Maps of Dust IR Emission for Use in Estimation of Reddening and CMBR Foregrounds
TLDR
In this paper, the authors presented a reprocessed composite of the COBE/DIRBE and IRAS/ISSA maps, with the zodiacal foreground and confirmed point sources removed.Abstract:
We present a full sky 100 micron map that is a reprocessed composite of the COBE/DIRBE and IRAS/ISSA maps, with the zodiacal foreground and confirmed point sources removed. Before using the ISSA maps, we remove the remaining artifacts from the IRAS scan pattern. Using the DIRBE 100 micron and 240 micron data, we have constructed a map of the dust temperature, so that the 100 micron map can be converted to a map proportional to dust column density. The result of these manipulations is a map with DIRBE-quality calibration and IRAS resolution.
To generate the full sky dust maps, we must first remove zodiacal light contamination as well as a possible cosmic infrared background (CIB). This is done via a regression analysis of the 100 micron DIRBE map against the Leiden- Dwingeloo map of H_I emission, with corrections for the zodiacal light via a suitable expansion of the DIRBE 25 micron flux. For the 100 micron map, no significant CIB is detected. In the 140 micron and 240 micron maps, where the zodiacal contamination is weaker, we detect the CIB at surprisingly high flux levels of 32 \pm 13 nW/m^2/sr at 140 micron, and 17 \pm 4 nW/m^2/sr at 240 micron (95% confidence). This integrated flux is ~2 times that extrapolated from optical galaxies in the Hubble Deep Field.
The primary use of these maps is likely to be as a new estimator of Galactic extinction. We demonstrate that the new maps are twice as accurate as the older Burstein-Heiles estimates in regions of low and moderate reddening. These dust maps will also be useful for estimating millimeter emission that contaminates CMBR experiments and for estimating soft X-ray absorption.read more
Figures
![FIG. 1.ÈThe 100 kmÈH I correlation with (a) no correction, (b) linear correction, and (c) quadratic correction for zodiacal contamination. The Ðts in the range [0, 200] K km s~1 are shown as solid lines.](/figures/fig-1-ethe-100-kmeh-i-correlation-with-a-no-correction-b-j2j6qo00.png)
FIG. 1.ÈThe 100 kmÈH I correlation with (a) no correction, (b) linear correction, and (c) quadratic correction for zodiacal contamination. The Ðts in the range [0, 200] K km s~1 are shown as solid lines. 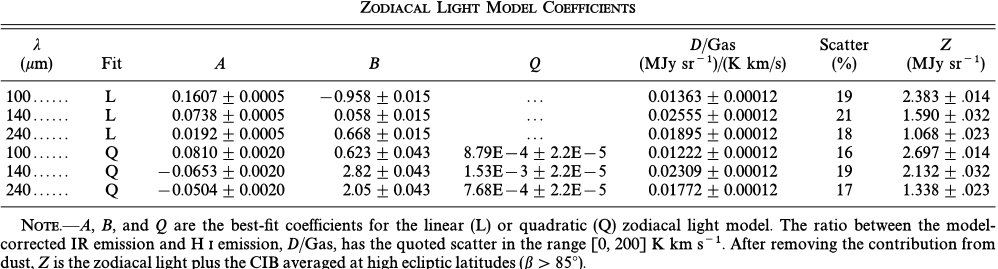
TABLE 2 
FIG. 13.ÈColor-color diagram for PSC sources. The diagonal line efficiently discriminates between galaxies (above the line) and stars (below the line). The square box is a strict color cut that retains 70% of stars. For clarity, only 1/10 of the stars are plotted. 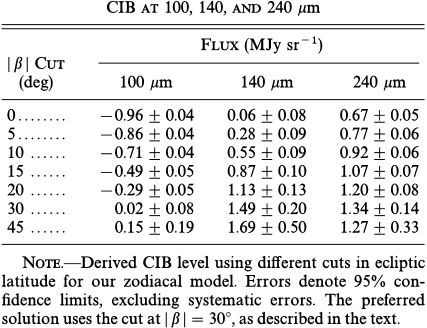
TABLE 3 ![FIG. 7.ÈSlice of sky from (a) the BH map, (b) the Leiden-Dwingeloo H I map, (c) our dust map with DIRBE resolution, and (d) our dust map with IRAS resolution. The slice measures approximately 90¡ ] 30¡, centered at l \ 100¡, b \ ]35¡.](/figures/fig-7-eslice-of-sky-from-a-the-bh-map-b-the-leiden-dwingeloo-1rzt4l41.png)
FIG. 7.ÈSlice of sky from (a) the BH map, (b) the Leiden-Dwingeloo H I map, (c) our dust map with DIRBE resolution, and (d) our dust map with IRAS resolution. The slice measures approximately 90¡ ] 30¡, centered at l \ 100¡, b \ ]35¡. 
