A Detection of Water in the Transmission Spectrum of the Hot Jupiter WASP-12b and Implications for its Atmospheric Composition
Laura Kreidberg,Michael R. Line,Jacob L. Bean,Kevin B. Stevenson,Jean-Michel Desert,Nikku Madhusudhan,Jonathan J. Fortney,Joanna K. Barstow,Gregory W. Henry,Michael H. Williamson,Adam P. Showman +10 more
Reads0
Chats0
TLDR
In this article, a near-infrared transmission spectrum for WASP-12b based on six transit observations with the Hubble Space Telescope/Wide Field Camera 3 (HST-WFC) was reported.Abstract:
Detailed characterization of exoplanets has begun to yield measurements of their atmospheric properties that constrain the planets’ origins and evolution. For example, past observations of the dayside emission spectrum of the hot Jupiter WASP-12b indicated that its atmosphere has a high carbon-tooxygen ratio (C/O > 1), suggesting it had a dierent formation pathway than is commonly assumed for giant planets. Here we report a precise near-infrared transmission spectrum for WASP-12b based on six transit observations with the Hubble Space Telescope/Wide Field Camera 3. We bin the data in 13 spectrophotometric light curves from 0.84 - 1.67 m and measure the transit depths to a median precision of 51 ppm. We retrieve the atmospheric properties using the transmission spectrum and nd strong evidence for water absorption (7 condence). This detection marks the rst high-condence, spectroscopic identication of a molecule in the atmosphere of WASP-12b. The retrieved 1 water volume mixing ratio is between 10 5 10 2 , which is consistent with C/O > 1 to within 2 . However, we also introduce a new retrieval parameterization that ts for C/O and metallicity under the assumption of chemical equilibrium. With this approach, we constrain C/O to 0:5 +0:2 0:3 at 1 and rule out a carbon-rich atmosphere composition (C/O> 1) at > 3 condence. Further observations and modeling of the planet’s global thermal structure and dynamics would aid in resolving the tension between our inferred C/O and previous constraints. Our ndings highlight the importance of obtaining high-precision data with multiple observing techniques in order to obtain robust constraints on the chemistry and physics of exoplanet atmospheres. Subject headings: planets and satellites: atmospheres | planets and satellites: composition | planets and satellites: individual: WASP-12bread more
Figures
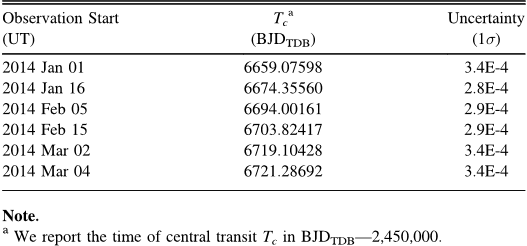
Table 2 Transit Times 
Figure 6. Systematics decorrelation parameters from the light curve fits plotted as a function of normalization c. We show (from top to bottom) the visit-long slope v, ramp rate constant a, ramp amplitude b, and ramp delay d. The normalization constant c is linearly proportional to the per-pixel flux in a spectroscopic channel. Measurements from the G102 and G141 data are shown in light and dark gray, respectively. The error bars indicate 1σ uncertainties from an MCMC fit to the light curves using the analytic model for instrument systematics. 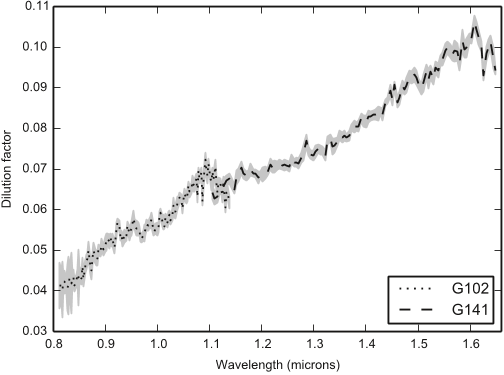
Figure 7. Dilution factor αComp, determined from the ratio of flux from WASP12 BC to WASP-12 A. The median dilution (over the 10 staring mode observations) is shown with black lines (dotted for G102 and dashed for G141). The gray shaded region indicates 1σ uncertainty, determined from the median absolute deviation. To calculate the dilution and uncertainty, we interpolate the spectra from each grism onto a common wavelength scale. 
Figure 12. Retrieval results from the C-C parameterization. The left and middle panels show the marginalized distribution for C/O and metallicity. The right panel shows the median (black lines) and 1σ range (shaded regions) of 1000 randomly sampled temperature–pressure profiles for each scenario. Yellow, blue, and red shading correspond to constraints from the fiducial scenario (an uninformative prior on C/O), the oxygen-rich scenario (C/O < 1), and a carbon-rich scenario (C/O > 1). The distribution of C/O values for the carbon-rich model is normalized to have a probability mass of unity over the plotted range; however, the distribution has an extended tail toward higher C/O values that is not shown. 
Table 1 Summary of Photometric Observations for WASP-12 
Figure 1. Raw HST/WFC3 images taken with the G102 grism. Spatial scan and staring mode data are shown in the top and bottom panels, respectively. The images are cutouts from a 256 × 256 pixel subarray. The spectrum of WASP-12A’s binary companion is visible in the bottom panel near row 10.
Citations
More filters
Book ChapterDOI
Atmospheric Retrieval of Exoplanets
TL;DR: Exoplanetary atmospheric retrieval refers to the inference of atmospheric properties of an exoplanet given an observed spectrum as discussed by the authors, which can provide key insights into the atmospheric physicochemical processes of exoplanets as well as their formation mechanisms.
