Maps of Dust IR Emission for Use in Estimation of Reddening and CMBR Foregrounds
TLDR
In this paper, the authors presented a reprocessed composite of the COBE/DIRBE and IRAS/ISSA maps, with the zodiacal foreground and confirmed point sources removed.Abstract:
We present a full sky 100 micron map that is a reprocessed composite of the COBE/DIRBE and IRAS/ISSA maps, with the zodiacal foreground and confirmed point sources removed. Before using the ISSA maps, we remove the remaining artifacts from the IRAS scan pattern. Using the DIRBE 100 micron and 240 micron data, we have constructed a map of the dust temperature, so that the 100 micron map can be converted to a map proportional to dust column density. The result of these manipulations is a map with DIRBE-quality calibration and IRAS resolution.
To generate the full sky dust maps, we must first remove zodiacal light contamination as well as a possible cosmic infrared background (CIB). This is done via a regression analysis of the 100 micron DIRBE map against the Leiden- Dwingeloo map of H_I emission, with corrections for the zodiacal light via a suitable expansion of the DIRBE 25 micron flux. For the 100 micron map, no significant CIB is detected. In the 140 micron and 240 micron maps, where the zodiacal contamination is weaker, we detect the CIB at surprisingly high flux levels of 32 \pm 13 nW/m^2/sr at 140 micron, and 17 \pm 4 nW/m^2/sr at 240 micron (95% confidence). This integrated flux is ~2 times that extrapolated from optical galaxies in the Hubble Deep Field.
The primary use of these maps is likely to be as a new estimator of Galactic extinction. We demonstrate that the new maps are twice as accurate as the older Burstein-Heiles estimates in regions of low and moderate reddening. These dust maps will also be useful for estimating millimeter emission that contaminates CMBR experiments and for estimating soft X-ray absorption.read more
Figures
![FIG. 1.ÈThe 100 kmÈH I correlation with (a) no correction, (b) linear correction, and (c) quadratic correction for zodiacal contamination. The Ðts in the range [0, 200] K km s~1 are shown as solid lines.](/figures/fig-1-ethe-100-kmeh-i-correlation-with-a-no-correction-b-j2j6qo00.png)
FIG. 1.ÈThe 100 kmÈH I correlation with (a) no correction, (b) linear correction, and (c) quadratic correction for zodiacal contamination. The Ðts in the range [0, 200] K km s~1 are shown as solid lines. 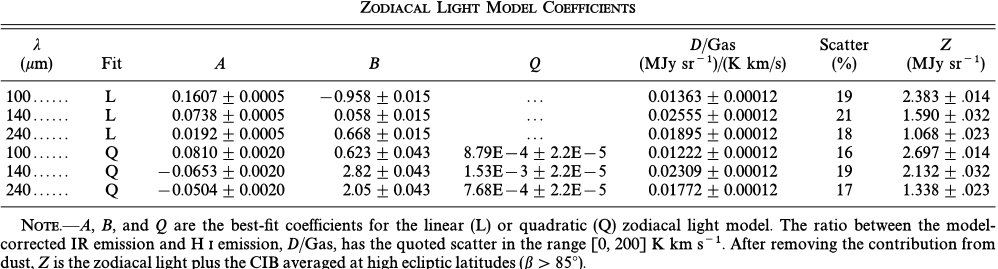
TABLE 2 
FIG. 13.ÈColor-color diagram for PSC sources. The diagonal line efficiently discriminates between galaxies (above the line) and stars (below the line). The square box is a strict color cut that retains 70% of stars. For clarity, only 1/10 of the stars are plotted. 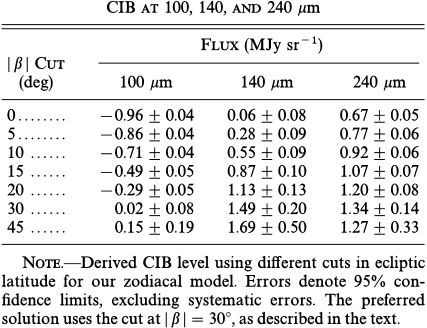
TABLE 3 ![FIG. 7.ÈSlice of sky from (a) the BH map, (b) the Leiden-Dwingeloo H I map, (c) our dust map with DIRBE resolution, and (d) our dust map with IRAS resolution. The slice measures approximately 90¡ ] 30¡, centered at l \ 100¡, b \ ]35¡.](/figures/fig-7-eslice-of-sky-from-a-the-bh-map-b-the-leiden-dwingeloo-1rzt4l41.png)
FIG. 7.ÈSlice of sky from (a) the BH map, (b) the Leiden-Dwingeloo H I map, (c) our dust map with DIRBE resolution, and (d) our dust map with IRAS resolution. The slice measures approximately 90¡ ] 30¡, centered at l \ 100¡, b \ ]35¡. 
