Maps of Dust IR Emission for Use in Estimation of Reddening and CMBR Foregrounds
TLDR
In this paper, the authors presented a reprocessed composite of the COBE/DIRBE and IRAS/ISSA maps, with the zodiacal foreground and confirmed point sources removed.Abstract:
We present a full sky 100 micron map that is a reprocessed composite of the COBE/DIRBE and IRAS/ISSA maps, with the zodiacal foreground and confirmed point sources removed. Before using the ISSA maps, we remove the remaining artifacts from the IRAS scan pattern. Using the DIRBE 100 micron and 240 micron data, we have constructed a map of the dust temperature, so that the 100 micron map can be converted to a map proportional to dust column density. The result of these manipulations is a map with DIRBE-quality calibration and IRAS resolution.
To generate the full sky dust maps, we must first remove zodiacal light contamination as well as a possible cosmic infrared background (CIB). This is done via a regression analysis of the 100 micron DIRBE map against the Leiden- Dwingeloo map of H_I emission, with corrections for the zodiacal light via a suitable expansion of the DIRBE 25 micron flux. For the 100 micron map, no significant CIB is detected. In the 140 micron and 240 micron maps, where the zodiacal contamination is weaker, we detect the CIB at surprisingly high flux levels of 32 \pm 13 nW/m^2/sr at 140 micron, and 17 \pm 4 nW/m^2/sr at 240 micron (95% confidence). This integrated flux is ~2 times that extrapolated from optical galaxies in the Hubble Deep Field.
The primary use of these maps is likely to be as a new estimator of Galactic extinction. We demonstrate that the new maps are twice as accurate as the older Burstein-Heiles estimates in regions of low and moderate reddening. These dust maps will also be useful for estimating millimeter emission that contaminates CMBR experiments and for estimating soft X-ray absorption.read more
Figures
![FIG. 1.ÈThe 100 kmÈH I correlation with (a) no correction, (b) linear correction, and (c) quadratic correction for zodiacal contamination. The Ðts in the range [0, 200] K km s~1 are shown as solid lines.](/figures/fig-1-ethe-100-kmeh-i-correlation-with-a-no-correction-b-j2j6qo00.png)
FIG. 1.ÈThe 100 kmÈH I correlation with (a) no correction, (b) linear correction, and (c) quadratic correction for zodiacal contamination. The Ðts in the range [0, 200] K km s~1 are shown as solid lines. 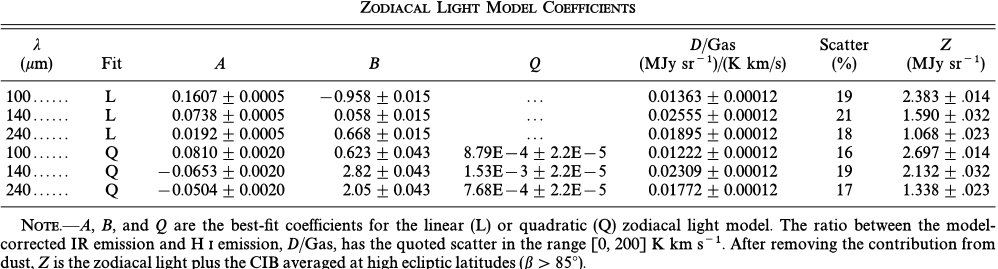
TABLE 2 
FIG. 13.ÈColor-color diagram for PSC sources. The diagonal line efficiently discriminates between galaxies (above the line) and stars (below the line). The square box is a strict color cut that retains 70% of stars. For clarity, only 1/10 of the stars are plotted. 
TABLE 3 ![FIG. 7.ÈSlice of sky from (a) the BH map, (b) the Leiden-Dwingeloo H I map, (c) our dust map with DIRBE resolution, and (d) our dust map with IRAS resolution. The slice measures approximately 90¡ ] 30¡, centered at l \ 100¡, b \ ]35¡.](/figures/fig-7-eslice-of-sky-from-a-the-bh-map-b-the-leiden-dwingeloo-1rzt4l41.png)
FIG. 7.ÈSlice of sky from (a) the BH map, (b) the Leiden-Dwingeloo H I map, (c) our dust map with DIRBE resolution, and (d) our dust map with IRAS resolution. The slice measures approximately 90¡ ] 30¡, centered at l \ 100¡, b \ ]35¡. 
FIG. 2.ÈRatio of recovered vs. true column density of dust using a single-temperature Ðt to two components. A fraction of dust at tem-f Bperature is added to 18 K dust. The recovered column density is alwaysT Blower than the true column density, with contours spaced in units of 0.1.
Citations
More filters
Journal ArticleDOI
A Description of Quasar Variability Measured Using Repeated SDSS and POSS Imaging
Chelsea L. MacLeod,Željko Ivezić,Branimir Sesar,Wim de Vries,Christopher S. Kochanek,Brandon C. Kelly,Andrew C. Becker,Robert H. Lupton,Patrick B. Hall,Gordon T. Richards,Scott F. Anderson,Donald P. Schneider +11 more
TL;DR: In this paper, the authors provide a quantitative description and statistical interpretation of the optical continuum variability of quasars and use it to predict the incidence of quasar contamination in transient surveys such as those from the Palomar Transient Factory and Large Synoptic Survey Telescope.
Journal ArticleDOI
Optical Photometry of the Type Ia Supernova 1999ee and the Type Ib/c Supernova 1999ex in IC 5179
Maximilian Stritzinger,Maximilian Stritzinger,Mario Hamuy,Mario Hamuy,Nicholas B. Suntzeff,R. C. Smith,Mark M. Phillips,José Maza,Louis-Gregory Strolger,R. Antezana,Luis González,M. Wischnjewsky,Pablo Candia,Juan Espinoza,David Gonzalez,Christopher W. Stubbs,Andrew C. Becker,Andrew C. Becker,Eric P. Rubenstein,Gaspar Galaz,Gaspar Galaz +20 more
TL;DR: In this article, the authors present UBVRIz light curves of the Type Ia SN 1999ee and the Type Ib/c SN 1999ex, both located in the galaxy IC 5179.
