Clinical practice with anti-dementia drugs: A revised (third) consensus statement from the British Association for Psychopharmacology
John T. O'Brien,Clive Holmes,Matthew Jones,Roy W. Jones,Gill Livingston,Ian G. McKeith,Peter Mittler,Peter Passmore,Craig W. Ritchie,Louise Robinson,Elizabeth L Sampson,John-Paul Taylor,Alan J. Thomas,Alistair Burns +13 more
TLDR
The British Association for Psychopharmacology coordinated a meeting of experts to review and revise its previous 2011 guidelines for clinical practice with anti-dementia drugs, with the consensus statement focusing on medication.Abstract:
The British Association for Psychopharmacology coordinated a meeting of experts to review and revise its previous 2011 guidelines for clinical practice with anti-dementia drugs. As before, levels of evidence were rated using accepted standards which were then translated into grades of recommendation A-D, with A having the strongest evidence base (from randomised controlled trials) and D the weakest (case studies or expert opinion). Current clinical diagnostic criteria for dementia have sufficient accuracy to be applied in clinical practice (B) and both structural (computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging) and functional (positron emission tomography and single photon emission computerised tomography) brain imaging can improve diagnostic accuracy in particular situations (B). Cholinesterase inhibitors (donepezil, rivastigmine, and galantamine) are effective for cognition in mild to moderate Alzheimer's disease (A), memantine for moderate to severe Alzheimer's disease (A) and combination therapy (cholinesterase inhibitors and memantine) may be beneficial (B). Drugs should not be stopped just because dementia severity increases (A). Until further evidence is available other drugs, including statins, anti-inflammatory drugs, vitamin E, nutritional supplements and Ginkgo biloba, cannot be recommended either for the treatment or prevention of Alzheimer's disease (A). Neither cholinesterase inhibitors nor memantine are effective in those with mild cognitive impairment (A). Cholinesterase inhibitors are not effective in frontotemporal dementia and may cause agitation (A), though selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors may help behavioural (but not cognitive) features (B). Cholinesterase inhibitors should be used for the treatment of people with Lewy body dementias (both Parkinson's disease dementia and dementia with Lewy bodies), and memantine may be helpful (A). No drugs are clearly effective in vascular dementia, though cholinesterase inhibitors are beneficial in mixed dementia (B). Early evidence suggests multifactorial interventions may have potential to prevent or delay the onset of dementia (B). Though the consensus statement focuses on medication, psychological interventions can be effective in addition to pharmacotherapy, both for cognitive and non-cognitive symptoms. Many novel pharmacological approaches involving strategies to reduce amyloid and/or tau deposition in those with or at high risk of Alzheimer's disease are in progress. Though results of pivotal studies in early (prodromal/mild) Alzheimer's disease are awaited, results to date in more established (mild to moderate) Alzheimer's disease have been equivocal and no disease modifying agents are either licensed or can be currently recommended for clinical use.read more
Figures
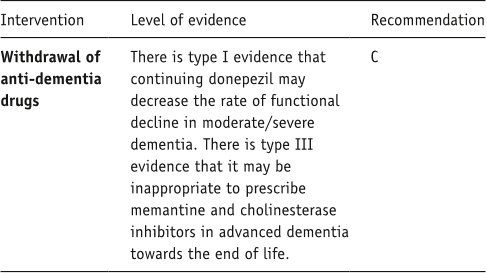
Table 10. Summary box: end of life care. 
Table 9. Summary box: primary care. 
Figure 2. Evidence base supporting benefits of co-prescription of a cholinesterase inhibitor and memantine. Reproduced from Schmidt R, Hofer E, Bouwman FH, et al. (2015) EFNS-ENS/EAN Guideline on concomitant use of cholinesterase inhibitors and memantine in moderate to severe Alzheimer’s disease. Eur J Neurol 22: 889–898 with permission from John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 
Table 12. Summary box: disease-modifying therapies. 
