Maps of Dust IR Emission for Use in Estimation of Reddening and CMBR Foregrounds
Reads0
Chats0
TLDR
In this paper, the authors presented a reprocessed composite of the COBE/DIRBE and IRAS/ISSA maps, with the zodiacal foreground and confirmed point sources removed.Abstract:
We present a full sky 100 micron map that is a reprocessed composite of the COBE/DIRBE and IRAS/ISSA maps, with the zodiacal foreground and confirmed point sources removed. Before using the ISSA maps, we remove the remaining artifacts from the IRAS scan pattern. Using the DIRBE 100 micron and 240 micron data, we have constructed a map of the dust temperature, so that the 100 micron map can be converted to a map proportional to dust column density. The result of these manipulations is a map with DIRBE-quality calibration and IRAS resolution.
To generate the full sky dust maps, we must first remove zodiacal light contamination as well as a possible cosmic infrared background (CIB). This is done via a regression analysis of the 100 micron DIRBE map against the Leiden- Dwingeloo map of H_I emission, with corrections for the zodiacal light via a suitable expansion of the DIRBE 25 micron flux. For the 100 micron map, no significant CIB is detected. In the 140 micron and 240 micron maps, where the zodiacal contamination is weaker, we detect the CIB at surprisingly high flux levels of 32 \pm 13 nW/m^2/sr at 140 micron, and 17 \pm 4 nW/m^2/sr at 240 micron (95% confidence). This integrated flux is ~2 times that extrapolated from optical galaxies in the Hubble Deep Field.
The primary use of these maps is likely to be as a new estimator of Galactic extinction. We demonstrate that the new maps are twice as accurate as the older Burstein-Heiles estimates in regions of low and moderate reddening. These dust maps will also be useful for estimating millimeter emission that contaminates CMBR experiments and for estimating soft X-ray absorption.read more
Figures
![FIG. 1.ÈThe 100 kmÈH I correlation with (a) no correction, (b) linear correction, and (c) quadratic correction for zodiacal contamination. The Ðts in the range [0, 200] K km s~1 are shown as solid lines.](/figures/fig-1-ethe-100-kmeh-i-correlation-with-a-no-correction-b-j2j6qo00.png)
FIG. 1.ÈThe 100 kmÈH I correlation with (a) no correction, (b) linear correction, and (c) quadratic correction for zodiacal contamination. The Ðts in the range [0, 200] K km s~1 are shown as solid lines. 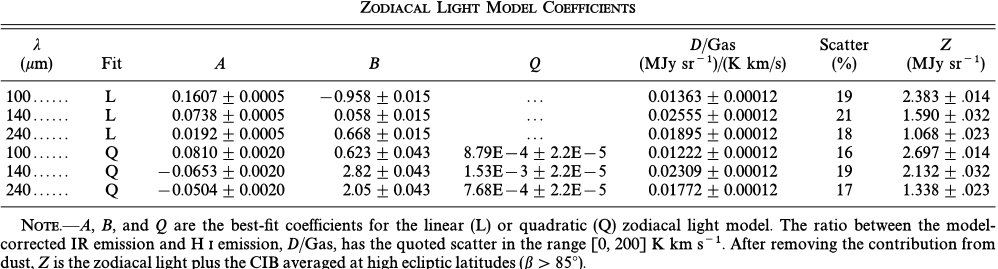
TABLE 2 
FIG. 13.ÈColor-color diagram for PSC sources. The diagonal line efficiently discriminates between galaxies (above the line) and stars (below the line). The square box is a strict color cut that retains 70% of stars. For clarity, only 1/10 of the stars are plotted. 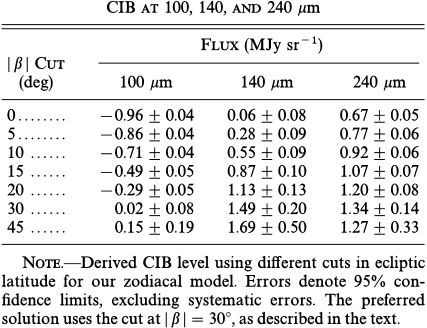
TABLE 3 ![FIG. 7.ÈSlice of sky from (a) the BH map, (b) the Leiden-Dwingeloo H I map, (c) our dust map with DIRBE resolution, and (d) our dust map with IRAS resolution. The slice measures approximately 90¡ ] 30¡, centered at l \ 100¡, b \ ]35¡.](/figures/fig-7-eslice-of-sky-from-a-the-bh-map-b-the-leiden-dwingeloo-1rzt4l41.png)
FIG. 7.ÈSlice of sky from (a) the BH map, (b) the Leiden-Dwingeloo H I map, (c) our dust map with DIRBE resolution, and (d) our dust map with IRAS resolution. The slice measures approximately 90¡ ] 30¡, centered at l \ 100¡, b \ ]35¡. 
