Type Ia supernova discoveries at z > 1 from the Hubble Space Telescope: Evidence for past deceleration and constraints on dark energy evolution
Adam G. Riess,Louis-Gregory Strolger,John L. Tonry,Stefano Casertano,Henry C. Ferguson,Bahram Mobasher,Peter Challis,Alexei V. Filippenko,Saurabh Jha,Weidong Li,Ryan Chornock,Robert P. Kirshner,Bruno Leibundgut,Mark Dickinson,Mario Livio,Mauro Giavalisco,Charles C. Steidel,Txitxo Benítez,Zlatan Tsvetanov +18 more
TLDR
For a flat universe with a cosmological constant, the transition between the two epochs is constrained to be at z = 0.46 ± 0.13 as mentioned in this paper, and w = -1.02 ± (and w < -0.76 at the 95% confidence level) for an assumed static equation of state of dark energy.Abstract:
We have discovered 16 Type Ia supernovae (SNe Ia) with the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) and have used them to provide the first conclusive evidence for cosmic deceleration that preceded the current epoch of cosmic acceleration. These objects, discovered during the course of the GOODS ACS Treasury program, include 6 of the 7 highest redshift SNe Ia known, all at z > 1.25, and populate the Hubble diagram in unexplored territory. The luminosity distances to these objects and to 170 previously reported SNe Ia have been determined using empirical relations between light-curve shape and luminosity. A purely kinematic interpretation of the SN Ia sample provides evidence at the greater than 99% confidence level for a transition from deceleration to acceleration or, similarly, strong evidence for a cosmic jerk. Using a simple model of the expansion history, the transition between the two epochs is constrained to be at z = 0.46 ± 0.13. The data are consistent with the cosmic concordance model of ΩM ≈ 0.3, ΩΛ ≈ 0.7 (χ = 1.06) and are inconsistent with a simple model of evolution or dust as an alternative to dark energy. For a flat universe with a cosmological constant, we measure ΩM = 0.29 ± (equivalently, ΩΛ = 0.71). When combined with external flat-universe constraints, including the cosmic microwave background and large-scale structure, we find w = -1.02 ± (and w < -0.76 at the 95% confidence level) for an assumed static equation of state of dark energy, P = wρc2. Joint constraints on both the recent equation of state of dark energy, w0, and its time evolution, dw/dz, are a factor of ~8 more precise than the first estimates and twice as precise as those without the SNe Ia discovered with HST. Our constraints are consistent with the static nature of and value of w expected for a cosmological constant (i.e., w0 = -1.0, dw/dz = 0) and are inconsistent with very rapid evolution of dark energy. We address consequences of evolving dark energy for the fate of the universe.read more
Figures

TABLE 2 SN Ia Imaging 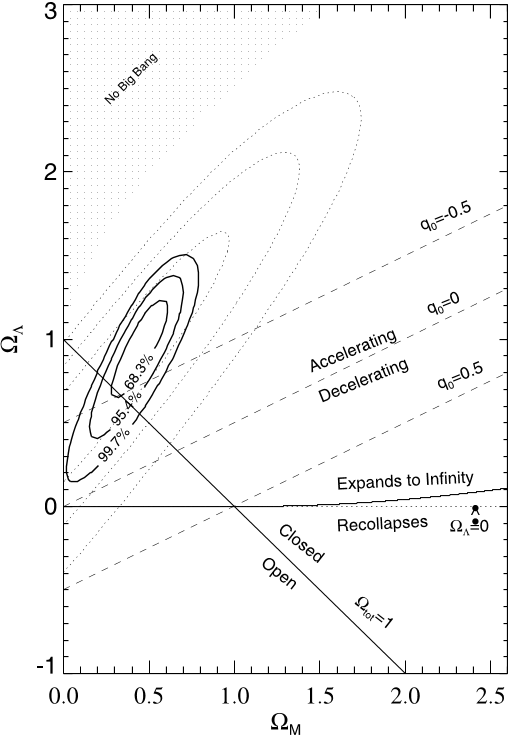
Fig. 8.—Joint confidence intervals for ( M , ) from SNe Ia. The solid contours are results from the gold sample of 157 SNe Ia presented here. The dotted contours are the results from Riess et al. (1998) illustrating the earlier evidence for > 0. Regions representing specific cosmological scenarios are illustrated. Contours are closed by their intersection with the line M ¼ 0. 