FIG. 2.ÈRatio of recovered vs. true column density of dust using a single-temperature Ðt to two components. A fraction of dust at tem-f Bperature is added to 18 K dust. The recovered column density is alwaysT Blower than the true column density, with contours spaced in units of 0.1.
Citations
More filters
Journal ArticleDOI
An empirical relation between sodium absorption and dust extinction
TL;DR: In this article, a study of the correlation between extinction in the Milky Way and the equivalent width of the Na'i'D absorption doublet is presented, and the authors provide a brief guide on how to best estimate extinction to extragalactic sources such as supernovae, under a variety of circumstances.
Journal ArticleDOI
BlackCAT: A catalogue of stellar-mass black holes in X-ray transients
Jesus M. Corral-Santana,Jorge Casares,Jorge Casares,Teo Muñoz-Darias,Teo Muñoz-Darias,Franz E. Bauer,Franz E. Bauer,Franz E. Bauer,I. G. Martínez-Pais,I. G. Martínez-Pais,David M. Russell +10 more
TL;DR: In this paper, the population of black holes in X-ray transients as a whole has been studied and the most updated catalogue of black hole transients is presented, together with their astrometric and dynamical properties.
Journal ArticleDOI
Atlas and Catalog of Dark Clouds Based on Digitized Sky Survey I
Kazuhito Dobashi,Hayato Uehara,Ryo Kandori,Tohko Sakurai,Masahiro Kaiden,Tomofumi Umemoto,Fumio Sato +6 more
TL;DR: Dobashi et al. as mentioned in this paper introduced a quantitative atlas and catalog of dark clouds derived by using the optical database "Digitized Sky Survey I" and applied a traditional starcount technique to 1043 plates contained in the database, they produced an AV map covering the entire region in the galactic latitude range |b| ≤ 40◦.
Journal ArticleDOI
The arecibo legacy fast alfa survey: the galaxy population detected by alfalfa*
TL;DR: In this paper, the global scaling relations and fundamental planes linking stars and gas for a sample of 9417 common galaxies: the α.40-SDSS-GALEX sample were derived from the ALFALFA data set.
Journal ArticleDOI
Gamma-Ray Bursts as a Probe of the Very High Redshift Universe
D. Q. Lamb,Daniel E. Reichart +1 more
TL;DR: In this paper, it was shown that GRBs and their afterglows can be used as beacons to locate core collapse SNe at redshifts z > 1, and to study the properties of these SNe.