FIG. 2.ÈRatio of recovered vs. true column density of dust using a single-temperature Ðt to two components. A fraction of dust at tem-f Bperature is added to 18 K dust. The recovered column density is alwaysT Blower than the true column density, with contours spaced in units of 0.1.
Citations
More filters
Journal ArticleDOI
Co-formation of the disc and the stellar halo
Belokurov,Belokurov,Denis Erkal,Denis Erkal,Nick Evans,Sergey E. Koposov,Sergey E. Koposov,Alis J. Deason +7 more
TL;DR: In this article, a large sample of Main Sequence stars with 7-D measurements supplied by Gaia and SDSS was used to study the kinematic properties of the local stellar stellar halo.
Journal ArticleDOI
The SDSS-IV extended baryon oscillation spectroscopic survey: Overview and early data
Kyle S. Dawson,Jean-Paul Kneib,Will J. Percival,Shadab Alam,Franco D. Albareti,Scott F. Anderson,Eric Armengaud,Éric Aubourg,Stephen Bailey,Julian E. Bautista,Andreas A. Berlind,Matthew A. Bershady,Florian Beutler,Dmitry Bizyaev,Dmitry Bizyaev,Michael R. Blanton,Michael Blomqvist,Adam S. Bolton,Jo Bovy,W. N. Brandt,Jon Brinkmann,Joel R. Brownstein,Etienne Burtin,Nicolás G. Busca,Zheng Cai,Chia-Hsun Chuang,Nicolas Clerc,Johan Comparat,Frances Cope,Rupert A. C. Croft,Irene Cruz-González,Luiz N. da Costa,M. C. Cousinou,Jeremy Darling,Axel de la Macorra,Sylvain de la Torre,Timothée Delubac,Hélion du Mas des Bourboux,Tom Dwelly,Anne Ealet,Daniel J. Eisenstein,Michael Eracleous,Stephanie Escoffier,Xiaohui Fan,Alexis Finoguenov,Andreu Font-Ribera,Peter M. Frinchaboy,Patrick Gaulme,Antonis Georgakakis,Paul J. Green,Hong Guo,Hong Guo,Julien Guy,Shirley Ho,Diana Holder,Joe Huehnerhoff,Timothy A. Hutchinson,Yipeng Jing,Eric Jullo,Vikrant Kamble,Karen Kinemuchi,D. Kirkby,Francisco-Shu Kitaura,Mark A. Klaene,Russ R. Laher,Dustin Lang,Pierre Laurent,Jean Marc Le Goff,Cheng Li,Yu Liang,Marcos Lima,Qiufan Lin,Wei-Peng Lin,Wei-Peng Lin,Yen-Ting Lin,Dan Long,Britt Lundgren,Nicholas MacDonald,Marcio A. G. Maia,Elena Malanushenko,Viktor Malanushenko,Vivek Mariappan,Cameron K. McBride,Ian D. McGreer,Brice Ménard,Brice Ménard,Andrea Merloni,Andres Meza,Antonio D. Montero-Dorta,Demitri Muna,Adam D. Myers,Kirpal Nandra,Tracy Naugle,Jeffrey A. Newman,Pasquier Noterdaeme,Peter Nugent,Peter Nugent,Ricardo L. C. Ogando,Matthew D. Olmstead,Audrey Oravetz,Daniel Oravetz,Nikhil Padmanabhan,Nathalie Palanque-Delabrouille,Kaike Pan,John K. Parejko,Isabelle Pâris,John A. Peacock,Patrick Petitjean,Matthew M. Pieri,Alice