Journal ArticleDOI
Localization and broadband follow-up of the gravitational-wave transient GW150914
B. P. Abbott,Richard J. Abbott,T. D. Abbott,M. R. Abernathy,Fausto Acernese,Kendall Ackley,C. Adams,Todd Adams,Paolo Addesso,Rana X. Adhikari,V. B. Adya,C. Affeldt,M. Agathos,Kazuhiro Agatsuma,Nancy Aggarwal,Odylio D. Aguiar,Lloyd Paul Aiello,A. Ain,P. Ajith,Benjamin William Allen,Benjamin William Allen,Benjamin William Allen,A. Allocca,P. A. Altin,S. B. Anderson,W. G. Anderson,Koji Arai,M. C. Araya,C. C. Arceneaux,J. S. Areeda,N. Arnaud,K. G. Arun,S. Ascenzi,Gregory Ashton,M. Ast,S. M. Aston,P. Astone,P. Aufmuth,C. Aulbert,Stanislav Babak,P. Bacon,M. K. M. Bader,P. T. Baker,F. Baldaccini,G. Ballardin,S. W. Ballmer,J. C. Barayoga,S. E. Barclay,Barry C. Barish,D. Barker,Fabrizio Barone,B. Barr,Lisa Barsotti,M. Barsuglia,D. Barta,Scott Barthelmy,James G. Bartlett,Imre Bartos,Riccardo Bassiri,A. Basti,J. C. Batch,C. Baune,Viswanath Bavigadda,Marco Bazzan,B. Behnke,M. Bejger,A. S. Bell,C. J. Bell,B. K. Berger,J. Bergman,G. Bergmann,Christopher P. L. Berry,D. Bersanetti,Alessandro Bertolini,J. Betzwieser,Swetha Bhagwat,R. Bhandare,I. A. Bilenko,G. Billingsley,Jens Birch,R. Birney,Sebastien Biscans,A. Bisht,A. Bisht,M. Bitossi,Christopher M. Biwer,Marie-Anne Bizouard,J. K. Blackburn,Carl Blair,David Blair,R. M. Blair,Steven Bloemen,O. Bock,T. P. Bodiya,M. Boer,G. Bogaert,C. Bogan,A. Bohe,P. Bojtos,C. Bond,François Bondu,R. Bonnand,B. A. Boom,R. Bork,V. Boschi,Suvadeep Bose,Suvadeep Bose,Yann Bouffanais,A. Bozzi,C. Bradaschia,Patrick Brady,Vladimir B. Braginsky,M. Branchesi,J. E. Brau,Tristan Briant,A. Brillet,M. Brinkmann,V. Brisson,P. Brockill,A. F. Brooks,Duncan A. Brown,D. D. Brown,N. M. Brown,C. C. Buchanan,Aaron Buikema,Tomasz Bulik,H. J. Bulten,Alessandra Buonanno,Alessandra Buonanno,D. Buskulic,C. Buy,Robert L. Byer,Laura Cadonati,Gianpietro Cagnoli,Gianpietro Cagnoli,C. Cahillane,Juan Calderón Bustillo,Juan Calderón Bustillo,T. A. Callister,Enrico Calloni,J. B. Camp,Kipp Cannon,Junwei Cao,Collin D. Capano,E. Capocasa,F. Carbognani,S. Caride,Julia Casanueva Diaz,C. Casentini,Sarah Caudill,Marco Cavaglia,F. Cavalier,R. Cavalieri,G. Cella,Carlos Cepeda,L. C. Baiardi,G. Cerretani,E. Cesarini,R. Chakraborty,T. Chalermsongsak,S. J. Chamberlin,M. Chan,Shiuh Chao,P. Charlton,E. Chassande-Mottin,H. S. Chen,Yi Chen,Chia-Liang Cheng,Andrea Chincarini,A. Chiummo,H. S. Cho,M. Cho,Jong H. Chow,Nelson Christensen,Q. Chu,Sheon Chua,S. Chung,Giacomo Ciani,F. Clara,John A. Clark,F. Cleva,E. Coccia,P. F. Cohadon,A. Colla,Christophe Collette,L. Cominsky,M. Constancio,A. Conte,L. Conti,David O. Cook,Thomas Corbitt,Neil J. Cornish,Alessandra Corsi,Samuele Cortese,C. A. Costa,Michael W. Coughlin,S. B. Coughlin,J.-P. Coulon,S. T. Countryman,P. Couvares,E. E. Cowan,David Coward,M. J. Cowart,D. C. Coyne,R. Coyne,Kieran Craig,Jolien D. E. Creighton,Jonathan Cripe,S. G. Crowder,A. Cumming,Liam Cunningham,E. Cuoco,T. Dal Canton,S. L. Danilishin,S. D'Antonio,Karsten Danzmann,Karsten Danzmann,N. S. Darman,V. Dattilo,I. Dave,H. P. Daveloza,M. Davier,Gavin Davies,E. J. Daw,R. Day,D.B. DeBra,G. Debreczeni,Jerome Degallaix,M. De Laurentis,Samuel Deléglise,W. Del Pozzo,T. Denker,T. Denker,Thomas Dent,H. Dereli,Vladimir Dergachev,R. T. DeRosa,R. De Rosa,R. DeSalvo,Sanjeev Dhurandhar,M. C. Díaz,L. Di Fiore,M. Di Giovanni,A. Di Lieto,S. Di Pace,I. Di Palma,A. Di Virgilio,G. Dojcinoski,V. Dolique,F. Donovan,K. L. Dooley,S. Doravari,S. Doravari,R. Douglas,T. P. Downes,M. Drago,M. Drago,R. W. P. Drever,J. C. Driggers,Zhihui Du,M. Ducrot,S. E. Dwyer,T. B. Edo,M. C. Edwards,A. Effler,Heinz-Bernd Eggenstein,P. Ehrens,J. Eichholz,S. S. Eikenberry,W. Engels,Reed Essick,T. Etzel,Matthew Evans,Timothy Evans,R. Everett,M. Factourovich,V. Fafone,H. Fair,Stephen Fairhurst,Xiaohui Fan,Qi Fang,S. Farinon,Ben Farr,Will M. Farr,Marc Favata,M. Fays,H. Fehrmann,Martin M. Fejer,I. Ferrante,E. C. Ferreira,Federico Ferrini,F. Fidecaro,I. Fiori,D. Fiorucci,Rebecca Fisher,R. Flaminio,R. Flaminio,M. Fletcher,J.