Q2. What are the future works mentioned in the paper "A comprehensive model of pmos nbti degradation" ?
One of the key goal of their future work would be to clarify the role of such processing changes on NBTI performance.
read more
![Fig. 5. Time evolution of (normalized) drain current shift for PMOS inversion and NMOS accumulation NBTI stress. Degradation at low VG for all time and high VG at shorter time is due to interface-trap generation, while long-time enhanced degradation at high VG is due to bulk-trap generation [15,16]. Under identical oxide field ðVGjinv ¼ VGjacc 1 V to account for difference in flatband voltage) PMOS inversion and NMOS accumulation (short time) stress show similar degradation, which characterizes the role of holes for NBTI.](/figures/fig-5-time-evolution-of-normalized-drain-current-shift-for-25rnsgi7.png)

![Fig. 7. Experimental and theoretical time evolution of threshold voltage shift data for a wide range of stress VG. The calculated bulk trap contributions are shown by dashed lines [15]. Theory matches well with experiment. Bulk trap generation at large oxide fields (high VG) affects overall threshold voltage shift and must be taken into account for properly estimating the forward reaction rate of the R–D model.](/figures/fig-7-experimental-and-theoretical-time-evolution-of-2fr9nut9.png)
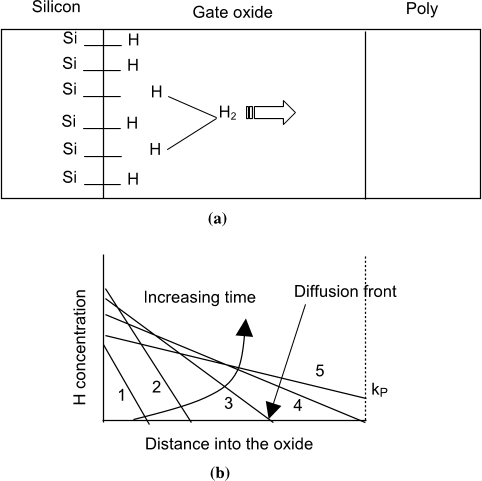

![Fig. 9. Temperature activation of 1=tBREAK and DH. The DH is calculated from the universal scaling of temperature dependent (fixed oxide field) generated interface trap data. Obtained activation energy supports neutral H2 diffusion [32].](/figures/fig-9-temperature-activation-of-1-tbreak-and-dh-the-dh-is-2c3pb1to.png)
One of the key goal of their future work would be to clarify the role of such processing changes on NBTI performance.