Pisani,Alice Pisani,Alice Pisani,Francisco Prada,Francisco Prada,Abhishek Prakash,Anand Raichoor,Beth Reid,James Rich,J. Ridl,Sergio Rodríguez-Torres,Aurelio Carnero Rosell,Ashley J. Ross,Ashley J. Ross,Graziano Rossi,John J. Ruan,Mara Salvato,Conor Sayres,Donald P. Schneider,David J. Schlegel,Uroš Seljak,Uroš Seljak,Hee-Jong Seo,Branimir Sesar,Sarah Shandera,Yiping Shu,Anže Slosar,Flavia Sobreira,Alina Streblyanska,Alina Streblyanska,Nao Suzuki,Donna Taylor,Charling Tao,Charling Tao,Jeremy L. Tinker,Rita Tojeiro,Mariana Vargas-Magaña,Yuting Wang,Benjamin A. Weaver,David H. Weinberg,Martin White,Martin White,W. M. Wood-Vasey,Christophe Yèche,Zhongxu Zhai,Cheng Zhao,Gong-Bo Zhao,Zheng Zheng,Guangtun Zhu,Hu Zou +158 more
TL;DR: The Extended Baryon Oscillation Spectroscopic Survey (eBOSS) as mentioned in this paper uses four different tracers of the underlying matter density field to expand the volume covered by BOSS and map the large-scale structures over the relatively unconstrained redshift range 0.6 0.87.
Journal ArticleDOI
The SuperCOSMOS Sky Survey – I. Introduction and description
Nigel Hambly,H. T. MacGillivray,Mike Read,S. B. Tritton,E. B. Thomson,B. D. Kelly,D. H. Morgan,Robert E. Smith,Simon P. Driver,John Williamson,Quentin A. Parker,Michael R. S. Hawkins,Peredur M. Williams,Andy Lawrence +13 more
TL;DR: The SuperCOSMOS Sky Survey (SSSSS) as mentioned in this paper is a wide-scale survey of images collected by the International Journal of Astronomy and Geophysics.
Journal ArticleDOI
The Radius-Luminosity Relationship For Active Galactic Nuclei: The Effect of Host-Galaxy Starlight On Luminosity Measurements. II. The Full Sample of Reverberation-Mapped AGNs
Misty C. Bentz,Misty C. Bentz,Bradley M. Peterson,Hagai Netzer,Richard W. Pogge,Marianne Vestergaard +5 more
TL;DR: In this paper, the authors presented high-resolution Hubble Space Telescope images of all 35 active galactic nuclei (AGNs) with optical reverberation-mapping results, which they have modeled to create a nucleus-free image of each AGN host galaxy.
Journal ArticleDOI
The 2dF QSO Redshift Survey – XII. The spectroscopic catalogue and luminosity function
Scott M. Croom,Robert J. Smith,B. J. Boyle,Tom Shanks,Lance Miller,P. J. Outram,N. S. Loaring +6 more
TL;DR: The 2DF QSO Redshift Survey (2QZ) as discussed by the authors is the most complete QSO catalogue to date, consisting of 23 338 quasi-stellar objects, 12, 292 galactic stars and 4558 compact narrow emission-line galaxies.