-D. Fournier,S. Franco,S. Frasca,F. Frasconi,Z. Frei,Andreas Freise,R. Frey,V. Frey,T. T. Fricke,Peter Fritschel,V. V. Frolov,P. Fulda,M. Fyffe,H. A. G. Gabbard,Jonathan R. Gair,Luca Gammaitoni,S. G. Gaonkar,F. Garufi,Alberto Gatto,G. Gaur,Neil Gehrels,G. Gemme,Bruce Gendre,E. Genin,A. Gennai,Jimin George,László Á. Gergely,V. Germain,Archisman Ghosh,Sourav Ghosh,J. A. Giaime,J. A. Giaime,K. D. Giardina,A. Giazotto,K. Gill,A. Glaefke,Evan Goetz,R. Goetz,László Gondán,Gabriela Gonzalez,J. M.G. Castro,Achamveedu Gopakumar,N. A. Gordon,Michael L. Gorodetsky,S. E. Gossan,M. Gosselin,R. Gouaty,C. Graef,P. B. Graff,M. Granata,A. Grant,Slawomir Gras,C. Gray,G. Greco,A. C. Green,Paul J. Groot,Hartmut Grote,S. Grunewald,G. M. Guidi,X. Guo,A. Gupta,M. K. Gupta,K. E. Gushwa,E. K. Gustafson,R. Gustafson,J. J. Hacker,B. R. Hall,E. D. Hall,G. D. Hammond,M. Haney,M. M. Hanke,J. Hanks,Chad Hanna,Mark Hannam,J. Hanson,T. Hardwick,K. Haris,Jan Harms,G. M. Harry,I. W. Harry,M. J. Hart,M. T. Hartman,Carl-Johan Haster,K. Haughian,Antoine Heidmann,Matthew Heintze,Matthew Heintze,H. Heitmann,Patrice Hello,G. Hemming,Martin Hendry,Ik Siong Heng,J. Hennig,A. W. Heptonstall,M. Heurs,M. Heurs,Stefan Hild,D. Hoak,K. A. Hodge,David Jonathan Hofman,S. E. Hollitt,K. Holt,Daniel E. Holz,Philip F. Hopkins,D. J. Hosken,J. H. Hough,E. A. Houston,Eric Howell,Yi-Ming Hu,Shuiyao Huang,E. A. Huerta,E. A. Huerta,D. Huet,B. Hughey,Sascha Husa,S. H. Huttner,T. Huynh-Dinh,A. Idrisy,N. Indik,D. R. Ingram,R. Inta,H. N. Isa,J.-M. Isac,Maximiliano Isi,G. Islas,T. Isogai,Bala R. Iyer,K. Izumi,Thibaut Jacqmin,H. J. Jang,Karan Jani,Piotr Jaranowski,S. Jawahar,F. Jiménez-Forteza,W. W. Johnson,David Jones,Roger Jones,R. J. G. Jonker,Li Ju,C. V. Kalaghatgi,Vicky Kalogera,S. Kandhasamy,G. Kang,J. B. Kanner,S. Karki,M. Kasprzack,M. Kasprzack,E. Katsavounidis,W. Katzman,S. Kaufer,Tejinder Kaur,K. Kawabe,F. Kawazoe,F. Kawazoe,Fabien Kéfélian,M. S. Kehl,David Keitel,David Keitel,D. B. Kelley,W. Kells,Rebecca Kennedy,Joey Shapiro Key,Alexander Khalaidovski,F. Y. Khalili,I. Khan,Sebastian Khan,Zahoor Ali Khan,Efim A. Khazanov,N. Kijbunchoo,Chi-Woong Kim,Jongsoo Kim,Kyungmin Kim,Nam-Gyu Kim,Y. M. Kim,E. J. King,P. J. King,D. L. Kinzel,J. S. Kissel,L. Kleybolte,S. Klimenko,S. M. Koehlenbeck,K. Kokeyama,S. Koley,V. Kondrashov,Antonios Kontos,M. Korobko,W. Z. Korth,I. Kowalska,D. B. Kozak,V. Kringel,A. Królak,C. Krueger,G. Kuehn,P. Kumar,L. Kuo,A. Kutynia,B. D. Lackey,M. Landry,J. S. Lange,B. Lantz,Paul D. Lasky,Albert Lazzarini,C. Lazzaro,P. Leaci,P. Leaci,S. Leavey,E. O. Lebigot,Chang-Hwan Lee,Hyun Lee,Ho-Gyu Lee,Kejia Lee,A. Lenon,M. Leonardi,J. R. Leong,N. Leroy,N. Letendre,Yuri Levin,B. M. Levine,Tjonnie G. F. Li,Adam A. Libson,Tyson Littenberg,N. A. Lockerbie,J. Logue,A. L. Lombardi,J. E. Lord,M. Lorenzini,V. Loriette,M. Lormand,G. Losurdo,J. D. Lough,J. D. Lough,Harald Lück,Harald Lück,Andrew Lundgren,J. Luo,Ryan Lynch,Yinfa Ma,Timothy MacDonald,B. Machenschalk,M. MacInnis,D. M. Macleod,F. Magaña-Sandoval,R. M. Magee,M. Mageswaran,Ettore Majorana,I. Maksimovic,V. Malvezzi,N. Man,Ilya Mandel,Vuk Mandic,V. Mangano,G. L. Mansell,Magnus Manske,M. Mantovani,Fabio Marchesoni,F. Marion,S. Márka,Z. Márka,A. S. Markosyan,E. Maros,F. Martelli,Lionel Martellini,I. W. Martin,R. M. Martin,Denis Martynov,J. N. Marx,K. Mason,A. Masserot,T. J. Massinger,M. Masso-Reid,Fabrice