FIG. 2.ÈRatio of recovered vs. true column density of dust using a single-temperature Ðt to two components. A fraction of dust at tem-f Bperature is added to 18 K dust. The recovered column density is alwaysT Blower than the true column density, with contours spaced in units of 0.1.
Citations
More filters
Journal ArticleDOI
The Relation Between Compact, Quiescent High Redshift Galaxies and Massive Nearby Elliptical Galaxies: Evidence for Hierarchical, Inside-Out Growth
Rachel Bezanson,Pieter G. van Dokkum,Tomer Tal,Danilo Marchesini,Mariska Kriek,Marijn Franx,Paolo De Coppi +6 more
TL;DR: In this paper, the authors compare the radial stellar density profiles and the number density of a sample of massive galaxies at z = 2.3 to nearby massive elliptical galaxies, and find that the densities measured within a constant physical radius of 1 kpc, rho(<1 kpc), are higher by a factor of 2-3 only.
Journal ArticleDOI
UBVRI Light Curves of 44 Type Ia Supernovae
Saurabh Jha,Saurabh Jha,Robert P. Kirshner,Peter Challis,Peter M. Garnavich,Thomas Matheson,Alicia M. Soderberg,Genevieve J. Graves,Malcolm Hicken,João Alves,Héctor G. Arce,Zoltan Balog,Pauline Barmby,Elizabeth J. Barton,Perry Berlind,Ann Bragg,Cesar Briceno,Warren R. Brown,J. H. Buckley,Nelson Caldwell,Michael L. Calkins,B. J. Carter,Kristi Dendy Concannon,R. Hank Donnelly,Kristoffer A. Eriksen,Daniel G. Fabricant,Emilio E. Falco,Fabrizio Fiore,Michael R. Garcia,Mercedes Gomez,Norman A. Grogin,Ted Groner,Paul J. Groot,Karl E. Haisch,Lee Hartmann,Carl Hergenrother,Matthew J. Holman,John P. Huchra,Ray Jayawardhana,D. Jerius,Sheila J. Kannappan,Dong-Woo Kim,Jan T. Kleyna,Christopher S. Kochanek,Daniel M. Koranyi,M. Krockenberger,Charles J. Lada,Kevin Luhman,Jane Luu,Lucas M. Macri,J. Mader,Andisheh Mahdavi,Massimo Marengo,Brian G. Marsden,Brian McLeod,Brian R. McNamara,S. Thomas Megeath,Dan Moraru,A. Mossman,August Muench,J. A. Muñoz,James Muzerolle,Orlando Naranjo,Kristin Nelson-Patel,Michael A. Pahre,Brian M. Patten,J. Peters,Wayne Peters,John C. Raymond,Kenneth J. Rines,Rudolph E. Schild,Gregory J. Sobczak,Timothy Spahr,John R. Stauffer,Robert P. Stefanik,Andrew Szentgyorgyi,Eric V. Tollestrup,Petri Vaisanen,Alexey Vikhlinin,Zhong Wang,S. P. Willner,Scott J. Wolk,Joseph Zajac,Ping Zhao,Krzysztof Z. Stanek +84 more
TL;DR: In this article, the authors present UBVRI photometry of 44 Type Ia supernovae (SNe Ia) observed from 1997 to 2001 as part of a continuing monitoring campaign at the Fred Lawrence Whipple Observatory of the Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics.
Journal ArticleDOI
Consistently large cosmic flows on scales of 100 h−1 Mpc: a challenge for the standard ΛCDM cosmology
TL;DR: In this paper, the authors introduce a new method of calculating bulk flow moments where velocities are weighted to give an optimal estimate of the bulk flow of an idealized survey, with the variance of the difference between the estimate and the actual flow being minimized.
