jcp/copyright.jsp
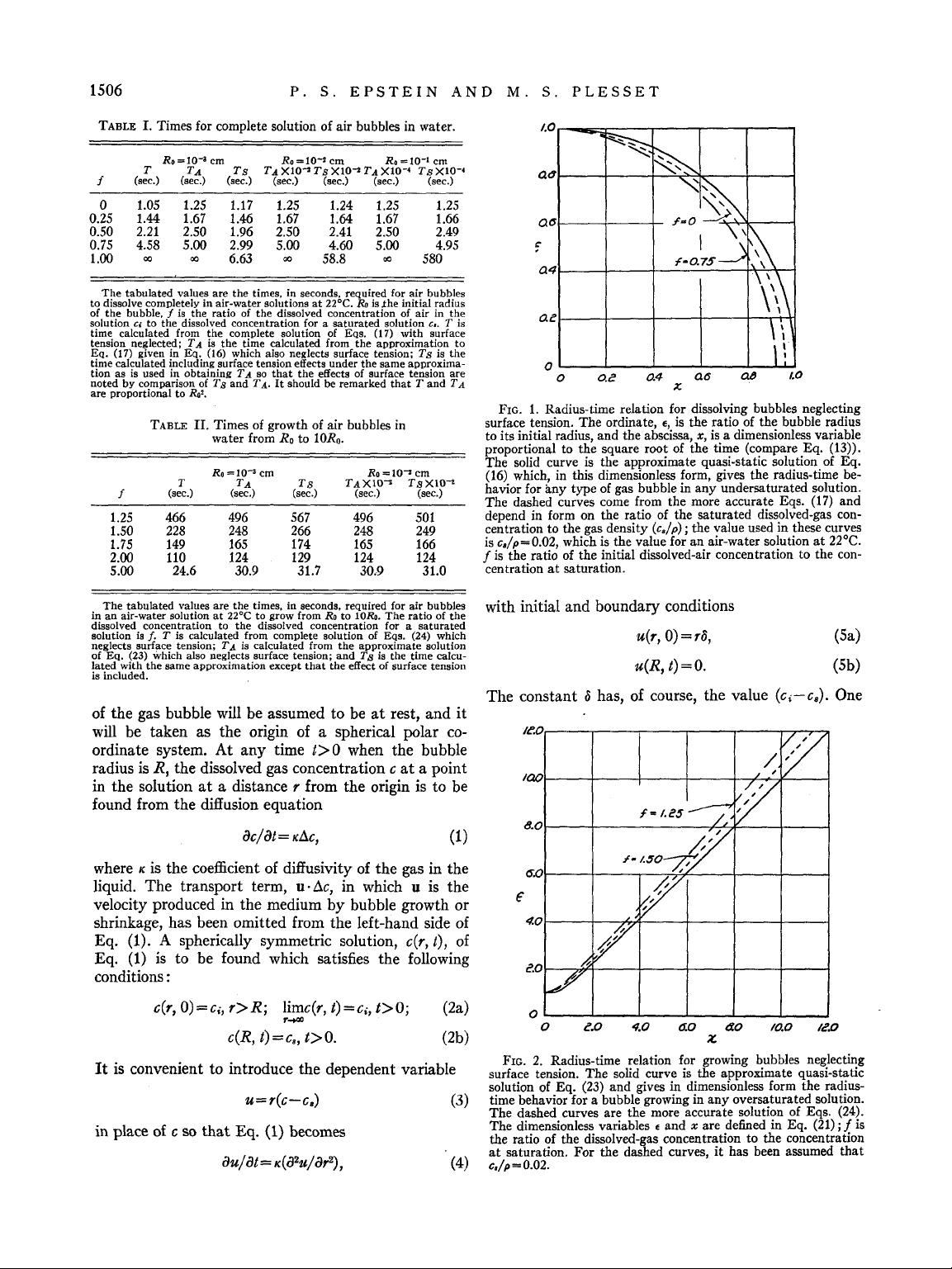
Downloaded 02 Apr 2006 to 131.215.240.9. Redistribution subject to AIP license or copyright, see http://jcp.aip.org/jcp/copyright.jsp

Downloaded 02 Apr 2006 to 131.215.240.9. Redistribution subject to AIP license or copyright, see http://jcp.aip.org/jcp/copyright.jsp

Downloaded 02 Apr 2006 to 131.215.240.9. Redistribution subject to AIP license or copyright, see http://jcp.aip.org/jcp/copyright.jsp

Downloaded 02 Apr 2006 to 131.215.240.9. Redistribution subject to AIP license or copyright, see http://jcp.aip.org/jcp/copyright.jsp