Journal ArticleDOI
A mirage of the cosmic shoreline: Venus-like clouds as a statistical false positive for exoplanet atmospheric erosion.
TL;DR: In this article, the authors used a self-consistent cloud formation of the seven TRAPPIST-1 exoplanets to investigate the atmospheric depth that can be probed using both transmission and emission spectroscopy.
Journal ArticleDOI
Hot Exoplanet Atmospheres Resolved with Transit Spectroscopy (HEARTS) - VI. Non-detection of sodium with HARPS on the bloated super-Neptune WASP-127b
Julia V. Seidel,Monika Lendl,Vincent Bourrier,David Ehrenreich,Romain Allart,S. G. Sousa,Heather M. Cegla,Heather M. Cegla,Xavier Bonfils,U. Conod,A. Grandjean,Aurélien Wyttenbach,Nicola Astudillo-Defru,Daniel Bayliss,Kevin Heng,Baptiste Lavie,C. Lovis,Claudio Melo,Francesco Pepe,Damien Ségransan,Stéphane Udry +20 more
TL;DR: In this article, the authors used combined EulerCam and TESS light curves to recalculate the system parameters, and presented an in-depth search for sodium in four transit observations of WASP-127b, obtained as part of the Hot Exoplanet Atmosphere Resolved with Transit Spectroscopy (HEARTS) survey with the High Accuracy Radial velocity Planet Searcher (HARPS) spectrograph.
Journal ArticleDOI
The Exoplanet Perspective on Future Ice Giant Exploration
Hannah R. Wakeford,Paul A. Dalba +1 more
TL;DR: In this paper, the authors discuss what characteristics we can measure for exoplanets, and why a mission to the ice giants in our solar system is the logical next step for understanding ex-oplanets.
Journal ArticleDOI
From cold to hot irradiated gaseous exoplanets: Toward an observation-based classification scheme
TL;DR: In this paper, the authors quantify the C/O ratios at which this separation occurs by calculating a large self-consistent grid of cloud-free atmospheric models in chemical equilibrium, using the latest version of petitCODE.
References
More filters
Journal ArticleDOI
emcee: The MCMC Hammer
TL;DR: The emcee algorithm as mentioned in this paper is a Python implementation of the affine-invariant ensemble sampler for Markov chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) proposed by Goodman & Weare (2010).
Journal ArticleDOI
The Chemical Composition of the Sun
TL;DR: The solar chemical composition is an important ingredient in our understanding of the formation, structure, and evolution of both the Sun and our Solar System as discussed by the authors, and it is an essential refer...
Journal ArticleDOI
emcee: The MCMC Hammer
TL;DR: This document introduces a stable, well tested Python implementation of the affine-invariant ensemble sampler for Markov chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) proposed by Goodman & Weare (2010).
Journal ArticleDOI
Analytic Lightcurves for Planetary Transit Searches
Kaisey S. Mandel,Eric Agol +1 more
TL;DR: In this paper, exact analytic formulae for the eclipse of a star described by quadratic or nonlinear limb darkening are presented for the HST observations of HD 209458, showing that the ratio of the planetary to stellar radii is 0.1207+-0.0003.
Journal ArticleDOI
Analytic Light Curves for Planetary Transit Searches
Kaisey S. Mandel,Eric Agol +1 more
TL;DR: In this paper, the exact analytic formulae for the eclipse of a star described by quadratic or nonlinear limb darkening were presented, and the authors applied these results to the Hubble Space Telescope observations of HD 209458, showing that the ratio of the planetary to stellar radii is 0.1207 ± 0.0003.
Related Papers (5)
A continuum from clear to cloudy hot-Jupiter exoplanets without primordial water depletion
David K. Sing,Jonathan J. Fortney,Nikolay Nikolov,Hannah R. Wakeford,Tiffany Kataria,Thomas M. Evans,Suzanne Aigrain,Gilda E. Ballester,Adam Burrows,Drake Deming,Jean-Michel Desert,Neale P. Gibson,Gregory W. Henry,Catherine M. Huitson,Heather Knutson,Alain Lecavelier des Etangs,Frederic Pont,Adam P. Showman,Alfred Vidal-Madjar,Michael H. Williamson,Paul Wilson +20 more
INFRARED TRANSMISSION SPECTROSCOPY OF THE EXOPLANETS HD 209458b AND XO-1b USING THE WIDE FIELD CAMERA-3 ON THE HUBBLE SPACE TELESCOPE
Drake Deming,Drake Deming,A. Wilkins,Peter R. McCullough,Adam Burrows,Jonathan J. Fortney,Eric Agol,Eric Agol,Ian Dobbs-Dixon,Ian Dobbs-Dixon,Nikku Madhusudhan,Nicolas Crouzet,Jean-Michel Desert,Ronald L. Gilliland,Korey Haynes,Korey Haynes,Heather Knutson,Michael R. Line,Zazralt Magic,Avi Mandell,Sukrit Ranjan,David Charbonneau,Mark Clampin,Sara Seager,Adam P. Showman +24 more
Infrared Transmission Spectroscopy of the Exoplanets HD209458b and XO-1b Using the Wide Field Camera-3 on the Hubble Space Telescope
Drake Deming,Ashlee Wilkins,Peter R. McCullough,Adam Burrows,Jonathan J. Fortney,Eric Agol,Ian Dobbs-Dixon,Nikku Madhusudhan,Nicolas Crouzet,Jean-Michel Desert,Ronald L. Gilliland,Korey Haynes,Heather Knutson,Michael R. Line,Zazralt Magic,Avi Mandell,Sukrit Ranjan,David Charbonneau,Mark Clampin,Sara Seager,Adam P. Showman +20 more