Matichard,L. Matone,Nergis Mavalvala,N. Mazumder,G. Mazzolo,Robert J. McCarthy,David E. McClelland,S. McCormick,S. C. McGuire,G. McIntyre,J. McIver,D. J. McManus,Sean T. McWilliams,Duncan Meacher,G. D. Meadors,J. Meidam,Andrew Melatos,G. Mendell,D. Mendoza-Gandara,R. A. Mercer,E. L. Merilh,M. Merzougui,S. Meshkov,C. Messenger,Cody Messick,P. M. Meyers,F. Mezzani,Haixing Miao,C. Michel,H. Middleton,Eugeniy E. Mikhailov,Leopoldo Milano,Jon M. Miller,Margaret Millhouse,Y. Minenkov,J. Ming,S. Mirshekari,Chandra Kant Mishra,S. Mitra,V. P. Mitrofanov,Guenakh Mitselmakher,R. Mittleman,A. Moggi,M. Mohan,Satya Mohapatra,M. Montani,Blake Moore,Christopher J. Moore,D. Moraru,G. Moreno,S. R. Morriss,Kasem Mossavi,B. Mours,C. M. Mow-Lowry,C. L. Mueller,Guido Mueller,A. W. Muir,Anindya Mukherjee,Debnandini Mukherjee,Soma Mukherjee,N. Mukund,A. Mullavey,Jesper Munch,David Murphy,P. G. Murray,A. Mytidis,I. Nardecchia,L. Naticchioni,R. K. Nayak,V. Necula,K. Nedkova,Gijs Nelemans,M. Neri,A. Neunzert,G. P. Newton,T. T. Nguyen,Alex B. Nielsen,Samaya Nissanke,A. Nitz,F. Nocera,D. Nolting,M. E. N. Normandin,L. K. Nuttall,J. Oberling,Evan Ochsner,J. O'Dell,Eric Oelker,G. H. Ogin,John J. Oh,Seog Oh,F. Ohme,M. Oliver,P. Oppermann,Richard J. Oram,B. O'Reilly,Richard O'Shaughnessy,David J. Ottaway,R. S. Ottens,H. Overmier,Benjamin J. Owen,Archana Pai,S. A. Pai,J. R. Palamos,O. V. Palashov,Nipuni Palliyaguru,C. Palomba,A. Pal-Singh,Howard Pan,C. Pankow,Francesco Pannarale,B. C. Pant,F. Paoletti,A. Paoli,Maria Alessandra Papa,Maria Alessandra Papa,H. R. Paris,William Parker,D. Pascucci,A. Pasqualetti,R. Passaquieti,D. Passuello,B. Patricelli,Z. Patrick,B. L. Pearlstone,M. Pedraza,R. Pedurand,Larne Pekowsky,A. Pele,S. Penn,A. Perreca,M. Phelps,O. J. Piccinni,M. Pichot,F. Piergiovanni,Vincenzo Pierro,G. Pillant,L. Pinard,Innocenzo M. Pinto,Matthew Pitkin,Rosa Poggiani,P. Popolizio,A. Post,Jade Powell,J. Prasad,V. Predoi,S. S. Premachandra,T. Prestegard,Larry R. Price,M. Prijatelj,Maria Ilaria Del Principe,S. Privitera,G. A. Prodi,L. Prokhorov,O. Puncken,M. Punturo,P. Puppo,M. Pürrer,H. Qi,Jiayi Qin,V. Quetschke,E. A. Quintero,R. Quitzow-James,F. J. Raab,D. S. Rabeling,H. Radkins,P. Raffai,S. Raja,M. Rakhmanov,P. Rapagnani,Vivien Raymond,M. Razzano,V. Re,J. F. Read,C. M. Reed,T. Regimbau,L. Rei,Stuart Reid,David H. Reitze,David H. Reitze,H. Rew,Steven Reyes,F. Ricci,K. Riles,N. A. Robertson,N. A. Robertson,R. Robie,F. Robinet,A. Rocchi,L. Rolland,J. G. Rollins,V. J. Roma,Rocco Romano,Gleb Romanov,J. H. Romie,D. Rosińska,D. Rosińska,Sheila Rowan,A. Rüdiger,P. Ruggi,Kevin M. Ryan,Surabhi Sachdev,T. Sadecki,Laleh Sadeghian,L. Salconi,M. Saleem,Francesco Salemi,A. Samajdar,L. Sammut,L. Sammut,E. J. Sanchez,V. Sandberg,B. Sandeen,J. R. Sanders,J. R. Sanders,B. Sassolas,Bangalore Suryanarayana Sathyaprakash,Peter R. Saulson,O. E. S. Sauter,R. L. Savage,A. Sawadsky,P. Schale,Roland Schilling,J. Schmidt,Patricia Schmidt,Roman Schnabel,R. M. S. Schofield,A. Schönbeck,E. Schreiber,D. Schuette,D. Schuette,Bernard F. Schutz,Bernard F. Schutz,Jennifer Scott,Susan M. Scott,D. Sellers,D. Sentenac,V. Sequino,A. M. Sergeev,G. Serna,Y. Setyawati,A. Sevigny,Daniel A. Shaddock,Sweta Shah,M. S. Shahriar,M. Shaltev,Z. Shao,B. Shapiro,P. Shawhan,A. Sheperd,D. H. Shoemaker,D. M. Shoemaker,K. Siellez,Xavier Siemens,D. Sigg,A. D. Silva,D. Simakov,A. Singer,Aviral Singh,Robinjeet Singh,A. Singhal,A. M. Sintes,B. J. J. Slagmolen,J. R. Smith,Nicholas Smith,Rory Smith,Edwin J. Son,B. Sorazu,Fiodor Sorrentino,Tarun Souradeep,A. K. Srivastava,A. Staley,M. Steinke,Jessica Steinlechner,Sebastian Steinlechner,D. Steinmeyer,D. Steinmeyer,B. C. Stephens,Robert