Q2. What are the future works in "A 5-step reduced mechanism for combustion of co/h2/h2o/ch4/co2 mixtures with low hydrogen/methane and high h2o content" ?
The computational results are compared to experimental measurements of the flame speeds available in the literature for a wide range of pressure, 1-20 atm., temperature, 298- 700 K and thermo-chemical conditions. The authors thank the reviewers for suggesting many validation data which helped to show the robustness of the mechanisms over wide range of conditions for flame speeds and autoignition delay times.
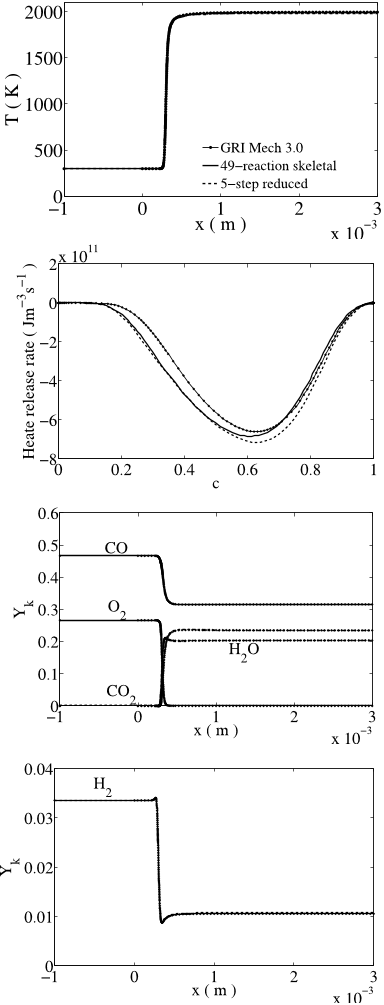
![Fig. 4: Laminar flame speeds of CO/H2-air mixtures using the reduced (dashed lines) and skeletal (full lines) mechanisms. Symbols: experimental results of Vagelopoulos and Egolfopoulos [48]. Tu = 298 K, p = 1 atm, XN2/XO2 = 3.76.](/figures/fig-4-laminar-flame-speeds-of-co-h2-air-mixtures-using-the-209eopff.png)
![Fig. 3: Laminar flame speeds of syngas mixtures ( CO/H2/CH4/CO2/N2-air ) using the reduced (dashed lines) and the skeletal (full lines) mechanisms. Symbols: experimental results of Yong et al. [27]. fCH4 = 0.24 with 11% CO2 and 42.7% N2 in the fuel mixture. Tu = 298 K, p = 1 atm, XN2/XO2 = 3.76. Error bars from [27] are also shown.](/figures/fig-3-laminar-flame-speeds-of-syngas-mixtures-co-h2-ch4-co2-3u6a11oi.png)

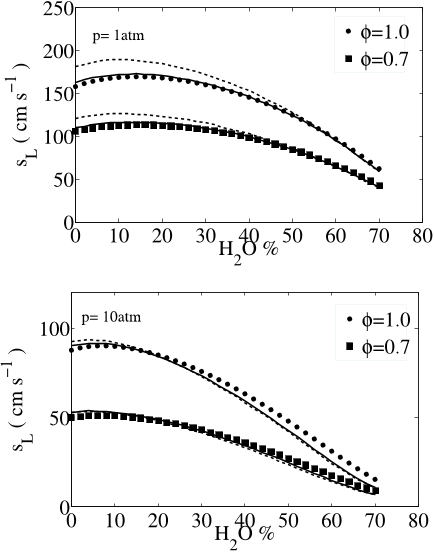
![Fig. 8: Laminar flame speeds of CO/H2 mixtures using the reduced (dashed lines) and skeletal (continuous lines) mechanisms. Symbols: experimental results of Sun et al. [33]. At p = 1 atm the oxidizer is O2,N2 with XN2/XO2 = 3.76. At p = 5, 10, 20 atm the oxidizer is O2 and He with XHe/XO2 = 7.0. Open symbols: experimental results of Singh et al. [21].](/figures/fig-8-laminar-flame-speeds-of-co-h2-mixtures-using-the-1l00yv4j.png)