Journal ArticleDOI
First data release of the Hyper Suprime-Cam Subaru Strategic Program
Hiroaki Aihara,Robert Armstrong,Steven J. Bickerton,James Bosch,Jean Coupon,Hisanori Furusawa,Yusuke Hayashi,Hiroyuki Ikeda,Yukiko Kamata,Hiroshi Karoji,Hiroshi Karoji,Satoshi Kawanomoto,Michitaro Koike,Yutaka Komiyama,Yutaka Komiyama,Dustin Lang,Robert H. Lupton,Sogo Mineo,Hironao Miyatake,Hironao Miyatake,Satoshi Miyazaki,Satoshi Miyazaki,Tomoki Morokuma,Yoshiyuki Obuchi,Yukie Oishi,Yuki Okura,Paul A. Price,Tadafumi Takata,Tadafumi Takata,Manobu Tanaka,Masayuki Tanaka,Yoko Tanaka,Tomohisa Uchida,Fumihiro Uraguchi,Yousuke Utsumi,Shiang-Yu Wang,Yoshihiko Yamada,Hitomi Yamanoi,Naoki Yasuda,Nobuo Arimoto,Nobuo Arimoto,Masashi Chiba,François Finet,Hiroki Fujimori,Seiji Fujimoto,J. Furusawa,Tomotsugu Goto,Andy D. Goulding,James E. Gunn,Yuichi Harikane,Takashi Hattori,Masao Hayashi,Krzysztof G. Hełminiak,Ryo Higuchi,Chiaki Hikage,Paul T. P. Ho,Bau-Ching Hsieh,Kuiyun Huang,Song Huang,Song Huang,Masatoshi Imanishi,Masatoshi Imanishi,Ikuru Iwata,Ikuru Iwata,Anton T. Jaelani,Hung-Yu Jian,Nobunari Kashikawa,Nobunari Kashikawa,Nobuhiko Katayama,Takashi Kojima,Akira Konno,S. Koshida,Haruka Kusakabe,Alexie Leauthaud,Chien-Hsiu Lee,Lihwai Lin,Yen-Ting Lin,Rachel Mandelbaum,Yoshiki Matsuoka,Yoshiki Matsuoka,Elinor Medezinski,Shoken Miyama,Shoken Miyama,Rieko Momose,Anupreeta More,Surhud More,Shiro Mukae,Ryoma Murata,Hitoshi Murayama,Hitoshi Murayama,Hitoshi Murayama,Tohru Nagao,Fumiaki Nakata,Mana Niida,Hiroko Niikura,Atsushi J. Nishizawa,Masamune Oguri,Nobuhiro Okabe,Yoshiaki Ono,Masato Onodera,M. Onoue,M. Onoue,Masami Ouchi,Tae-Soo Pyo,Takatoshi Shibuya,Kazuhiro Shimasaku,Melanie Simet,Joshua S. Speagle,Joshua S. Speagle,David N. Spergel,Michael A. Strauss,Yuma Sugahara,Naoshi Sugiyama,Naoshi Sugiyama,Yasushi Suto,Nao Suzuki,Philip J. Tait,Masahiro Takada,Tsuyoshi Terai,Yoshiki Toba,Edwin L. Turner,Edwin L. Turner,Hisakazu Uchiyama,Keiichi Umetsu,Yuji Urata,Tomonori Usuda,Tomonori Usuda,Sherry Yeh,Suraphong Yuma +128 more
TL;DR: This paper presents the second data release of the Hyper Suprime-Cam Subaru Strategic Program, a wide-field optical imaging survey on the 8.2 meter Subaru Telescope, including a major update to the processing pipeline, including improved sky subtraction, PSF modeling, object detection, and artifact rejection.
Journal ArticleDOI
The sloan digital sky survey data release 7 spectroscopic m dwarf catalog. i. data
Andrew A. West,Andrew A. West,Dylan P. Morgan,John J. Bochanski,John J. Bochanski,J. M. Andersen,Keaton J. Bell,Adam F. Kowalski,James R. A. Davenport,Suzanne L. Hawley,Sarah J. Schmidt,David Bernat,Eric J. Hilton,Philip S. Muirhead,Kevin R. Covey,Kevin R. Covey,Bárbara Rojas-Ayala,Everett Schlawin,Mary Gooding,Kyle Schluns,Saurav Dhital,J. Sebastian Pineda,David O. Jones +22 more
TL;DR: In this paper, a spectroscopic catalog of 70,841 visually inspected M dwarfs from the seventh data release of the Sloan Digital Sky Survey is presented, which is cross-matched to Two Micron All Sky Survey infrared data, and contains photometric distances for each star.