Stone,Kenneth A. Strain,N. Straniero,G. Stratta,N. A. Strauss,S. E. Strigin,Riccardo Sturani,A. L. Stuver,T. Z. Summerscales,L. Sun,Patrick J. Sutton,B. L. Swinkels,Marek Szczepanczyk,M. Tacca,D. Talukder,David B. Tanner,Márton Tápai,S. P. Tarabrin,Andrea Taracchini,R. Taylor,T. Theeg,M. P. Thirugnanasambandam,E. G. Thomas,Michael Thomas,P. Thomas,K. A. Thorne,Kip S. Thorne,Eric Thrane,S. N. Tiwari,V. Tiwari,K. V. Tokmakov,C. Tomlinson,M. Tonelli,C. V. Torres,C. I. Torrie,D. Töyrä,F. Travasso,G. Traylor,Daniele Trifirò,M. C. Tringali,L. Trozzo,M. Tse,M. Turconi,D. Tuyenbayev,D. Ugolini,C. S. Unnikrishnan,A. L. Urban,S. A. Usman,H. Vahlbruch,G. Vajente,G. Valdes,N. van Bakel,M. van Beuzekom,J. F. J. van den Brand,C. Van Den Broeck,D. C. Vander-Hyde,D. C. Vander-Hyde,L. van der Schaaf,J. V. van Heijningen,A. A. van Veggel,M. Vardaro,S. Vass,M. Vasúth,Ruslan Vaulin,Alberto Vecchio,G. Vedovato,John Veitch,P. J. Veitch,K. Venkateswara,D. Verkindt,F. Vetrano,A. Viceré,Serena Vinciguerra,D. J. Vine,J-Y. Vinet,Salvatore Vitale,T. Vo,H. Vocca,C. Vorvick,D. V. Voss,W. D. Vousden,Sergey P. Vyatchanin,A. R. Wade,L. E. Wade,Madeline Wade,Michelle E. Walker,L. Wallace,S. Walsh,S. Walsh,G. Wang,Hua Wang,Meng Wang,Xiangyu Wang,Y. Wang,R. L. Ward,J. Warner,M. Was,B. A. Weaver,L.-W. Wei,M. Weinert,A. J. Weinstein,Rainer Weiss,Timothy A Welborn,Linqing Wen,P. Weßels,Tobias Westphal,K. Wette,James Whelan,James Whelan,D. J. White,B. F. Whiting,Roy Williams,A. R. Williamson,J. L. Willis,Benno Willke,Benno Willke,M. H. Wimmer,M. H. Wimmer,Walter Winkler,C. C. Wipf,H. Wittel,H. Wittel,Graham Woan,J. Worden,J. L. Wright,G. Wu,Joshua Yablon,William Yam,H. Yamamoto,C. C. Yancey,M. J. Yap,Hang Yu,M. Yvert,A. K. Zadrożny,L. Zangrando,Michele Zanolin,J. P. Zendri,M. Zevin,Fan Zhang,Lei Zhang,Mi Zhang,Yanxi Zhang,C. Zhao,Minchuan Zhou,Zifan Zhou,Xing-Jiang Zhu,M. E. Zucker,M. E. Zucker,S. E. Zuraw,J. Zweizig,James R. Allison,Keith W. Bannister,Martin Bell,Shami Chatterjee,Aaron Chippendale,Philip G. Edwards,Lisa Harvey-Smith,Ian Heywood,Ian Heywood,Aidan Hotan,Balthasar T. Indermuehle,J. Marvil,David McConnell,Tara Murphy,Attila Popping,John Reynolds,Robert J. Sault,Robert J. Sault,Maxim Voronkov,Matthew Whiting,A. J. Castro-Tirado,A. J. Castro-Tirado,Ronan Cunniffe,Martin Jelínek,J. C. Tello,S. R. Oates,Y. D. Hu,Petr Kubánek,Sergei Guziy,A. Castellon,Alfonso García-Cerezo,Victor F. Muñoz,C. Perez del Pulgar,S. Castillo-Carrión,J. M. Castro Cerón,René Hudec,René Hudec,M. D. Caballero-Garcia,Petr Páta,Stanislav Vítek,José Antonio Adame,S. Konig,F. Rendón,F. Rendón,T. de J. Mateo Sanguino,Rafael Fernández-Muñoz,P. C. M. Yock,Nicholas J. Rattenbury,William H. Allen,Richard Querel,S. Jeong,S. Jeong,Inkyu Park,J. Bai,Ch. Cui,Y. Fan,C. Wang,David Hiriart,William H. Lee,A. Claret,R. Sanchez-Ramirez,S. B. Pandey,T. Mediavilla,L. Sabau-Graziati,T. M. C. Abbott,F. B. Abdalla,F. B. Abdalla,S. Allam,J. Annis,Robert Armstrong,A. Benoit-Lévy,A. Benoit-Lévy,A. Benoit-Lévy,Edo Berger,R. A. Bernstein,E. Bertin,E. Bertin,D. Brout,E. Buckley-Geer,D. L. Burke,Diego Capozzi,J. Carretero,Francisco J. Castander,Ryan Chornock,Philip S. Cowperthwaite,Martin Crocce,Carlos E. Cunha,C. B. D'Andrea,C. B. D'Andrea,L. N. da Costa,Shantanu Desai,H. T. Diehl,J. P. Dietrich,Zoheyr Doctor,Alex Drlica-Wagner,Maria R. Drout,Tim Eifler,Tim Eifler,Juan Estrada,August E. Evrard,Enrique J. Fernández,D. A. Finley,B. Flaugher,Ryan J. Foley,Wen-fai Fong,Pablo Fosalba,D. B. Fox,Joshua A. Frieman,Joshua A. Frieman,Chris L. Fryer,Enrique Gaztanaga,D. W. Gerdes,Daniel A. Goldstein,Daniel A. Goldstein,Daniel Gruen,Robert A. Gruendl,G. Gutierrez,K. Herner,K. Honscheid,David