Q2. How many times does taboo search take to solve a problem?
let us mention5 that an iteration of taboo search needs about 4.10-6.n2.m seconds on a “Silicon Graphics” personal workstation (10 Mips).
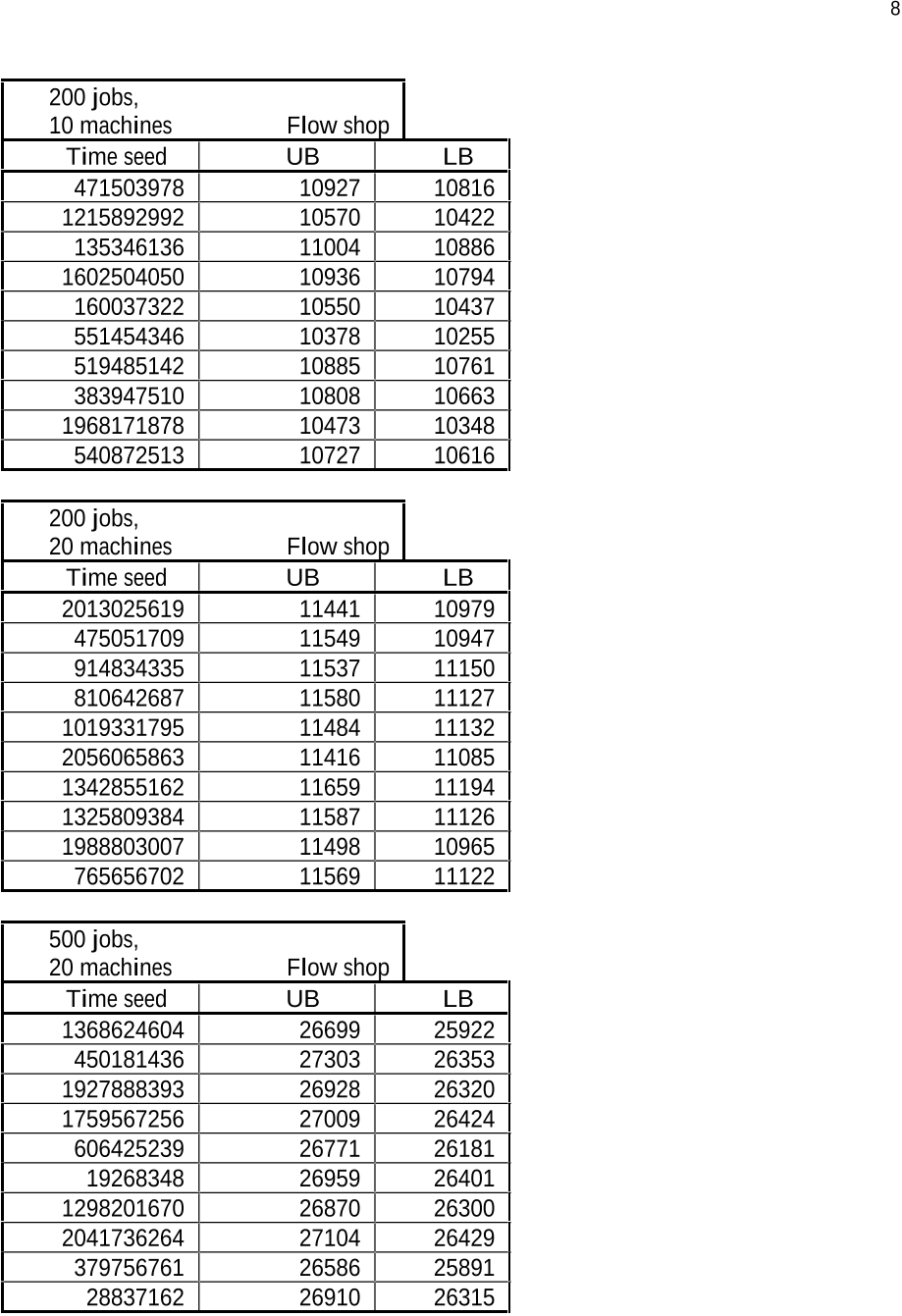
Q3. What is the value of the machine seed?
The machine Mij on which the jth operation of job i has to be performed is given by the following procedure :0) Mij := j (1 L Q M P 1) For i = 1 to nFor j = 1 to m Swap Mij and MiU[j,m]Let us note the use of another initial seed for the choice of the machines : Machine seed.
Q4. What is the LB of a flow shop problem?
The proportion of problems for which the authors found a solution for which the makespan was equal to the lower bound (or equal to the lower bound augmented by 2% for the 500-job 20-machine problems).
Q5. What is the implementation of the random number generator?
This implementation uses only 32-bit integers and provides a uniformly distributed sequence of numbers between 0 and 1 (not contained) :3 0) Initial seed and X0 (0 < X0 < 231- 1) constants : a = 16 807, b = 127 773, c = 2 836, m = 231 - 11) Modification of k := Xi/b the seed : Xi+1 := a(Xi mod b) - kcIf Xi+1 < 0 then let Xi+1 := Xi+1 + m2) New value of the seed : Xi+1 Current value of the generator : Xi+1/mBelow, the authors shall denote by U(0,1) the pseudorandom number that this generator provides.
Q6. What is the implementation of the linear congruential generator?
The random number generator Let us recall the implementation of the linear congruential generator the authors have used which is based on the recursive formula Xi+1 = (16 807 Xi) mod (231 - 1).
Q7. What is the way to generate a random number generator?
In order to implement the integer random procedure only with 32-bit integers, the problems have been chosen in such a way that one never has to deal with a seed X such that :a + P DE; )1( +−⋅ ≠ a + )1( +−