Related Papers (5)
Maps of Dust Infrared Emission for Use in Estimation of Reddening and Cosmic Microwave Background Radiation Foregrounds
The relationship between infrared, optical, and ultraviolet extinction
The Sloan Digital Sky Survey: Technical summary
Donald G. York,Jennifer Adelman,John E. Anderson,Scott F. Anderson,James Annis,Neta A. Bahcall,J. A. Bakken,Robert H. Barkhouser,Steven Bastian,E. Berman,William N. Boroski,Steve Bracker,Charlie Briegel,John W. Briggs,Jon Brinkmann,Robert J. Brunner,Scott Burles,Larry N. Carey,Michael A. Carr,Francisco J. Castander,Francisco J. Castander,Bing Chen,Patrick L. Colestock,Andrew J. Connolly,James H. Crocker,István Csabai,István Csabai,Paul C. Czarapata,John Eric Davis,Mamoru Doi,Tom Dombeck,Daniel J. Eisenstein,Nancy Ellman,Brian R. Elms,Brian R. Elms,Michael L. Evans,Xiaohui Fan,Glenn R. Federwitz,Larry Fiscelli,Scott D. Friedman,Joshua A. Frieman,Joshua A. Frieman,Masataka Fukugita,Bruce Gillespie,James E. Gunn,Vijay K. Gurbani,Ernst De Haas,M. Haldeman,Frederick H. Harris,Jeffrey J. E. Hayes,Timothy M. Heckman,Gregory S. Hennessy,Robert B. Hindsley,S. Holm,Donald J. Holmgren,Chi Hao Huang,Charles L. Hull,Don Husby,Shin-Ichi Ichikawa,Takashi Ichikawa,Zěljko Ivezić,Stephen M. Kent,Rita S. J. Kim,E. Kinney,Mark A. Klaene,A. N. Kleinman,Scot Kleinman,Gillian R. Knapp,John Korienek,Richard G. Kron,Richard G. Kron,Peter Z. Kunszt,D. Q. Lamb,Brian C. Lee,R. French Leger,Siriluk Limmongkol,Carl Lindenmeyer,Dan Long,Craig Loomis,Jon Loveday,Rich Lucinio,Robert H. Lupton,Bryan Mackinnon,Bryan Mackinnon,Edward J. Mannery,Paul M. Mantsch,Bruce Margon,Peregrine M. McGehee,Timothy A. McKay,Avery Meiksin,Aronne Merelli,David G. Monet,Jeffrey A. Munn,Vijay K. Narayanan,Thomas Nash,Eric H. Neilsen,Rich Neswold,Heidi Jo Newberg,Heidi Jo Newberg,Robert C. Nichol,T. Nicinski,T. Nicinski,Mario Nonino,Norio Okada,Sadanori Okamura,Jeremiah P. Ostriker,Russell Owen,A. George Pauls,John Peoples,R. Peterson,Don Petravick,Jeffrey R. Pier,Adrian Pope,Ruth Pordes,Angela Prosapio,R. Rechenmacher,Thomas R. Quinn,Gordon T. Richards,Michael Richmond,Claudio H. Rivetta,Constance M. Rockosi,Kurt Ruthmansdorfer,Dale Sandford,David J. Schlegel,Donald P. Schneider,Maki Sekiguchi,G. Sergey,Kazuhiro Shimasaku,Walter A. Siegmund,Stephen A. Smee,J. Allyn Smith,S. A. Snedden,Robert Stone,Chris Stoughton,Michael A. Strauss,Christopher W. Stubbs,Mark SubbaRao,Alexander S. Szalay,István Szapudi,Gyula P. Szokoly,Anirudda R. Thakar,Christy Tremonti,Douglas L. Tucker,Alan Uomoto,Daniel E. Vanden Berk,Michael S. Vogeley,Patrick Waddell,Shu I. Wang,Masaru Watanabe,David H. Weinberg,Brian Yanny,Naoki Yasuda +151 more
The Two Micron All Sky Survey (2MASS)
Michael F. Skrutskie,Michael F. Skrutskie,Roc M. Cutri,R. Stiening,Martin D. Weinberg,Stephen E. Schneider,John M. Carpenter,Chas Beichman,R. Capps,T. Chester,J. Elias,John P. Huchra,James Liebert,C. Lonsdale,David G. Monet,Stephan D. Price,Patrick Seitzer,Thomas H. Jarrett,J. D. Kirkpatrick,John E. Gizis,E. Howard,T. Evans,John W. Fowler,L. Fullmer,Robert L. Hurt,R. M. Light,E. L. Kopan,K. A. Marsh,H. McCallon,R. Tam,S. D. Van Dyk,S. Wheelock +31 more