J. James,M. D. Johnson,M. W. G. Johnson,I. Karliner,Daniel Kasen,Daniel Kasen,Steve Kent,Richard Kessler,A. G. Kim,Matias Carrasco Kind,Kyler Kuehn,N. Kuropatkin,Ofer Lahav,T. S. Li,Marcos Lima,Han Lin,M. A. G. Maia,Raffaella Margutti,John Marriner,Paul Martini,Thomas Matheson,Peter Melchior,Brian D. Metzger,Christopher J. Miller,Ramon Miquel,Eric H. Neilsen,Robert C. Nichol,Brian Nord,Peter Nugent,R. L. C. Ogando,Don Petravick,A. A. Plazas,Eliot Quataert,Natalie A. Roe,A. K. Romer,A. Roodman,A. C. Rosell,Eli S. Rykoff,M. Sako,E. J. Sanchez,V. Scarpine,R. H. Schindler,Michael Schubnell,Daniel Scolnic,I. Sevilla-Noarbe,Erin Sheldon,Nathan Smith,R. C. Smith,Marcelle Soares-Santos,Flavia Sobreira,Albert Stebbins,E. Suchyta,M. E. C. Swanson,Gregory Tarle,J. J. Thaler,Daniel Thomas,R. C. Thomas,Douglas L. Tucker,Vinu Vikram,Alistair R. Walker,Risa H. Wechsler,W. C. Wester,Brian Yanny,Joe Zuntz,Valerie Connaughton,Eric Burns,Adam Goldstein,Michael S. Briggs,Bin-Bin Zhang,Bin-Bin Zhang,C. M. Hui,P. A. Jenke,Colleen A. Wilson-Hodge,P. N. Bhat,Elisabetta Bissaldi,W. H. Cleveland,G. Fitzpatrick,Misty Giles,Melissa Gibby,Jochen Greiner,A. von Kienlin,R. M. Kippen,Sheila McBreen,Bagrat Mailyan,Charles A. Meegan,William S. Paciesas,Robert D. Preece,Oliver J. Roberts,Linda S. Sparke,M. Stanbro,K. Toelge,Péter Veres,Haocun Yu,Lindy Blackburn,Markus Ackermann,Marco Ajello,Andrea Albert,Brandon Anderson,W. B. Atwood,Magnus Axelsson,Magnus Axelsson,Luca Baldini,Luca Baldini,Guido Barbiellini,Denis Bastieri,R. Bellazzini,Roger Blandford,Elliott D. Bloom,R. Bonino,Eugenio Bottacini,T. J. Brandt,P. Bruel,Sara Buson,Sara Buson,G. A. Caliandro,R. A. Cameron,M. Caragiulo,P. A. Caraveo,E. Cavazzuti,E. Charles,A. Chekhtman,James Chiang,G. Chiaro,S. Ciprini,Johann Cohen-Tanugi,L. R. Cominsky,F. Costanza,Alessandro Cuoco,Filippo D'Ammando,F. de Palma,R. Desiante,Seth Digel,N. Di Lalla,M. Di Mauro,L. Di Venere,Aaron Dominguez,Persis S. Drell,Richard Dubois,C. Favuzzi,Elizabeth C. Ferrara,A. Franckowiak,Yasushi Fukazawa,Seb. Funk,P. Fusco,F. Gargano,Dario Gasparrini,Nicola Giglietto,P. Giommi,F. Giordano,Marcello Giroletti,T. Glanzman,G.L. Godfrey,G. A. Gomez-Vargas,David H. Green,David H. Green,I. A. Grenier,J. E. Grove,Sylvain Guiriec,D. Hadasch,Alice K. Harding,E. Hays,John W. Hewitt,A. B. Hill,A. B. Hill,D. Horan,T. Jogler,Gudlaugur Johannesson,A. S. Johnson,S. Kensei,Daniel Kocevski,M. Kuss,G. La Mura,G. La Mura,Stefan Larsson,Luca Latronico,Jui-Lin Li,Liang Li,Francesco Longo,F. Loparco,M. N. Lovellette,P. Lubrano,J. D. Magill,S. Maldera,Alberto Manfreda,M. Marelli,M. Mayer,M. N. Mazziotta,Julie McEnery,Julie McEnery,Manuel Meyer,P. F. Michelson,Nestor Mirabal,Tsunefumi Mizuno,A. A. Moiseev,A. A. Moiseev,M. E. Monzani,E. Moretti,A. Morselli,Igor V. Moskalenko,Matteo Negro,E. Nuss,T. Ohsugi,Nicola Omodei,M. Orienti,E. Orlando,J. F. Ormes,David Paneque,David Paneque,J. S. Perkins,Melissa Pesce-Rollins,F. Piron,G. Pivato,T. A. Porter,Judith Racusin,S. Rainò,Riccardo Rando,Soebur Razzaque,A. Reimer,A. Reimer,Olaf Reimer,Olaf Reimer,D. Salvetti,P. M. Saz Parkinson,P. M. Saz Parkinson,Carmelo Sgrò,D. Simone,E. J. Siskind,F. Spada,Gloria Spandre,P. Spinelli,D. J. Suson,H. Tajima,H. Tajima,J. B. Thayer,D. J. Thompson,L. Tibaldo,Diego F. Torres,Eleonora Troja,Eleonora Troja,Yasunobu Uchiyama,Tonia M. Venters,Giacomo Vianello,K. S. Wood,Matthew Wood,Sylvia J. Zhu,Stephan Zimmer,Enzo Brocato,Enrico Cappellaro,Stefano Covino,A. Grado,Luciano Nicastro,Eliana Palazzi,Elena Pian,Lorenzo Amati,Louis Antonelli,Massimo Capaccioli,P. D'Avanzo,Valerio D'Elia,Fedor Getman,G. Giuffrida,G. Iannicola,Luca Limatola,M. Lisi,S. Marinoni,P. M. Marrese,A. Melandri,S. Piranomonte,A. Possenti,L. Pulone,Andrea