Fig. 16.—Predicted lensing magnifications of SNe Ia and of random positions in the CDF-S and HDF-N. For the SNe Ia discovered in the GOODS fields, the expected magnification was calculated using a multiple-lens plane formalism, with estimates of foreground lens redshifts and masses derived from the GOODS catalog. Expected magnifications were also calculated for 100 randomly selected positions (redshift and angular position). The solid and dotted lines show redshift bin averages and dispersion, respectively. SNe Ia found in the GOODS survey and in other HST searches are indicated. 
Fig. 15.—Comparison of individual distance differences estimated by the MLCS2k2 and BATM methods for the HST and ground-discovered SNe Ia. The zero points of both methods are normalized by using the same set of SNe Ia. 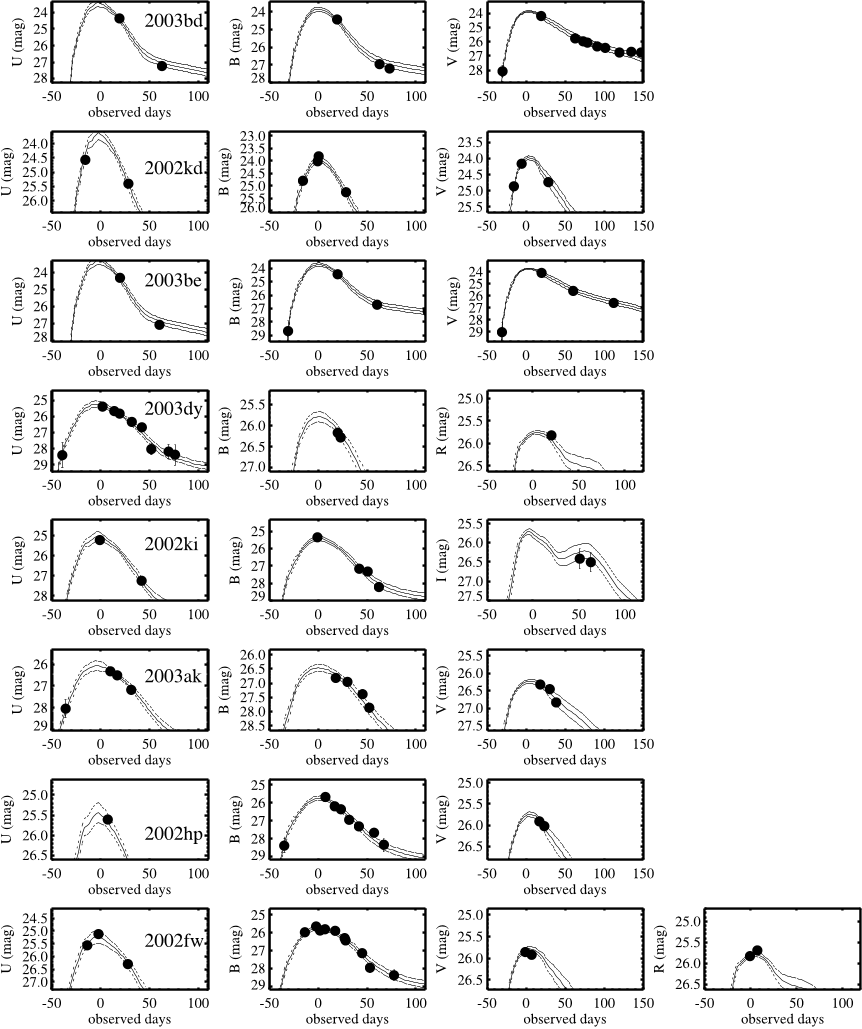
Fig. 2.—Multicolor light curves of SNe Ia. For each SN Ia, multicolor photometry transferred to rest-frame passbands is plotted. The individual, best-fit MLCS2k2 model is shown as a solid line, with a 1 model uncertainty, derived from the model covariance matrix, above and below the best fit. 
Fig. 17.—Correlation of the predicted magnification and the best-fit cosmological model residual for individual SNe Ia. The predicted magnifications are as described in Fig. 16. The residuals are the difference in distance modulus as predicted from the best-fit model ( M ¼ 0:3, ¼ 0:7) and as observed. The empirical correlation is expected to be unity (if the lens light traces their mass) and is shown for the whole sample and without SN 1997ff, the SN with the largest residual and predicted magnification.
Citations
More filters
Journal ArticleDOI
Constraints on perturbative f(R) gravity via neutron stars
TL;DR: In this article, the authors studied the structure of neutron stars in perturbative f(R) gravity models with realistic equations of state and found that deviations from the results of general relativity, comparable to the variations due to using different EoS' are induced for |α| ~ 109 cm2.