Figure 3. Results from the DOMINO study, showing the deleterious effects of withdrawing stable donepezil therapy in Alzheimer’s disease once the point of severe dementia (MMSE<10) has been reached. BADLS: Bristol Activities of Daily Living Scale; SMMSE: Standardised Mini-Mental State Examination. Reproduced from Howard R, McShane R, Lindesay J, et al. (2012) Donepezil and memantine for moderate-to-severe Alzheimer’s disease. N Engl J Med 366: 893–903 with permission from Massachusetts Medical Society. 
Table 6. Summary box: frontotemporal dementia.
Citations
More filters
Journal ArticleDOI
Multilingualism and Dementia Risk: Longitudinal Analysis of the Nun Study.
TL;DR: Linguistic ability broadly was a significant predictor of dementia, although it was written linguistic ability (specifically idea density) rather than multilingualism that was the strongest predictor.
Journal ArticleDOI
Alzheimer’s Disease, Cerebrovascular Disease and Dementia: APotentially Preventable and Modifiable Syndrome
TL;DR: In several countries the age-specific prevalence of dementia is decreasing and the decrease has been attributed to a decrease in cardiovascular risk factors and an increase in cognitive reserve associated with better education and healthier life-styles in recent generations.
Journal ArticleDOI
Trends of antidementia drugs use in outpatients with Alzheimer's disease in six major cities of China: 2012-2017.
TL;DR: The number of Alzheimer's disease outpatients of sampling days increased from 10 239 in 2012 to 20 546 in 2017, and nonusers of antidementia drugs, cholinesterase inhibitors (ChEIs) and memantine slowly decreased over the study period.
Journal ArticleDOI
New insights and therapeutic opportunities for progranulin-deficient frontotemporal dementia
TL;DR: In this paper , the authors discuss some of the significant progress made in the past two years that links PGRN deficiency with microglial-associated neuroinflammation, TAR DNA-binding protein 43 kDa (TDP-43) aggregates, and lysosomal dysfunction.
Journal ArticleDOI
Management of end-stage dementia.
David Lussier,Marie-Andrée Bruneau,Marie-Andrée Bruneau,Juan Manuel Villalpando,Juan Manuel Villalpando +4 more
TL;DR: There is an urgent need for research and education on this topic, as well as palliative care services devoted to this population of patients with advanced dementia.
References
More filters
Journal ArticleDOI
Clinical diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease : report of the NINCDS-ADRDA Work Group under the auspices of Department of Health and Human Services Task Force on Alzheimer's Disease
Guy M. McKhann,David A. Drachman,Marshall F. Folstein,Robert Katzman,Donald L. Price,Emanuel M. Stadlan +5 more
TL;DR: The criteria proposed are intended to serve as a guide for the diagnosis of probable, possible, and definite Alzheimer's disease; these criteria will be revised as more definitive information becomes available.
Journal ArticleDOI
The diagnosis of dementia due to Alzheimer’s disease: Recommendations from the National Institute on Aging-Alzheimer’s Association workgroups on diagnostic guidelines for Alzheimer's disease
Guy M. McKhann,Guy M. McKhann,David S. Knopman,Howard Chertkow,Bradley T. Hyman,Clifford R. Jack,Claudia H. Kawas,William E. Klunk,Walter J. Koroshetz,Jennifer J. Manly,Richard Mayeux,Richard C. Mohs,John C. Morris,Martin N. Rossor,Philip Scheltens,Maria C. Carrillo,Bill Thies,Sandra Weintraub,Creighton H. Phelps +18 more
TL;DR: The workgroup sought to ensure that the revised criteria would be flexible enough to be used by both general healthcare providers without access to neuropsychological testing, advanced imaging, and cerebrospinal fluid measures, and specialized investigators involved in research or in clinical trial studies who would have these tools available.