Rossi,Antonio Stamerra,Luigi Stella,Vincenzo Testa,L. Tomasella,Sheng Yang,A. Bazzano,Enrico Bozzo,Søren Brandt,T. J. L. Courvoisier,Carlo Ferrigno,Lorraine Hanlon,E. Kuulkers,P. Laurent,Sandro Mereghetti,Jean-Pierre Roques,V. Savchenko,P. Ubertini,Mansi M. Kasliwal,Leo Singer,Y. Cao,G. Duggan,Shrinivas R. Kulkarni,Varun Bhalerao,Adam A. Miller,Tom A. Barlow,Eric C. Bellm,Ilan Manulis,Javed Rana,R. R. Laher,Frank J. Masci,Jason Surace,Umaa Rebbapragada,A. Van Sistine,Branimir Sesar,Daniel A. Perley,R. Ferreti,T. A. Prince,R. Kendrick,Assaf Horesh,Kevin Hurley,S. Golenetskii,R. Aptekar,D. Frederiks,Dmitry S. Svinkin,Arne Rau,Xiao-Ling Zhang,David M. Smith,T. L. Cline,H. A. Krimm,H. A. Krimm,Fumio Abe,Mamoru Doi,Kenta Fujisawa,Koji S. Kawabata,Tomoki Morokuma,Kentaro Motohara,Masaomi Tanaka,Kouji Ohta,K. Yanagisawa,Michitoshi Yoshida,C. Baltay,David Rabinowitz,Nancy Ellman,S. Rostami,D. Bersier,M. F. Bode,Chris A. Collins,Chris M. Copperwheat,M. J. Darnley,Duncan K. Galloway,Andreja Gomboc,Andreja Gomboc,Shiho Kobayashi,Paolo A. Mazzali,Carole Mundell,A. S. Piascik,Don Pollacco,Iain A. Steele,Krzysztof Ulaczyk,J. W. Broderick,Rob Fender,Peter G. Jonker,Peter G. Jonker,Antonia Rowlinson,Antonia Rowlinson,Ben Stappers,Ralph A. M. J. Wijers,V. M. Lipunov,E. S. Gorbovskoy,N. V. Tyurina,V. G. Kornilov,P. Balanutsa,A. Kuznetsov,David A. H. Buckley,Rafael Rebolo,Miquel Serra-Ricart,G. Israelian,N. M. Budnev,O. A. Gress,K. Ivanov,V. Poleshuk,A. G. Tlatov,V. Yurkov,Nobuyuki Kawai,Motoko Serino,Hitoshi Negoro,Satoshi Nakahira,T. Mihara,H. Tomida,S. Ueno,Hiroshi Tsunemi,M. Matsuoka,Steve Croft,Lu Feng,Thomas M. O. Franzen,Bryan Gaensler,Bryan Gaensler,Melanie Johnston-Hollitt,David L. Kaplan,Miguel F. Morales,Steven Tingay,Randall B. Wayth,Andrew Williams,Stephen J. Smartt,K. C. Chambers,Kirsty Smith,M. E. Huber,David Young,Darryl Wright,A. S. B. Schultz,Larry Denneau,H. Flewelling,Eugene A. Magnier,N. Primak,Armin Rest,A. Sherstyuk,B. Stalder,Christopher W. Stubbs,John L. Tonry,Christopher Waters,Mark Willman,E. F. Olivares,E. F. Olivares,Heather Campbell,Rubina Kotak,Jesper Sollerman,Mathew Smith,Michel Dennefeld,Joseph P. Anderson,M. T. Botticella,Ting-Wan Chen,M. D. Valle,Nancy Elias-Rosa,Morgan Fraser,Cosimo Inserra,Erkki Kankare,Thomas Kupfer,Jussi Harmanen,Lluís Galbany,Lluís Galbany,L. Le Guillou,J. D. Lyman,Kate Maguire,Ayan Mitra,Matt Nicholl,A. Razza,A. Razza,Giacomo Terreran,Stefano Valenti,Stefano Valenti,Avishay Gal-Yam,A. Cwiek,M. Cwiok,Lech Mankiewicz,R. Opiela,M. Zaremba,Aleksander Filip Żarnecki,Christopher A. Onken,Richard Scalzo,Brian P. Schmidt,Christian Wolf,Fang Yuan,Phil Evans,J. A. Kennea,David N. Burrows,Sergio Campana,S. B. Cenko,S. B. Cenko,F. E. Marshall,J. A. Nousek,P. T. O'Brien,J. P. Osborne,David Palmer,M. Perri,M. H. Siegel,Gianpiero Tagliaferri,Alain Klotz,D. Turpin,R. Laugier,M. Beroiz,M. Beroiz,T. Peñuela,T. Peñuela,Lucas M. Macri,R. J. Oelkers,Diego G. Lambas,R. Vrech,Juan B. Cabral,C. Colazo,Mariano Dominguez,Bruno Sanchez,Sebastián Gurovich,Marcelo Lares,Jennifer L. Marshall,Darren L. DePoy,Nelson Padilla,Nicolas A. Pereyra,Matthew Benacquista,Nial R. Tanvir,Klaas Wiersema,Andrew J. Levan,Danny Steeghs,Jens Hjorth,Johan P. U. Fynbo,D. Malesani,Bo Milvang-Jensen,Darach Watson,M. Irwin,C. G. Fernandez,Richard G. McMahon,Manda Banerji,Eduardo Gonzalez-Solares,Steve Schulze,Steve Schulze,A. de Ugarte Postigo,A. de Ugarte Postigo,C. C. Thoene,Zach Cano,Stephan Rosswog +1622 more
TL;DR: In this article, the sky localization of the first observed compact binary merger is presented, where the authors describe the low-latency analysis of the LIGO data and present a sky localization map.