Journal ArticleDOI
Kinematic constraints to the transition redshift from supernovae type Ia union data
TL;DR: In this paper, the authors considered a two-parameter expansion for the decelerating parameter, where the parameters were constrained by the union supernovae data and the best fit to the pair of free parameters was shown to be O(n) = 0.73, 1.5.
Journal ArticleDOI
Bi-galileon theory I: motivation and formulation
TL;DR: The bi-galileon Lagrangian as discussed by the authors is a generalisation of the single galileon model introduced by Nicolis et al. The theory contains two coupled scalar fields and is described by a Lagrangians that is invariant under Galilean shifts in those fields.
Journal ArticleDOI
Cosmology with Massive Neutrinos Coupled to Dark Energy
Anthony W. Brookfield,C. van de Bruck,David F. Mota,David F. Mota,Domenico Tocchini-Valentini +4 more
TL;DR: It is found that mass-varying neutrinos can leave a significant imprint on the anisotropies in the cosmic microwave background and even lead to a reduction of power on large angular scales.
Journal ArticleDOI
Interacting agegraphic dark energy
Hao Wei,Hao Wei,Rong-Gen Cai +2 more
TL;DR: In this article, the authors extend the original agegraphic dark energy model by including the interaction between agegraphics dark energy and pressureless (dark) matter, and the similarity and difference between the two models are discussed.
References
More filters
Journal ArticleDOI
Measurements of Omega and Lambda from 42 High-Redshift Supernovae
Saul Perlmutter,Saul Perlmutter,Greg Aldering,Gerson Goldhaber,Gerson Goldhaber,R. A. Knop,Peter Nugent,P. G. Castro,P. G. Castro,Susana E. Deustua,Sebastien Fabbro,Sebastien Fabbro,A. Goobar,A. Goobar,Donald E. Groom,I. M. Hook,I. M. Hook,A. G. Kim,A. G. Kim,A. G. Kim,M. Y. Kim,Julia C. Lee,Julia C. Lee,Nelson J. Nunes,Nelson J. Nunes,Reynald Pain,Reynald Pain,C. R. Pennypacker,C. R. Pennypacker,Robert Quimby,Christopher Lidman,Richard S. Ellis,Mike Irwin,Richard G. McMahon,Pilar Ruiz-Lapuente,Nicholas A. Walton,Bradley E. Schaefer,B. J. Boyle,Alexei V. Filippenko,Thomas Matheson,A. S. Fruchter,Nino Panagia,Nino Panagia,Heidi Jo Newberg,Warrick J. Couch +44 more
TL;DR: In this paper, the mass density, Omega_M, and cosmological-constant energy density of the universe were measured using the analysis of 42 Type Ia supernovae discovered by the Supernova Cosmology project.
Journal ArticleDOI
Observational Evidence from Supernovae for an Accelerating Universe and a Cosmological Constant
Adam G. Riess,Alexei V. Filippenko,Peter Challis,Alejandro Clocchiatti,Alan H. Diercks,Peter M. Garnavich,R. L. Gilliland,Craig J. Hogan,Saurabh Jha,Robert P. Kirshner,Bruno Leibundgut,Mark M. Phillips,David J Reiss,Brian P. Schmidt,R. A. Schommer,R. Chris Smith,R. Chris Smith,Jason Spyromilio,Christopher W. Stubbs,Nicholas B. Suntzeff,John L. Tonry +20 more
TL;DR: In this article, the authors used spectral and photometric observations of 10 Type Ia supernovae (SNe Ia) in the redshift range 0.16 " z " 0.62.
Journal ArticleDOI
Maps of Dust Infrared Emission for Use in Estimation of Reddening and Cosmic Microwave Background Radiation Foregrounds
TL;DR: In this article, a reprocessed composite of the COBE/DIRBE and IRAS/ISSA maps, with the zodiacal foreground and confirmed point sources removed, is presented.
Journal ArticleDOI
Maps of Dust IR Emission for Use in Estimation of Reddening and CMBR Foregrounds
TL;DR: In this paper, the authors presented a reprocessed composite of the COBE/DIRBE and IRAS/ISSA maps, with the zodiacal foreground and confirmed point sources removed.