Journal ArticleDOI
Toward defining the preclinical stages of Alzheimer's disease: Recommendations from the National Institute on Aging-Alzheimer's Association workgroups on diagnostic guidelines for Alzheimer's disease
Reisa A. Sperling,Paul S. Aisen,Laurel A. Beckett,David A. Bennett,Suzanne Craft,Anne M. Fagan,Takeshi Iwatsubo,Clifford R. Jack,Jeffrey Kaye,Thomas J. Montine,Denise C. Park,Eric M. Reiman,Christopher C. Rowe,Eric Siemers,Yaakov Stern,Kristine Yaffe,Maria C. Carrillo,Bill Thies,Marcelle Morrison-Bogorad,Molly V. Wagster,Creighton H. Phelps +20 more
TL;DR: A conceptual framework and operational research criteria are proposed, based on the prevailing scientific evidence to date, to test and refine these models with longitudinal clinical research studies and it is hoped that these recommendations will provide a common rubric to advance the study of preclinical AD.
Journal ArticleDOI
Vascular dementia Diagnostic criteria for research studies: Report of the NINDS‐AIREN International Workshop*
Gustavo C. Román,Thomas K. Tatemichi,T. Erkinjuntti,Jeffrey L. Cummings,Joseph C. Masdeu,J. H. Garcia,L. Amaducci,J. M. Orgogozo,A. Brun,Albert Hofman,D. M. Moody,M. D. O’Brien,T. Yamaguchi,Jordan Grafman,B. P. Drayer,D. A. Bennett,Marc Fisher,J. Ogata,E. Kokmen,F. Bermejo,Philip A. Wolf,P. B. Gorelick,K. L. Bick,A. K. Pajeau,M. A. Bell,Charles DeCarli,A. Culebras,Amos D. Korczyn,J. Bogousslavsky,A. Hartmann,P. Scheinberg +30 more
TL;DR: These criteria for the diagnosis of vascular dementia are intended as a guide for case definition in neuroepidemiologic studies, stratified by levels of certainty (definite, probable, and possible).
Related Papers (5)
Diagnosis and management of dementia with Lewy bodies: Third report of the DLB Consortium
Ian G. McKeith,Ian G. McKeith,Dennis W. Dickson,James Lowe,Murat Emre,John T. O'Brien,Howard Feldman,Jeffrey L. Cummings,John E. Duda,Carol F. Lippa,Elaine K. Perry,Dag Aarsland,Hiroyuki Arai,Clive Ballard,B. F. Boeve,David J. Burn,Durval C. Costa,T. Del Ser,Bruno Dubois,Douglas Galasko,Serge Gauthier,Christopher G. Goetz,Estrella Gómez-Tortosa,Glenda M. Halliday,L. A. Hansen,John Hardy,Takeshi Iwatsubo,Raj N. Kalaria,Daniel I. Kaufer,Rose Anne Kenny,Amos D. Korczyn,Kenji Kosaka,Virginia M.-Y. Lee,Andrew J. Lees,Irene Litvan,Elisabet Londos,Oscar L. Lopez,Satoshi Minoshima,Yoshikuni Mizuno,José Antonio Molina,Elizabeta B. Mukaetova-Ladinska,Florence Pasquier,Robert H. Perry,Jörg B. Schulz,John Q. Trojanowski,Masahito Yamada +45 more
The diagnosis of dementia due to Alzheimer’s disease: Recommendations from the National Institute on Aging-Alzheimer’s Association workgroups on diagnostic guidelines for Alzheimer's disease
Guy M. McKhann,Guy M. McKhann,David S. Knopman,Howard Chertkow,Bradley T. Hyman,Clifford R. Jack,Claudia H. Kawas,William E. Klunk,Walter J. Koroshetz,Jennifer J. Manly,Richard Mayeux,Richard C. Mohs,John C. Morris,Martin N. Rossor,Philip Scheltens,Maria C. Carrillo,Bill Thies,Sandra Weintraub,Creighton H. Phelps +18 more