Journal ArticleDOI
Black Hole Growth to z = 2 - I: Improved Virial Methods for Measuring M_BH and L/L_Edd
Benny Trakhtenbrot,Hagai Netzer +1 more
TL;DR: In this article, the authors analyzed several large samples of AGN in order to establish the best tools required to study the evolution of black hole mass (M_BH) and normalized accretion rate (L/L_Edd).
Journal ArticleDOI
A Study of the Afterglows of Four Gamma-Ray Bursts: Constraining the Explosion and Fireball Model
TL;DR: In this paper, the authors employ a fireball model of the gamma-ray burst (GRB) explosion to constrain intrinsic and environmental parameters of four events with good broadband afterglow data.
Related Papers (5)
Maps of Dust Infrared Emission for Use in Estimation of Reddening and Cosmic Microwave Background Radiation Foregrounds
The relationship between infrared, optical, and ultraviolet extinction
The Sloan Digital Sky Survey: Technical summary
Donald G. York,Jennifer Adelman,John E. Anderson,Scott F. Anderson,James Annis,Neta A. Bahcall,J. A. Bakken,Robert H. Barkhouser,Steven Bastian,E. Berman,William N. Boroski,Steve Bracker,Charlie Briegel,John W. Briggs,Jon Brinkmann,Robert J. Brunner,Scott Burles,Larry N. Carey,Michael A. Carr,Francisco J. Castander,Francisco J. Castander,Bing Chen,Patrick L. Colestock,Andrew J. Connolly,James H. Crocker,István Csabai,István Csabai,Paul C. Czarapata,John Eric Davis,Mamoru Doi,Tom Dombeck,Daniel J. Eisenstein,Nancy Ellman,Brian R. Elms,Brian R. Elms,Michael L. Evans,Xiaohui Fan,Glenn R. Federwitz,Larry Fiscelli,Scott D. Friedman,Joshua A. Frieman,Joshua A. Frieman,Masataka Fukugita,Bruce Gillespie,James E. Gunn,Vijay K. Gurbani,Ernst De Haas,M. Haldeman,Frederick H. Harris,Jeffrey J. E. Hayes,Timothy M. Heckman,Gregory S. Hennessy,Robert B. Hindsley,S. Holm,Donald J. Holmgren,Chi Hao Huang,Charles L. Hull,Don Husby,Shin-Ichi Ichikawa,Takashi Ichikawa,Zěljko Ivezić,Stephen M. Kent,Rita S. J. Kim,E. Kinney,Mark A. Klaene,A. N. Kleinman,Scot Kleinman,Gillian R. Knapp,John Korienek,Richard G. Kron,Richard G. Kron,Peter Z. Kunszt,D. Q. Lamb,Brian C. Lee,R. French Leger,Siriluk Limmongkol,Carl Lindenmeyer,Dan Long,Craig Loomis,Jon Loveday,Rich Lucinio,Robert H. Lupton,Bryan Mackinnon,Bryan Mackinnon,Edward J. Mannery,Paul M. Mantsch,Bruce Margon,Peregrine M. McGehee,Timothy A. McKay,Avery Meiksin,Aronne Merelli,David G. Monet,Jeffrey A. Munn,Vijay K. Narayanan,Thomas Nash,Eric H. Neilsen,Rich Neswold,Heidi Jo Newberg,Heidi Jo Newberg,Robert C. Nichol,T. Nicinski,T. Nicinski,Mario Nonino,Norio Okada,Sadanori Okamura,Jeremiah P. Ostriker,Russell Owen,A. George Pauls,John Peoples,R. Peterson,Don Petravick,Jeffrey R. Pier,Adrian Pope,Ruth Pordes,Angela Prosapio,R. Rechenmacher,Thomas R. Quinn,Gordon T. Richards,Michael Richmond,Claudio H. Rivetta,Constance M. Rockosi,Kurt Ruthmansdorfer,Dale Sandford,David J. Schlegel,Donald P. Schneider,Maki Sekiguchi,G. Sergey,Kazuhiro Shimasaku,Walter A. Siegmund,Stephen A. Smee,J. Allyn Smith,S. A. Snedden,Robert Stone,Chris Stoughton,Michael A. Strauss,Christopher W. Stubbs,Mark SubbaRao,Alexander S. Szalay,István Szapudi,Gyula P. Szokoly,Anirudda R. Thakar,Christy Tremonti,Douglas L. Tucker,Alan Uomoto,Daniel E. Vanden Berk,Michael S. Vogeley,Patrick Waddell,Shu I. Wang,Masaru Watanabe,David H. Weinberg,Brian Yanny,Naoki Yasuda +151 more
The Two Micron All Sky Survey (2MASS)
Michael F. Skrutskie,Michael F. Skrutskie,Roc M. Cutri,R. Stiening,Martin D. Weinberg,Stephen E. Schneider,John M. Carpenter,Chas Beichman,R. Capps,T. Chester,J. Elias,John P. Huchra,James Liebert,C. Lonsdale,David G. Monet,Stephan D. Price,Patrick Seitzer,Thomas H. Jarrett,J. D. Kirkpatrick,John E. Gizis,E. Howard,T. Evans,John W. Fowler,L. Fullmer,Robert L. Hurt,R. M. Light,E. L. Kopan,K. A. Marsh,H. McCallon,R. Tam,S. D. Van Dyk,S. Wheelock +31 more