Journal ArticleDOI
Observational Evidence from Supernovae for an Accelerating Universe and a Cosmological Constant
Adam G. Riess,Alexei V. Filippenko,Peter Challis,Alejandro Clocchiattia,Alan H. Diercks,Peter M. Garnavich,R. L. Gilliland,Craig J. Hogan,Saurabh Jha,Robert P. Kirshner,Bruno Leibundgut,Mark M. Phillips,David J Reiss,Brian P. Schmidt,Robert A. Schommer,R. Chris Smith,Jason Spyromilio,Christopher W. Stubbs,Nicholas B. Suntzeff,John L. Tonry +19 more
TL;DR: In this paper, the authors present observations of 10 type Ia supernovae (SNe Ia) between 0.16 0 and 4.0 sigma confidence levels, for two fitting methods respectively.
Related Papers (5)
Measurements of Omega and Lambda from 42 High-Redshift Supernovae
Saul Perlmutter,Saul Perlmutter,Greg Aldering,Gerson Goldhaber,Gerson Goldhaber,R. A. Knop,Peter Nugent,P. G. Castro,P. G. Castro,Susana E. Deustua,Sebastien Fabbro,Sebastien Fabbro,A. Goobar,A. Goobar,Donald E. Groom,I. M. Hook,I. M. Hook,A. G. Kim,A. G. Kim,A. G. Kim,M. Y. Kim,Julia C. Lee,Julia C. Lee,Nelson J. Nunes,Nelson J. Nunes,Reynald Pain,Reynald Pain,C. R. Pennypacker,C. R. Pennypacker,Robert Quimby,Christopher Lidman,Richard S. Ellis,Mike Irwin,Richard G. McMahon,Pilar Ruiz-Lapuente,Nicholas A. Walton,Bradley E. Schaefer,B. J. Boyle,Alexei V. Filippenko,Thomas Matheson,A. S. Fruchter,Nino Panagia,Nino Panagia,Heidi Jo Newberg,Warrick J. Couch +44 more
Observational Evidence from Supernovae for an Accelerating Universe and a Cosmological Constant
Adam G. Riess,Alexei V. Filippenko,Peter Challis,Alejandro Clocchiatti,Alan H. Diercks,Peter M. Garnavich,R. L. Gilliland,Craig J. Hogan,Saurabh Jha,Robert P. Kirshner,Bruno Leibundgut,Mark M. Phillips,David J Reiss,Brian P. Schmidt,R. A. Schommer,R. Chris Smith,R. Chris Smith,Jason Spyromilio,Christopher W. Stubbs,Nicholas B. Suntzeff,John L. Tonry +20 more
First year Wilkinson Microwave Anisotropy Probe (WMAP) observations: Determination of cosmological parameters
David N. Spergel,Licia Verde,Hiranya V. Peiris,Eiichiro Komatsu,M. R. Nolta,Charles L. Bennett,Mark Halpern,Gary Hinshaw,N. Jarosik,Alan J. Kogut,Michele Limon,Michele Limon,S. S. Meyer,Lyman A. Page,Gregory S. Tucker,Gregory S. Tucker,Gregory S. Tucker,Janet L. Weiland,Edward J. Wollack,Edward L. Wright +19 more
Detection of the baryon acoustic peak in the large-scale correlation function of SDSS luminous red galaxies
Daniel J. Eisenstein,Daniel J. Eisenstein,Idit Zehavi,David W. Hogg,Roman Scoccimarro,Michael R. Blanton,Robert C. Nichol,Ryan Scranton,Hee-Jong Seo,Max Tegmark,Max Tegmark,Zheng Zheng,Scott F. Anderson,James Annis,Neta A. Bahcall,Jon Brinkmann,Scott Burles,Francisco J. Castander,Andrew J. Connolly,István Csabai,Mamoru Doi,Masataka Fukugita,Joshua A. Frieman,Joshua A. Frieman,Karl Glazebrook,James E. Gunn,John S. Hendry,Greg Hennessy,Zeljko Ivezic,Stephen M. Kent,Gillian R. Knapp,Huan Lin,Yeong Shang Loh,Robert H. Lupton,Bruce Margon,Timothy A. McKay,Avery Meiksin,Jeffrey A. Munn,Adrian Pope,Michael W. Richmond,David J. Schlegel,Donald P. Schneider,Kazuhiro Shimasaku,Chris Stoughton,Michael A. Strauss,Mark SubbaRao,Mark SubbaRao,Alexander S. Szalay,István Szapudi,Douglas L. Tucker,Brian Yanny,Donald G. York +51 more