Related Papers (5)
Maps of Dust Infrared Emission for Use in Estimation of Reddening and Cosmic Microwave Background Radiation Foregrounds
The relationship between infrared, optical, and ultraviolet extinction
The Sloan Digital Sky Survey: Technical summary
Donald G. York,Jennifer Adelman,John E. Anderson,Scott F. Anderson,James Annis,Neta A. Bahcall,J. A. Bakken,Robert H. Barkhouser,Steven Bastian,E. Berman,William N. Boroski,Steve Bracker,Charlie Briegel,John W. Briggs,Jon Brinkmann,Robert J. Brunner,Scott Burles,Larry N. Carey,Michael A. Carr,Francisco J. Castander,Francisco J. Castander,Bing Chen,Patrick L. Colestock,Andrew J. Connolly,James H. Crocker,István Csabai,István Csabai,Paul C. Czarapata,John Eric Davis,Mamoru Doi,Tom Dombeck,Daniel J. Eisenstein,Nancy Ellman,Brian R. Elms,Brian R. Elms,Michael L. Evans,Xiaohui Fan,Glenn R. Federwitz,Larry Fiscelli,Scott D. Friedman,Joshua A. Frieman,Joshua A. Frieman,Masataka Fukugita,Bruce Gillespie,James E. Gunn,Vijay K. Gurbani,Ernst De Haas,M. Haldeman,Frederick H. Harris,Jeffrey J. E. Hayes,Timothy M. Heckman,Gregory S. Hennessy,Robert B. Hindsley,S. Holm,Donald J. Holmgren,Chi Hao Huang,Charles L. Hull,Don Husby,Shin-Ichi Ichikawa,Takashi Ichikawa,Zěljko Ivezić,Stephen M. Kent,Rita S. J. Kim,E. Kinney,Mark A. Klaene,A. N. Kleinman,Scot Kleinman,Gillian R. Knapp,John Korienek,Richard G. Kron,Richard G. Kron,Peter Z. Kunszt,D. Q. Lamb,Brian C. Lee,R. French Leger,Siriluk Limmongkol,Carl Lindenmeyer,Dan Long,Craig Loomis,Jon Loveday,Rich Lucinio,Robert H. Lupton,Bryan Mackinnon,Bryan Mackinnon,Edward J. Mannery,Paul M. Mantsch,Bruce Margon,Peregrine M. McGehee,Timothy A. McKay,Avery Meiksin,Aronne Merelli,David G. Monet,Jeffrey A. Munn,Vijay K. Narayanan,Thomas Nash,Eric H. Neilsen,Rich Neswold,Heidi Jo Newberg,Heidi Jo Newberg,Robert C. Nichol,T. Nicinski,T. Nicinski,Mario Nonino,Norio Okada,Sadanori Okamura,Jeremiah P. Ostriker,Russell Owen,A. George Pauls,John Peoples,R. Peterson,Don Petravick,Jeffrey R. Pier,Adrian Pope,Ruth Pordes,Angela Prosapio,R. Rechenmacher,Thomas R. Quinn,Gordon T. Richards,Michael Richmond,Claudio H. Rivetta,Constance M. Rockosi,Kurt Ruthmansdorfer,Dale Sandford,David J. Schlegel,Donald P. Schneider,Maki Sekiguchi,G. Sergey,Kazuhiro Shimasaku,Walter A. Siegmund,Stephen A. Smee,J. Allyn Smith,S. A. Snedden,Robert Stone,Chris Stoughton,Michael A. Strauss,Christopher W. Stubbs,Mark SubbaRao,Alexander S. Szalay,István Szapudi,Gyula P. Szokoly,Anirudda R. Thakar,Christy Tremonti,Douglas L. Tucker,Alan Uomoto,Daniel E. Vanden Berk,Michael S. Vogeley,Patrick Waddell,Shu I. Wang,Masaru Watanabe,David H. Weinberg,Brian Yanny,Naoki Yasuda +151 more
The Two Micron All Sky Survey (2MASS)
Michael F. Skrutskie,Michael F. Skrutskie,Roc M. Cutri,R. Stiening,Martin D. Weinberg,Stephen E. Schneider,John M. Carpenter,Chas Beichman,R. Capps,T. Chester,J. Elias,John P. Huchra,James Liebert,C. Lonsdale,David G. Monet,Stephan D. Price,Patrick Seitzer,Thomas H. Jarrett,J. D. Kirkpatrick,John E. Gizis,E. Howard,T. Evans,John W. Fowler,L. Fullmer,Robert L. Hurt,R. M. Light,E. L. Kopan,K. A. Marsh,H. McCallon,R. Tam,S. D. Van Dyk,S. Wheelock +31 more