Related Papers (5)
Maps of Dust Infrared Emission for Use in Estimation of Reddening and Cosmic Microwave Background Radiation Foregrounds
The relationship between infrared, optical, and ultraviolet extinction
The Sloan Digital Sky Survey: Technical summary
Donald G. York,Jennifer Adelman,John E. Anderson,Scott F. Anderson,James Annis,Neta A. Bahcall,J. A. Bakken,Robert H. Barkhouser,Steven Bastian,E. Berman,William N. Boroski,Steve Bracker,Charlie Briegel,John W. Briggs,Jon Brinkmann,Robert J. Brunner,Scott Burles,Larry N. Carey,Michael A. Carr,Francisco J. Castander,Francisco J. Castander,Bing Chen,Patrick L. Colestock,Andrew J. Connolly,James H. Crocker,István Csabai,István Csabai,Paul C. Czarapata,John Eric Davis,Mamoru Doi,Tom Dombeck,Daniel J. Eisenstein,Nancy Ellman,Brian R. Elms,Brian R. Elms,Michael L. Evans,Xiaohui Fan,Glenn R. Federwitz,Larry Fiscelli,Scott D. Friedman,Joshua A. Frieman,Joshua A. Frieman,Masataka Fukugita,Bruce Gillespie,James E. Gunn,Vijay K. Gurbani,Ernst De Haas,M. Haldeman,Frederick H. Harris,Jeffrey J. E. Hayes,Timothy M. Heckman,Gregory S. Hennessy,Robert B. Hindsley,S. Holm,Donald J. Holmgren,Chi Hao Huang,Charles L. Hull,Don Husby,Shin-Ichi Ichikawa,Takashi Ichikawa,Zěljko Ivezić,Stephen M. Kent,Rita S. J. Kim,E. Kinney,Mark A. Klaene,A. N. Kleinman,Scot Kleinman,Gillian R. Knapp,John Korienek,Richard G. Kron,Richard G. Kron,Peter Z. Kunszt,D. Q. Lamb,Brian C. Lee,R. French Leger,Siriluk Limmongkol,Carl Lindenmeyer,Dan Long,Craig Loomis,Jon Loveday,Rich Lucinio,Robert H. Lupton,Bryan Mackinnon,Bryan Mackinnon,Edward J. Mannery,Paul M. Mantsch,Bruce Margon,Peregrine M. McGehee,Timothy A. McKay,Avery Meiksin,Aronne Merelli,David G. Monet,Jeffrey A. Munn,Vijay K. Narayanan,Thomas Nash,Eric H. Neilsen,Rich Neswold,Heidi Jo Newberg,Heidi Jo Newberg,Robert C. Nichol,T. Nicinski,T. Nicinski,Mario Nonino,Norio Okada,Sadanori Okamura,Jeremiah P. Ostriker,Russell Owen,A. George Pauls,John Peoples,R. Peterson,Don Petravick,Jeffrey R. Pier,Adrian Pope,Ruth Pordes,Angela Prosapio,R. Rechenmacher,Thomas R. Quinn,Gordon T. Richards,Michael Richmond,Claudio H. Rivetta,Constance M. Rockosi,Kurt Ruthmansdorfer,Dale Sandford,David J. Schlegel,Donald P. Schneider,Maki Sekiguchi,G. Sergey,Kazuhiro Shimasaku,Walter A. Siegmund,Stephen A. Smee,J. Allyn Smith,S. A. Snedden,Robert Stone,Chris Stoughton,Michael A. Strauss,Christopher W. Stubbs,Mark SubbaRao,Alexander S. Szalay,István Szapudi,Gyula P. Szokoly,Anirudda R. Thakar,Christy Tremonti,Douglas L. Tucker,Alan Uomoto,Daniel E. Vanden Berk,Michael S. Vogeley,Patrick Waddell,Shu I. Wang,Masaru Watanabe,David H. Weinberg,Brian Yanny,Naoki Yasuda +151 more
The Two Micron All Sky Survey (2MASS)
Michael F. Skrutskie,Michael F. Skrutskie,Roc M. Cutri,R. Stiening,Martin D. Weinberg,Stephen E. Schneider,John M. Carpenter,Chas Beichman,R. Capps,T. Chester,J. Elias,John P. Huchra,James Liebert,C. Lonsdale,David G. Monet,Stephan D. Price,Patrick Seitzer,Thomas H. Jarrett,J. D. Kirkpatrick,John E. Gizis,E. Howard,T. Evans,John W. Fowler,L. Fullmer,Robert L. Hurt,R. M. Light,E. L. Kopan,K. A. Marsh,H. McCallon,R. Tam,S. D. Van Dyk,S. Wheelock +31 more