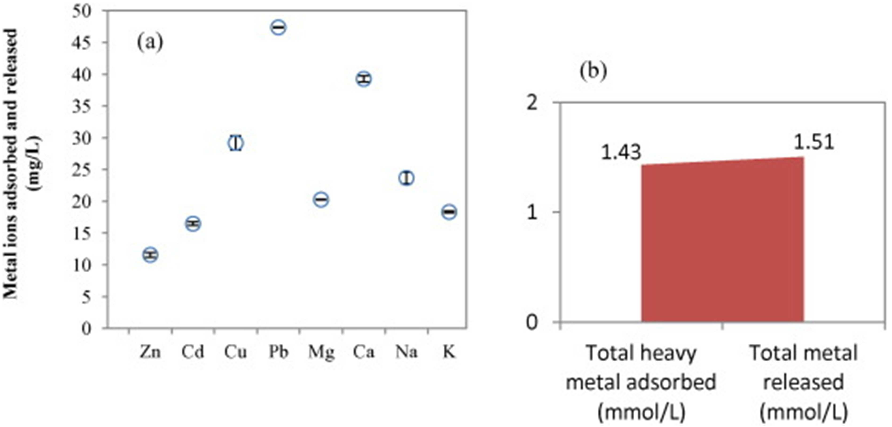
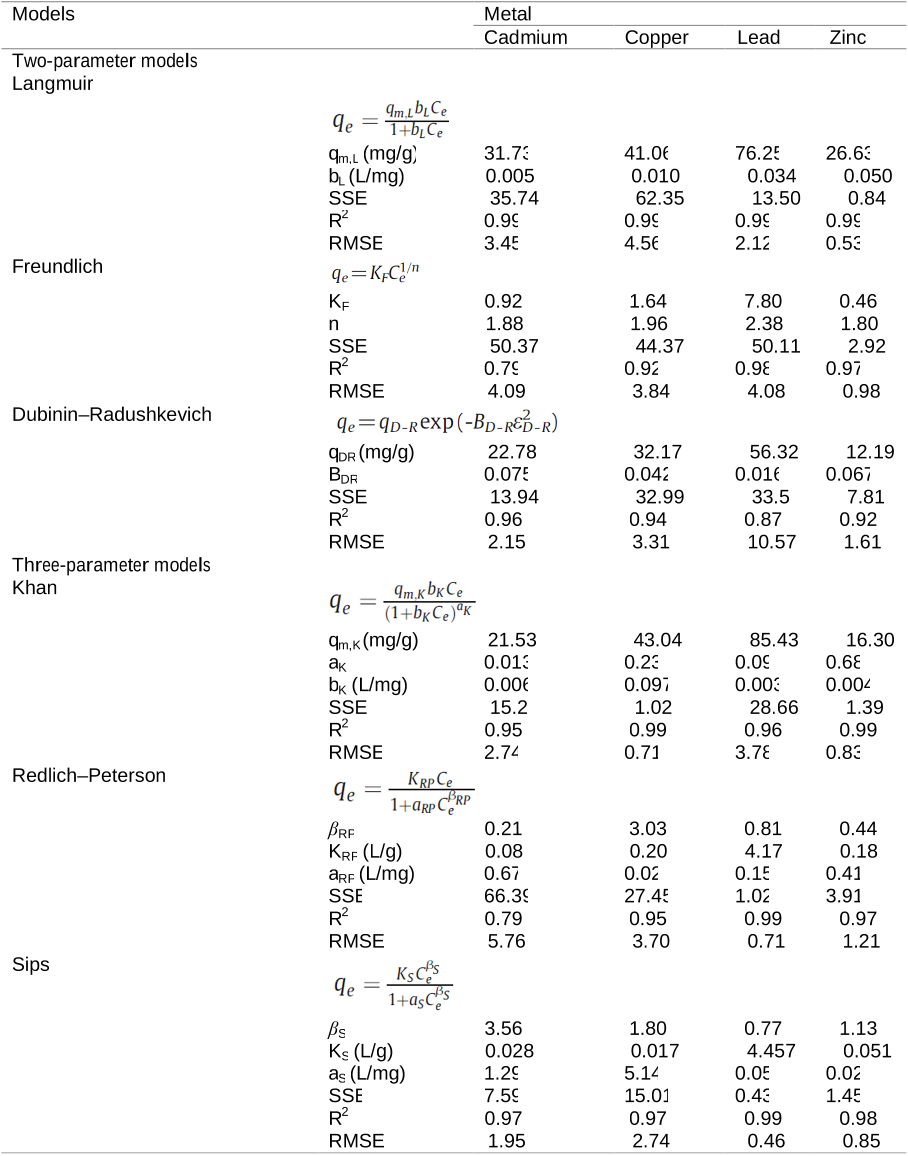
Q1. What have the authors contributed in "A breakthrough biosorbent in removing heavy metals: equilibrium, kinetic, thermodynamic and mechanism analyses in a lab-scale study" ?
For Cu ( II ) and Zn ( II ), the Khan isotherm describes better biosorption conditions while for Cd ( II ) and Pb ( II ), the Sips model was found to provide the best correlation of the biosorption equilibrium data.